Virtually any conductive metal can be melted in an induction furnace. This includes the full spectrum of industrial metals, from ferrous types like iron and steel to non-ferrous ones like copper, aluminum, and brass. The technology is also highly effective for melting precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum, and powerful enough to handle high-temperature refractory metals.
The critical question is not if a metal can be melted, but how efficiently it can be done. An induction furnace's operating frequency and power must be precisely matched to the target metal's unique electrical and magnetic properties to achieve an optimal and cost-effective melt.
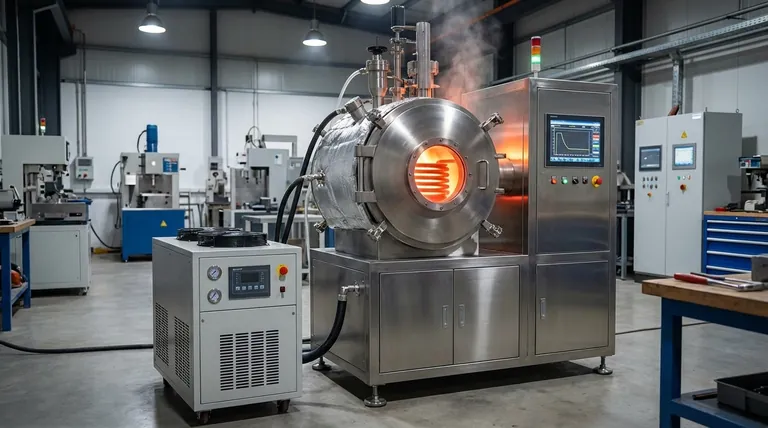

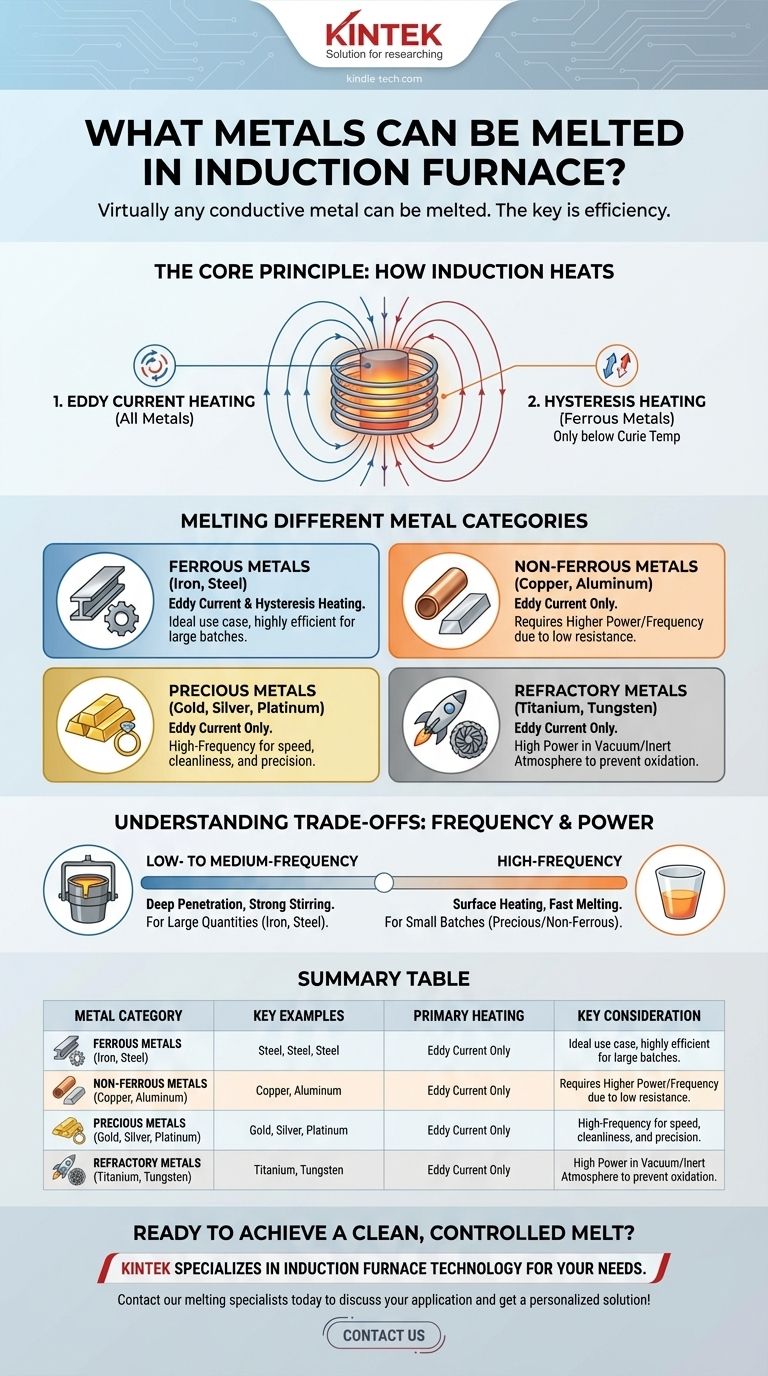
The Core Principle: How Induction Heats Metal
The versatility of induction melting stems from its fundamental physics. Unlike a traditional furnace that uses fuel or external heating elements, an induction furnace heats the metal directly and without contact.
The Primary Driver: Eddy Current Heating
An induction coil generates a powerful, alternating magnetic field. When a conductive metal is placed within this field, it induces electrical currents within the metal itself, known as eddy currents.
The metal's natural electrical resistance opposes these currents, generating intense heat. This phenomenon, called Joule heating, is the primary mechanism for all metals in an induction furnace.
The Ferrous Metal Bonus: Hysteresis Heating
For ferromagnetic metals like iron and steel, a second, highly efficient heating effect occurs. The rapidly alternating magnetic field causes the metal's magnetic domains to flip back and forth, creating internal friction and significant heat.
This hysteresis heating only works below the metal's Curie temperature (around 770°C for iron). Above this point, the metal loses its magnetic properties, and only eddy current heating continues the melting process. This dual effect makes induction exceptionally efficient for iron and steel.
Melting Different Metal Categories
While the principle is universal, the practical application varies by metal type. The furnace specifications are tuned to match the material's properties.
Ferrous Metals: Iron and Steel
This is the ideal use case for induction technology. The combination of eddy current and hysteresis heating makes the process fast and energy-efficient.
Induction furnaces are the backbone of modern foundries for melting everything from cast iron and carbon steel to specialized stainless and alloy steels.
Non-Ferrous Metals: Copper, Aluminum, Brass
These metals melt perfectly well but rely solely on eddy current heating. Because materials like aluminum and copper have very low electrical resistance, the furnace must be designed to induce very strong currents to generate sufficient heat.
This often requires furnaces with higher power ratings or different operating frequencies compared to those used for iron.
Precious Metals: Gold, Silver, and Platinum
Induction is favored for precious metals due to its speed, cleanliness, and precision, which minimize material loss.
High-frequency furnaces are typically used here. The higher frequency couples the energy more effectively into smaller charges and highly conductive materials, allowing for rapid and controlled melting in lab or jewelry-making environments.
Refractory Metals
For metals with extremely high melting points, the primary advantage of induction is the ability to generate intense heat in a clean, contained environment, often under a vacuum or in an inert atmosphere.
This prevents the metal from reacting with oxygen or other contaminants at high temperatures, which is a critical concern for materials like titanium or those used in aerospace alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Frequency and Power
Not all induction furnaces are the same. The choice of furnace is dictated by the intended application, primarily its size and operating frequency.
Low- to Medium-Frequency Furnaces
These units are the workhorses of the industry, used for melting large quantities (tons) of iron and steel. A lower frequency creates a deeper-penetrating magnetic field and a strong stirring action in the molten bath.
This electromagnetic stirring is a significant benefit, as it ensures the melt has a uniform temperature and helps mix in alloys for a homogenous final product.
High-Frequency Furnaces
These are better suited for small, specialized melts. The energy is concentrated closer to the surface of the charge, enabling very fast heating of smaller quantities.
This makes them ideal for labs, R&D, and melting non-ferrous or precious metals where large batch sizes are not required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision is less about the type of metal and more about the scale and specific goal of your operation.
- If your primary focus is large-scale iron and steel casting: A low-to-medium frequency furnace is the industry standard for its high efficiency and powerful stirring action.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper: You will need a furnace with sufficient power—and often a higher frequency—to efficiently overcome their low electrical resistance.
- If your primary focus is working with precious metals or small, specialized batches: A high-frequency benchtop furnace provides the precise control and rapid heating required for these applications.
By matching the furnace technology to the metal's properties and your production goals, you ensure a clean, controlled, and energy-efficient melting process.
Summary Table:
| Metal Category | Key Examples | Primary Heating Mechanism | Key Furnace Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Iron, Steel, Stainless Steel | Eddy Currents + Hysteresis | Low-to-Medium Frequency for large batches |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Aluminum, Copper, Brass | Eddy Currents | Higher Power/Frequency for low resistance |
| Precious Metals | Gold, Silver, Platinum | Eddy Currents | High Frequency for small, precise melts |
| Refractory Metals | Titanium, Tungsten Alloys | Eddy Currents | High Power, often with vacuum/inert atmosphere |
Ready to achieve a clean, controlled, and energy-efficient melt?
KINTEK specializes in providing the right induction furnace technology for your specific metal and production scale. Whether you are melting tons of steel in a foundry or precise batches of gold in a lab, our experts will help you select the ideal equipment for maximum efficiency and performance.
Contact our melting specialists today to discuss your application and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















