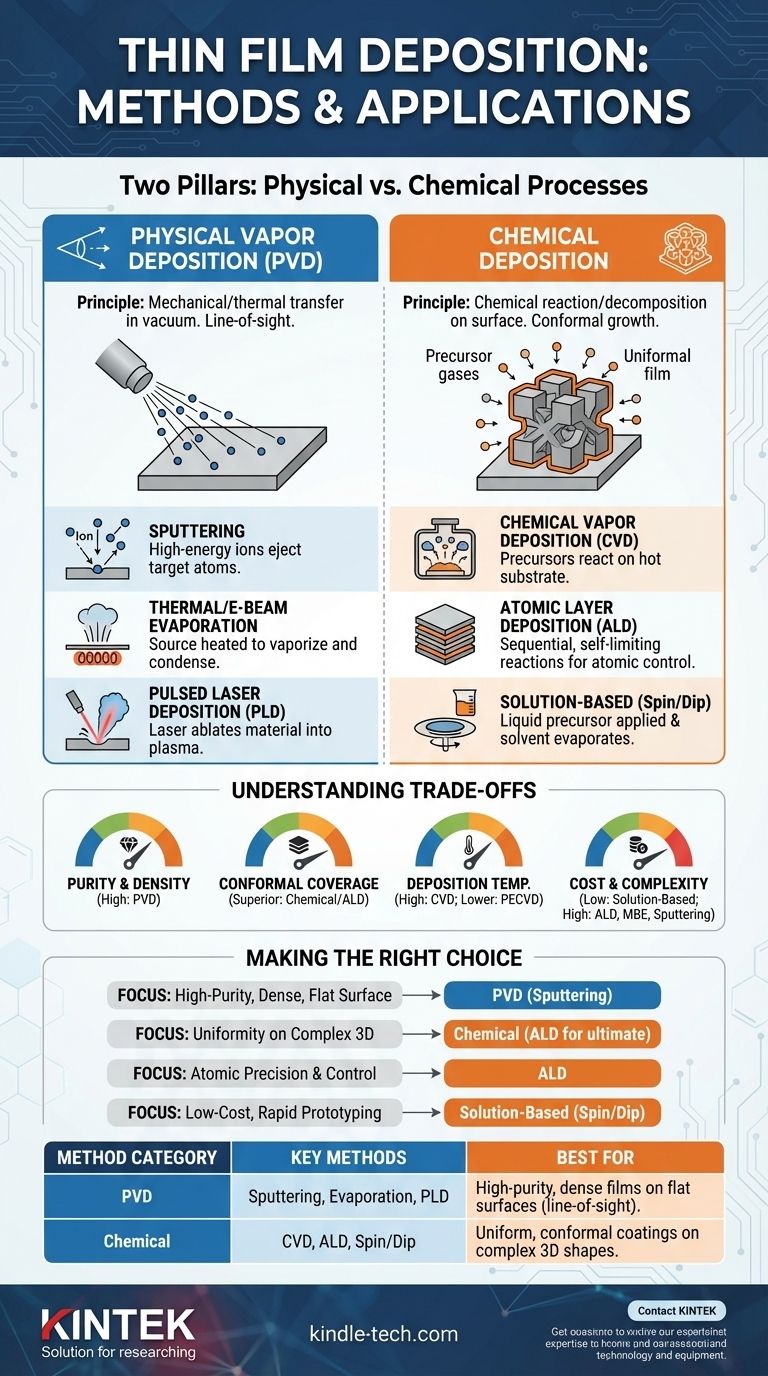
In thin film deposition, all methods fall into two primary categories: Physical Deposition and Chemical Deposition. Physical methods mechanically or thermally transfer a material from a source to a substrate, often in a vacuum, while chemical methods use a chemical reaction on the substrate's surface to grow the film.
The crucial distinction is not the specific technique but its underlying principle. Physical methods move solid material, while chemical methods build material from molecular precursors. Your choice depends entirely on whether you need the dense, line-of-sight coverage of a physical process or the uniform, conformal coating of a chemical one.

The Two Pillars of Deposition: Physical vs. Chemical
Thin film deposition is the process of applying a layer of material, from a few nanometers to many micrometers thick, onto a substrate to alter its properties. Understanding the fundamental difference between the two main families of techniques is the first step in selecting the correct process.
The Principle of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD encompasses a set of vacuum deposition methods. In all PVD processes, a solid or liquid source material is vaporized in a vacuum chamber, transported across the chamber, and condensed onto the substrate as a thin film.
Because the material travels in a straight line, PVD is considered a line-of-sight process. This makes it ideal for coating flat surfaces but challenging for coating complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden areas.
The Principle of Chemical Deposition
Chemical deposition methods use volatile precursor chemicals that react or decompose on the substrate's surface to produce the desired film. The film is essentially "grown" on the component.
These methods are not limited by line-of-sight. As long as the precursor gas or liquid can reach a surface, it can form a film, making chemical methods exceptionally good at producing highly conformal coatings on complex geometries.
Key Physical Deposition Methods
Physical methods are prized for creating dense, high-purity films with strong adhesion.
Sputtering
In sputtering, a target of the desired material is bombarded with high-energy ions (typically from a gas like Argon) inside a vacuum chamber. This bombardment ejects, or "sputters," atoms from the target, which then deposit onto the substrate.
Thermal & Electron Beam Evaporation
This is one of the simplest PVD methods. The source material is heated in a vacuum until it evaporates. The vapor then travels through the chamber and condenses on the cooler substrate. Heating can be done resistively (like in a toaster) or by using a high-energy electron beam (E-beam) for materials with higher melting points.
Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD)
In PLD, a high-power pulsed laser is focused on a target within a vacuum chamber. Each laser pulse ablates, or vaporizes, a tiny amount of the material, creating a plasma plume that expands toward the substrate and deposits as a thin film.
Key Chemical Deposition Methods
Chemical methods are chosen for their ability to coat complex shapes uniformly and, in some cases, for their atomic-level precision.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, the substrate is placed in a reaction chamber and heated. Precursor gases are introduced, which react or decompose on the hot surface to form a solid film. The byproducts of the reaction are then pumped away.
Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD)
ALD is a subtype of CVD that allows for exceptional thickness control. It uses a sequence of self-limiting chemical reactions. Precursor gases are introduced one at a time, with each pulse forming exactly one atomic or molecular layer, resulting in unparalleled uniformity and conformity.
Solution-Based Methods (Spin & Dip Coating)
These are among the simplest and most cost-effective methods. A liquid precursor (a "sol-gel" or chemical solution) is applied to the substrate by spinning it at high speed (spin coating) or by dipping it into the solution and withdrawing it at a controlled rate (dip coating). The film is formed as the solvent evaporates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is universally superior. The choice involves balancing film requirements against process limitations.
Purity and Density
PVD methods, conducted in a high vacuum, generally produce films with higher purity and density compared to many chemical processes. The vacuum environment minimizes the incorporation of contaminants into the growing film.
Conformal Coverage
This is the primary strength of chemical methods. The ability of precursor gases to reach all surfaces makes ALD and CVD far superior for uniformly coating complex parts, such as trenches in microelectronics or the interior of porous materials. PVD is fundamentally limited by shadowing.
Deposition Temperature
Traditional CVD often requires very high substrate temperatures (hundreds of degrees Celsius), which can damage sensitive substrates like plastics or certain electronic components. Variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) use plasma to enable reactions at lower temperatures, mitigating this issue.
Cost and Complexity
Solution-based methods like spin coating are simple, fast, and inexpensive, making them excellent for lab-scale research. In contrast, systems for ALD, MBE (Molecular Beam Epitaxy), and Sputtering are complex, require high vacuum, and represent a significant capital investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a method requires aligning the process capabilities with your primary goal for the thin film.
- If your primary focus is a high-purity, dense, wear-resistant coating on a relatively flat surface: PVD methods like sputtering are the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is a perfectly uniform coating on a complex 3D structure: Chemical methods are necessary, with ALD offering the ultimate conformal coverage.
- If your primary focus is atomic-level precision and control over film thickness: ALD is the only method that provides true layer-by-layer growth.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, rapid prototyping on simple substrates: Solution-based methods like spin coating or dip coating offer unmatched simplicity.
Ultimately, choosing the right deposition method is a matter of selecting the right tool for the specific engineering problem you need to solve.
Summary Table:
| Method Category | Key Methods | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Sputtering, Evaporation, PLD | High-purity, dense films on flat surfaces (line-of-sight). |
| Chemical Deposition | CVD, ALD, Spin/Dip Coating | Uniform, conformal coatings on complex 3D shapes. |
Ready to select the perfect thin film deposition method for your project? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables for your specific PVD, CVD, or ALD needs. Whether you require high-purity sputtering targets, robust thermal evaporation systems, or precise ALD reactors, we have the solutions to enhance your research and development. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's thin film deposition challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















