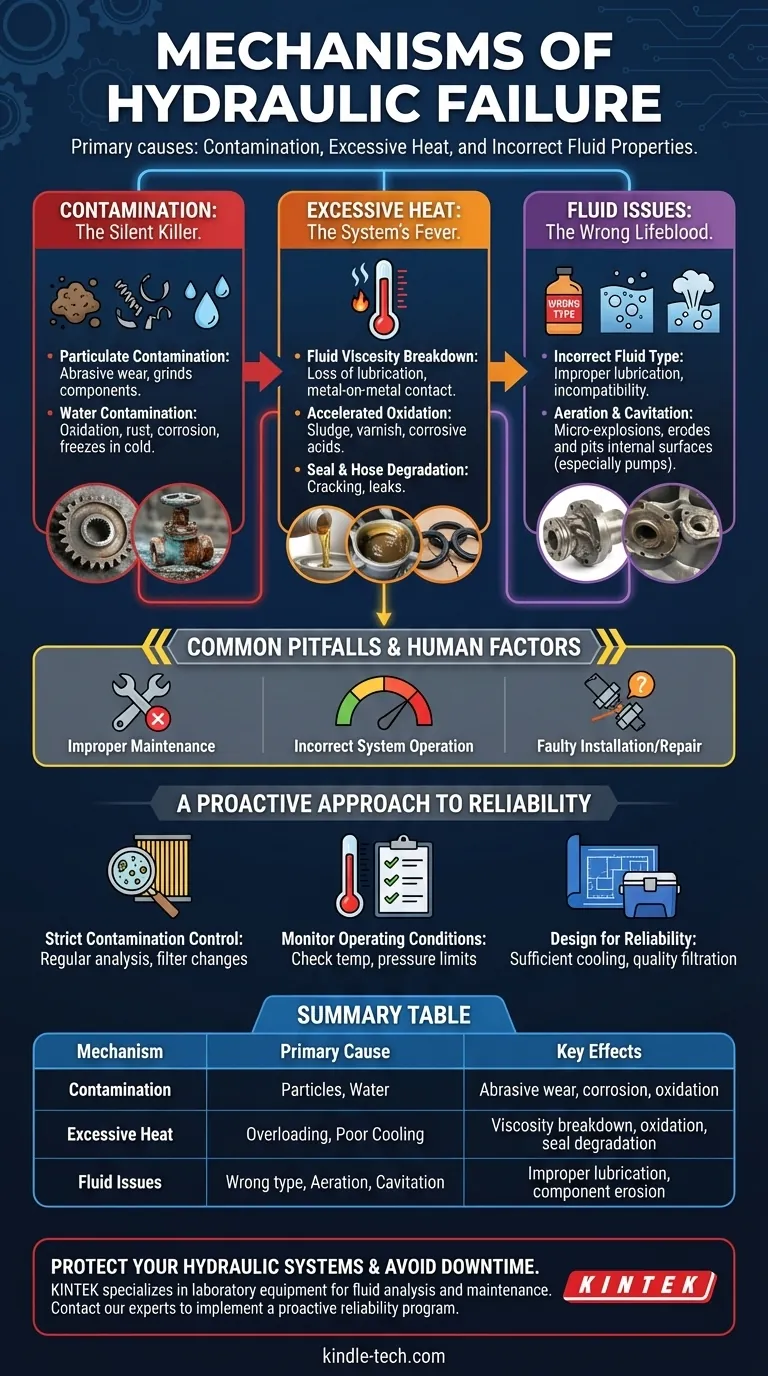
The primary mechanisms of hydraulic failure almost always trace back to three interconnected issues: contamination of the hydraulic fluid, excessive heat, and incorrect fluid properties. These factors degrade the fluid's ability to do its job, leading to a cascade of mechanical wear and eventual component breakdown.
The vast majority of hydraulic system failures are not caused by a sudden component defect, but by the slow, progressive degradation of the hydraulic fluid itself. Protecting the fluid is the single most critical factor in ensuring system reliability.

The Core Culprits of Hydraulic Failure
A hydraulic system is a closed loop, but it is never perfectly sealed from its environment or the byproducts of its own operation. Understanding how these elements cause failure is the first step toward prevention.
Contamination: The Silent Killer
Contamination is the leading cause of hydraulic failure. It introduces foreign materials into the fluid that should not be there, leading to predictable and damaging outcomes.
Particulate Contamination Solid particles like dirt, dust, and microscopic metal shavings from component wear are the most common offenders. They cause failure through abrasive wear, acting like liquid sandpaper that grinds away the tight tolerances inside pumps, valves, and cylinders.
This process accelerates component wear, increases internal leakage, and reduces system efficiency long before a catastrophic failure occurs.
Water Contamination Water is another highly destructive contaminant. It enters through worn seals or condensation in the reservoir.
Water degrades the fluid by promoting oxidation and depleting critical additives. It also causes rust and corrosion on internal metal surfaces and can freeze in cold conditions, blocking lines and damaging components.
Excessive Heat: The System's Fever
Heat is the enemy of hydraulic fluid. While some heat is a natural byproduct of operation, excessive heat causes rapid and irreversible damage to the fluid and system components.
Fluid Viscosity Breakdown The most immediate effect of high temperature is a drop in the fluid's viscosity (its thickness). As the fluid thins, it loses its ability to form a protective lubricating film between moving parts.
This loss of lubrication leads to direct metal-on-metal contact, dramatically increasing friction and component wear.
Accelerated Oxidation Heat acts as a catalyst for oxidation, a chemical reaction that permanently breaks down the fluid. This process creates sludge, varnish, and corrosive acids.
Varnish can coat internal surfaces, causing valves to stick and orifices to clog. Sludge accumulates in the reservoir and can be circulated through the system, causing further blockages and wear.
Seal and Hose Degradation High temperatures cause the elastomers in seals and hoses to become hard and brittle. This loss of flexibility leads to cracking, which is a primary source of external and internal leaks.
Fluid Issues: The Wrong Lifeblood
Using the wrong fluid or allowing air to enter the system creates immediate operational problems that can quickly lead to mechanical damage.
Incorrect Fluid Type Every system is designed for a fluid with a specific viscosity and additive package. Using the wrong fluid can lead to improper lubrication, inadequate heat dissipation, and incompatibility with seals.
Aeration and Cavitation Aeration is the presence of entrained air bubbles in the fluid, often caused by a leak on the pump's inlet side. Cavitation is the formation and collapse of vapor bubbles when the pressure in a part of the circuit drops too low.
Both phenomena are destructive. As these bubbles collapse under high pressure, they create a micro-explosion that erodes and pits internal component surfaces, particularly inside pumps.
Common Pitfalls and Human Factors
Mechanical issues are often enabled by human error. Flaws in maintenance, operation, and repair introduce the very conditions that lead to failure.
Improper Maintenance
The single most common pitfall is a reactive, "fix it when it breaks" approach. Failing to perform routine tasks like changing filters, analyzing fluid samples, and cleaning strainers allows contamination and degradation to proceed unchecked.
Incorrect System Operation
Consistently operating a system above its designed maximum pressure or temperature will drastically shorten its lifespan. This overloads components and accelerates fluid breakdown.
Faulty Installation or Repair
Incorrectly installing components can create misalignment that puts undue stress on parts. Using the wrong type of seals or failing to properly clean parts before assembly is a guaranteed way to introduce contaminants from day one.
A Proactive Approach to Hydraulic Reliability
Understanding the causes of failure allows you to shift from a reactive to a proactive strategy focused on prevention.
- If your primary focus is preventing failure in existing systems: Implement a strict contamination control program, centered on regular fluid analysis and adhering to a filter change schedule.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a current problem: Begin by analyzing a fluid sample for contamination and checking the system's operating temperature against its specified limits.
- If your primary focus is designing a new system: Ensure the design includes sufficient cooling capacity and specifies high-quality filtration to remove contaminants from the very beginning.
Ultimately, treating the hydraulic fluid as the system's most important component is the key to achieving long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Primary Cause | Key Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Contamination | Ingress of particles or water | Abrasive wear, corrosion, oxidation |
| Excessive Heat | Overloading, insufficient cooling | Viscosity breakdown, oxidation, seal degradation |
| Fluid Issues | Wrong fluid type, aeration, cavitation | Improper lubrication, component erosion, pump damage |
Protect your hydraulic systems and avoid costly downtime. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, including solutions for fluid analysis and maintenance. Our expertise can help you implement a proactive reliability program to extend the life of your equipment. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and ensure your systems run smoothly.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What creates heat in a hydraulic system? Understanding Energy Loss and Pressure Drop
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for 380 MPa in composite anodes? Unlock Peak Battery Performance
- What are the classification of presses? A Guide to Mechanical, Hydraulic, and Servo Presses
- How does temperature affect hydraulic oil? Optimize Viscosity for Peak System Performance
- Why is my hydraulic press not working? A Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose & Fix Common Issues
- What is the difference between sintering and compacting? A Guide to the Two-Step Powder Metallurgy Process
- What are two problems that could arise in the preparation of a KBr pellet for IR analysis? Avoid Moisture & Grinding Errors
- What are the safety rules when using a hydraulic press? Essential Guidelines for Secure Operation



















