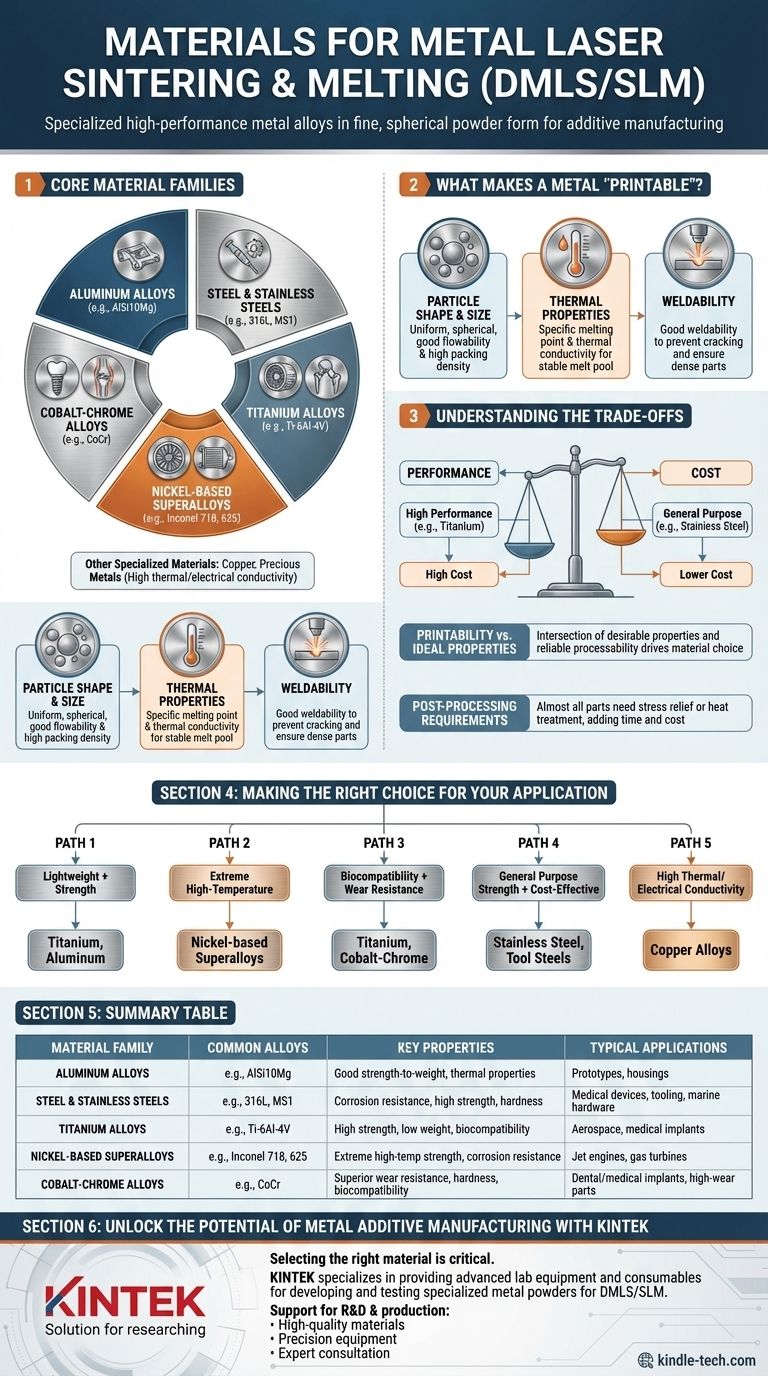
In short, a specialized range of high-performance metal alloys can be processed using laser-based powder bed fusion technologies like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Selective Laser Melting (SLM). The most common material families include specific grades of aluminum, stainless and tool steels, titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and cobalt-chrome. The key is that these are not just any metals, but fine, spherical powders engineered specifically for the printing process.
The choice of material for metal laser melting is not just about what is technically possible, but about a critical balance between the final part's required performance—such as strength, heat resistance, or weight—and the material's processability and cost.
A Note on Terminology: DMLS vs. SLM
While often used interchangeably, Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Selective Laser Melting (SLM) describe processes in the same family of metal additive manufacturing.
DMLS typically sinters the powder, heating it to the point where particles fuse together on a molecular level, while SLM uses a higher-power laser to achieve a full melt. For practical purposes, both produce dense, functional metal parts, and the material choices largely overlap.

The Core Material Families
The available materials are purpose-built for demanding industries like aerospace, medical, and high-performance automotive. They are chosen for their unique combination of mechanical properties and their ability to be reliably processed by a laser.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum is prized for its low density and good strength-to-weight ratio. It's a common choice for lightweighting applications.
The most widely used aluminum is AlSi10Mg, an alloy that offers good strength and thermal properties and is relatively easy to process. It is frequently used for prototypes, housings, and automotive components.
Steel and Stainless Steels
Steels offer an excellent balance of strength, hardness, and cost-effectiveness, making them a versatile workhorse material.
Stainless Steel 316L is a go-to for its exceptional corrosion resistance and good weldability, ideal for medical devices, food-grade applications, and marine hardware. Maraging Steel (MS1) is a tool steel known for its ultra-high strength and hardness after heat treatment, perfect for tooling, molds, and high-stress mechanical parts.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium is the premier material for applications demanding high strength, low weight, and excellent biocompatibility.
Titanium Ti-6Al-4V (Ti64) is the most common 3D-printed titanium alloy. Its properties make it the standard for high-performance aerospace components and life-saving medical implants like hip joints and spinal fusion cages.
Nickel-Based Superalloys
These materials are engineered to maintain exceptional mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and creep resistance at extremely high temperatures.
Inconel 718 and Inconel 625 are the dominant players. They are essential for parts inside jet engines, gas turbines, and other high-temperature, high-stress environments.
Cobalt-Chrome Alloys
Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr) is known for its incredible wear resistance, hardness, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility.
It is a leading choice for medical implants that face high wear cycles, such as knee and dental implants, and can also be used in high-temperature engineering applications.
Other Specialized Materials
The technology also supports other niche materials, including precious metals like gold and platinum for jewelry, and increasingly, copper alloys for applications requiring high thermal and electrical conductivity, such as heat exchangers and inductors.
What Makes a Metal Powder "Printable"?
Not every metal can be turned into a powder and successfully printed. The material must possess specific characteristics to be compatible with the laser melting process.
Particle Shape and Size
The powder must consist of uniform, spherical particles. This shape ensures good flowability so the recoater blade can spread a smooth, even layer on the build plate. It also allows for high packing density, minimizing voids in the powder bed and leading to a denser final part.
Thermal Properties
A material's melting point and thermal conductivity are critical. Materials with extremely high thermal conductivity, like pure copper, can be challenging because the laser energy dissipates too quickly, making it difficult to form a stable melt pool.
Weldability
At its core, SLM/DMLS is a micro-welding process. The material must have good weldability. Materials that are prone to cracking when welded will exhibit the same defects when 3D printed, resulting in failed parts. This is why specific alloys are developed and qualified for the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is a decision driven by balancing competing factors. Being aware of these trade-offs is crucial for a successful project.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between material performance and cost. General-purpose stainless steel is relatively inexpensive, while high-performance materials like titanium and Inconel are orders of magnitude more expensive, both in raw powder cost and processing time.
Printability vs. Ideal Properties
Sometimes the best material for an application from a traditional engineering standpoint is not the easiest to print. The available material library represents the intersection of desirable properties and reliable processability. This is why you see specific alloys like AlSi10Mg dominate over other aluminum series.
Post-Processing Requirements
The properties of a part "as-printed" are rarely its final properties. Nearly all metal 3D-printed parts require post-processing. This includes thermal treatments like stress relief to remove internal stresses built up during printing and heat treatments like aging or solution annealing to achieve the desired final strength and hardness. These steps add time, cost, and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material selection should be guided by the primary requirement of your component.
- If your primary focus is lightweighting with high strength: Titanium alloys (Ti64) or high-strength aluminum alloys are your best candidates.
- If you need extreme high-temperature performance: Nickel-based superalloys like Inconel 718 are the industry standard.
- If you require biocompatibility and high wear resistance: Look to titanium and cobalt-chrome alloys for medical and dental applications.
- If your priority is general-purpose strength and cost-effectiveness: Stainless steel (316L) and tool steels (MS1) offer a robust and versatile solution.
- If you need high thermal or electrical conductivity: Copper alloys are the emerging choice, though they present unique processing challenges.
Understanding the landscape of available materials and their inherent trade-offs is the first step toward successfully leveraging metal additive manufacturing for your goals.
Summary Table:
| Material Family | Common Alloys | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | AlSi10Mg | Good strength-to-weight ratio, thermal properties | Lightweight prototypes, housings, automotive parts |
| Steel & Stainless Steels | 316L, Maraging Steel (MS1) | Corrosion resistance, high strength, hardness | Medical devices, tooling, molds, marine hardware |
| Titanium Alloys | Ti-6Al-4V (Ti64) | High strength, low weight, excellent biocompatibility | Aerospace components, medical implants (hips, spinal cages) |
| Nickel-Based Superalloys | Inconel 718, Inconel 625 | Extreme high-temperature strength, corrosion resistance | Jet engine parts, gas turbines |
| Cobalt-Chrome Alloys | CoCr | Superior wear resistance, hardness, biocompatibility | Dental and knee implants, high-wear engineering parts |
| Other Materials | Copper, Precious Metals | High thermal/electrical conductivity | Heat exchangers, jewelry, inductors |
Unlock the Potential of Metal Additive Manufacturing with KINTEK
Selecting the right material is critical to the success of your metal 3D printing project. The high-performance alloys used in DMLS/SLM processes require specific expertise to ensure optimal results.
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and testing these specialized metal powders. Whether you are in aerospace, medical, or automotive manufacturing, we support your R&D and production needs with:
- High-quality materials for prototyping and testing.
- Precision equipment for analyzing powder characteristics and part properties.
- Expert consultation to help you navigate material selection and process optimization.
Let's build the future, layer by layer. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your metal additive manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between hot mounting and cold mounting? Choose the Right Method for Your Sample
- What role do laboratory grinding and polishing systems play in nitriding? Ensure Superior Mirror-Finish & Ion Penetration
- How should a sample be installed onto the sample holder? Ensure Mechanical Stability & Electrical Integrity
- How should an RVC sheet be handled and set up during an experiment? Ensure Precision and Data Integrity
- What is a hot mounting press machine? Precision Control for Metallurgy & Electronics Assembly



















