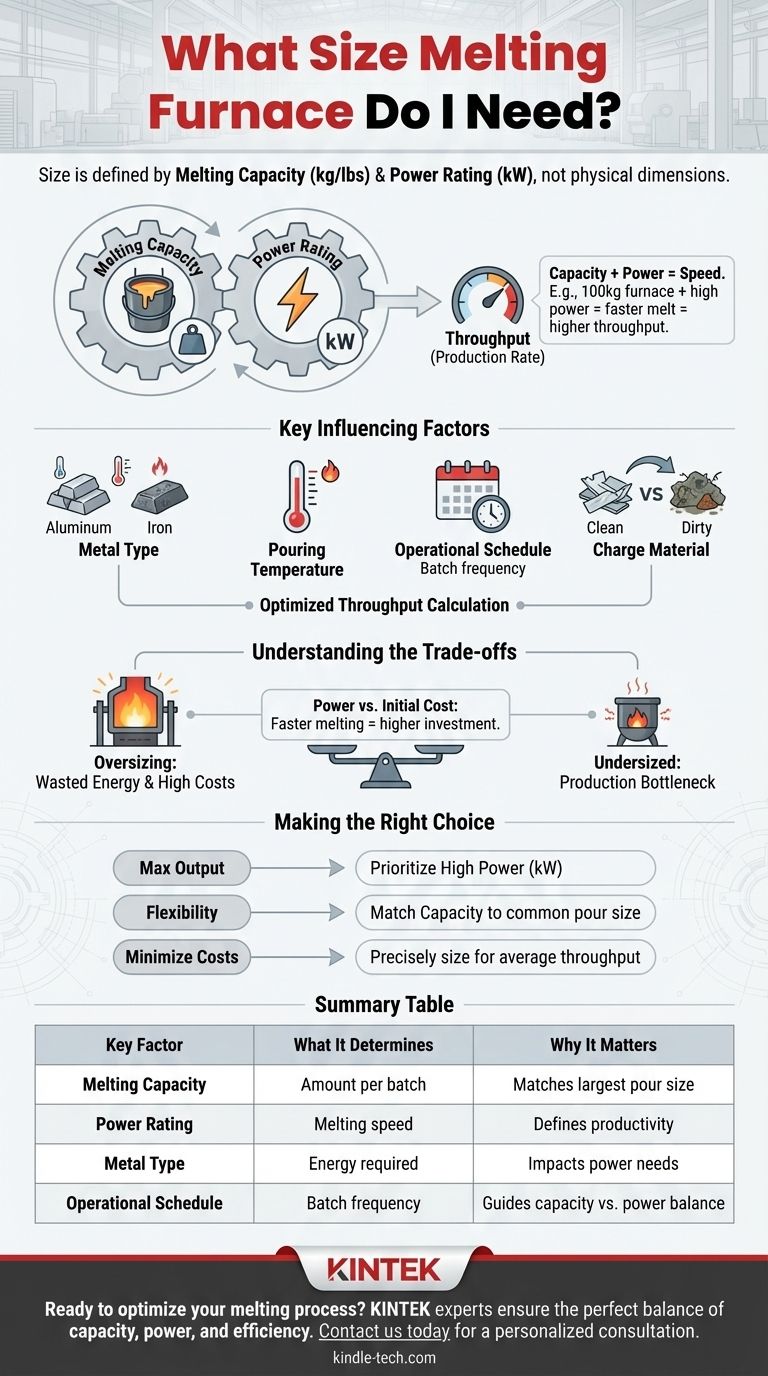
Choosing the right size melting furnace is a decision based on two interconnected factors: the amount of metal you need per batch and how quickly you need to melt it. The "size" is defined not by physical dimensions but by its melting capacity (in kg or lbs) and its power rating (in kW), which together determine your production throughput.
The right furnace "size" is not about its physical footprint but its performance capability. Your choice should be driven by your required production rate (e.g., kilograms per hour) and the specific metal you are melting, as these factors dictate the necessary power and capacity to achieve your goals efficiently.

Beyond "Size": The Two Core Metrics to Define
To make an informed decision, you must move beyond the general concept of "size" and focus on the two technical parameters that truly define a furnace's performance.
Melting Capacity (kg or lbs)
This is the most straightforward metric. It refers to the total weight of molten metal the furnace crucible can safely hold at one time.
Your required capacity is determined by the size of the parts you are casting or the amount of metal you need for a single pour.
Power Rating (kW)
The power rating dictates the melting speed or heating rate. A furnace with a higher kilowatt rating will melt a given amount of metal much faster than one with a lower rating.
Power is the engine of your melting operation. It directly influences your overall productivity and turnaround time.
The Critical Relationship: Calculating Throughput
The goal is to match the furnace to your required throughput, typically measured in kilograms or pounds per hour. Capacity and power are linked to determine this.
For example, a 100 kg furnace might melt its full capacity in one hour with a certain power rating, giving you a throughput of 100 kg/hr. A higher-power version of that same 100 kg furnace might melt the load in just 30 minutes, doubling your potential throughput to 200 kg/hr.
Key Factors That Influence Your Sizing Decision
Your specific application will determine the ideal balance between capacity and power. Consider these factors carefully.
Type of Metal Being Melted
Different metals have vastly different melting points and thermal properties. Melting 100 kg of aluminum requires significantly less energy and time than melting 100 kg of iron.
Always specify the primary metal you will be melting, as this is a fundamental input for any power calculation.
Required Pouring Temperature
The temperature required for pouring is often higher than the metal's actual melting point. Holding metal at this higher temperature consumes additional energy.
Factoring in your target pouring temperature ensures the furnace has enough power to not only melt the metal but also bring it to the correct state for casting.
Operational Schedule
Consider how you will use the furnace. Do you need to run multiple small, fast batches per day, or do you perform one large melt for an entire shift?
A high-throughput operation benefits from higher power, while a job shop with intermittent needs might prioritize capacity matched to their largest casting.
Charge Material and Method
Clean, densely packed charge material melts far more efficiently than loose, dirty, or oxidized scrap.
Your charging practice directly impacts the furnace's real-world melting rate. A well-managed process can maximize the output of a moderately powered furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance with cost. Misjudging your needs can lead to significant operational inefficiencies.
Oversizing: The Cost of Wasted Energy
A furnace that is too large for your needs—either in capacity or power—is inefficient. It will consume excess energy just to maintain temperature and will rarely operate at its peak efficiency point. This leads to higher per-unit costs.
Undersizing: The Bottleneck in Production
An undersized furnace will constantly struggle to keep up with demand. It will become the primary bottleneck in your production line, limiting your growth and forcing the equipment to run at its absolute limit, potentially reducing its operational lifespan.
Power vs. Initial Cost
A higher power rating delivers faster melting but comes with a higher upfront investment and can increase your peak electricity demand charges. You must balance the need for speed against your capital budget and utility costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
To select the correct furnace, align your choice with your primary operational driver.
- If your primary focus is maximum production output: Prioritize a higher power rating (kW) to achieve the fastest possible melting rates for your required batch size.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility: Choose a capacity that matches your most common pour size, ensuring the power supply is robust enough for efficient melting without being excessive.
- If your primary focus is minimizing costs: Opt for a furnace that is precisely sized for your average throughput, which avoids the energy waste of an oversized system and the production delays of an undersized one.
Ultimately, a thorough analysis of your required throughput—not just physical dimensions—will guide you to the most efficient and profitable furnace investment.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | What It Determines | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Capacity (kg/lbs) | Amount of metal per batch | Matches your largest pour size |
| Power Rating (kW) | Melting speed and throughput | Defines productivity and turnaround time |
| Metal Type | Energy required for melting | Impacts power needs (e.g., aluminum vs. iron) |
| Operational Schedule | Batch frequency and usage pattern | Guides capacity vs. power balance |
Ready to optimize your melting process?
Choosing the right furnace size is critical for your productivity and profitability. The experts at KINTEK specialize in matching lab equipment like melting furnaces to your specific operational needs, ensuring you get the perfect balance of capacity, power, and efficiency.
We serve laboratories and production facilities by providing reliable, high-performance equipment tailored to your metals and throughput requirements.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK help you achieve maximum efficiency in your melting operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















