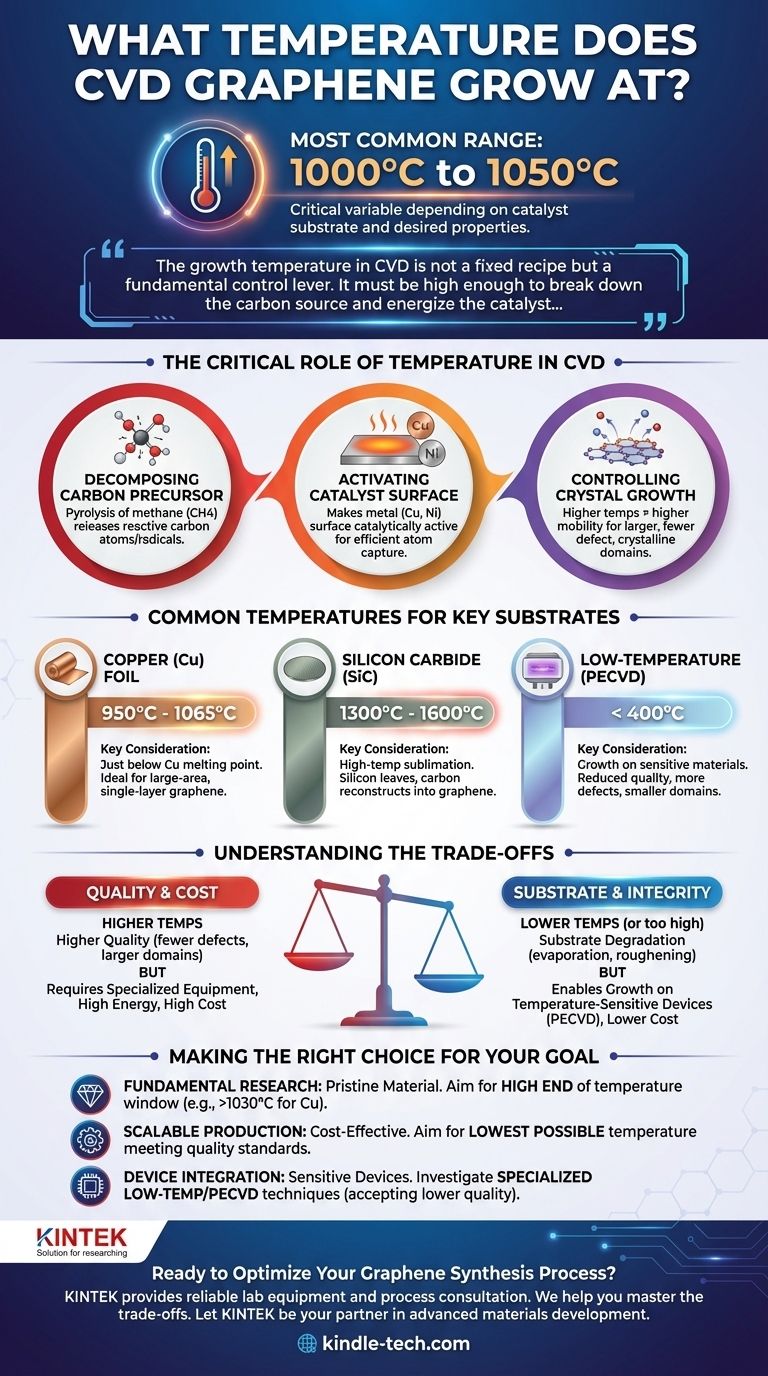
In practice, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) for high-quality graphene is most commonly performed at temperatures around 1000°C to 1050°C. However, this number is not absolute; it is a critical variable that depends heavily on the catalytic substrate being used and the desired properties of the final graphene film.
The growth temperature in CVD is not a fixed recipe but a fundamental control lever. It must be high enough to break down the carbon source and energize the catalyst, directly influencing the final quality, domain size, and defect density of the graphene sheet.
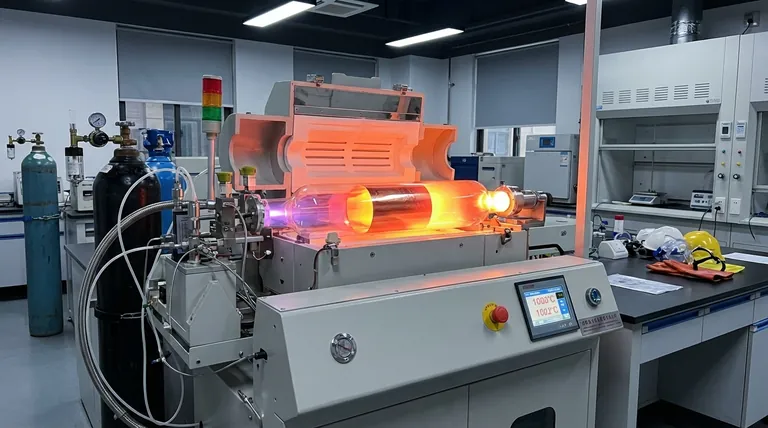

The Critical Role of Temperature in CVD
Temperature is arguably the most important parameter in the CVD synthesis of graphene. It directly governs the core chemical and physical processes that allow a single layer of carbon atoms to form a crystalline lattice.
Decomposing the Carbon Precursor
The process begins with a carbon-containing gas, most often methane (CH4). High temperatures provide the necessary thermal energy to break the strong chemical bonds in these precursor molecules.
This decomposition, or pyrolysis, releases reactive carbon atoms or radicals that can then be adsorbed onto the catalyst surface.
Activating the Catalyst Surface
Graphene CVD relies on a metal catalyst, typically a copper (Cu) or nickel (Ni) foil. The high temperature makes this metal surface catalytically active.
This activation allows the surface to efficiently capture the carbon atoms and facilitates their arrangement into the hexagonal honeycomb lattice structure of graphene.
Controlling Crystal Growth and Quality
Once on the surface, carbon atoms diffuse and nucleate, forming small islands of graphene called "domains." The temperature dictates the mobility of these atoms.
Higher temperatures allow atoms to move more freely across the surface, enabling them to find the most energetically favorable positions. This leads to larger, more perfectly crystalline domains and a final film with fewer defects.
Common Temperatures for Key Substrates
The ideal temperature is intrinsically linked to the chosen catalyst substrate. Different materials have different catalytic properties and melting points, defining the operational window for synthesis.
Growth on Copper (Cu) Foil
Copper is the most widely used catalyst for producing large-area, single-layer graphene.
The typical temperature range for growth on copper is between 950°C and 1065°C. This is strategically just below the melting point of copper (1085°C), maximizing surface atom mobility without melting the substrate.
Growth on Silicon Carbide (SiC)
An alternative method involves growing graphene directly on a silicon carbide wafer. This is not a traditional CVD process but a high-temperature sublimation where silicon atoms leave the surface, leaving behind carbon atoms that reconstruct into graphene.
This process requires significantly higher temperatures, typically in the range of 1300°C to 1600°C, to induce the necessary sublimation of silicon.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a growth temperature is a balance between achieving ideal material properties and managing practical process constraints.
Quality vs. Cost
Generally, higher temperatures yield higher-quality graphene with fewer defects and larger crystal domains.
However, maintaining temperatures above 1000°C requires specialized quartz tube furnaces and consumes significant energy, increasing the overall cost of the process.
Substrate Integrity
Operating too close to the catalyst's melting point increases the risk of substrate degradation. For copper, this can include evaporation (which contaminates the system) or surface roughening, both of which negatively impact the uniformity of the resulting graphene film.
The Push for Low-Temperature Growth
Significant research is dedicated to lowering the growth temperature. This would reduce costs and enable the direct growth of graphene on substrates that cannot withstand 1000°C heat, such as certain plastics or silicon wafers with pre-existing electronics.
These low-temperature methods, often using plasma-enhanced CVD (PECVD), can produce graphene below 400°C. However, this typically comes at the cost of reduced crystalline quality, introducing more defects and smaller domain sizes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal temperature is defined by your ultimate objective. Use this framework to guide your process decisions.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research on pristine material: You must operate at the high end of the temperature window for your chosen catalyst (e.g., >1030°C for copper) to maximize crystal size and minimize defects.
- If your primary focus is scalable, cost-effective production: You should aim for the lowest possible temperature that still produces graphene meeting the minimum quality standards for your commercial application.
- If your primary focus is integration with temperature-sensitive devices: You will need to investigate specialized low-temperature or PECVD growth techniques, fully accepting the inherent trade-off in material quality.
By understanding temperature as a key variable within a complex system of precursors, catalysts, and pressures, you can effectively control and optimize the outcome of your graphene synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Substrate | Typical Growth Temperature Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) Foil | 950°C - 1065°C | Most common for single-layer graphene; temperature is just below copper's melting point. |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1300°C - 1600°C | Used for direct growth via sublimation; requires significantly higher temperatures. |
| Low-Temperature (PECVD) | < 400°C | Enables growth on sensitive materials but often results in lower crystalline quality. |
Ready to Optimize Your Graphene Synthesis Process?
Choosing the right growth temperature is critical for achieving the desired quality and properties in your graphene films. The precise thermal control required for successful CVD is where KINTEK's expertise shines.
We provide the reliable lab equipment you need to master this complex process:
- High-Temperature Tube Furnaces: Engineered for stable operation up to 1200°C and beyond, ensuring the consistent heat necessary for high-quality graphene growth on copper and other substrates.
- Process Consultation: Our specialists can help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature, substrate choice, and final material quality to meet your specific research or production goals.
Let KINTEK be your partner in advanced materials development. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and accelerate your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some of the different methods of chemical vapour deposition? Choose the Best CVD Process for Your Application
- How does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment improve the lithiophilicity of copper? Boost Battery Stability
- What is chemical vapor deposition of CNT? A Guide to Scalable, Controlled Nanotube Synthesis
- Why is CVD important in fabrication? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Quality and Precision
- What are the different types of chemical vapour deposition process? A Guide to CVD Methods for Your Lab
- What role does a high-vacuum turbomolecular pump system play in ALD? Ensure Defect-Free, High-Density Coating Purity
- What is the function of a CVD system in tungsten film fabrication? Precision High-Purity Coating Solutions
- What is the pressure of sputtering process? Mastering the Key to High-Quality Thin Films



















