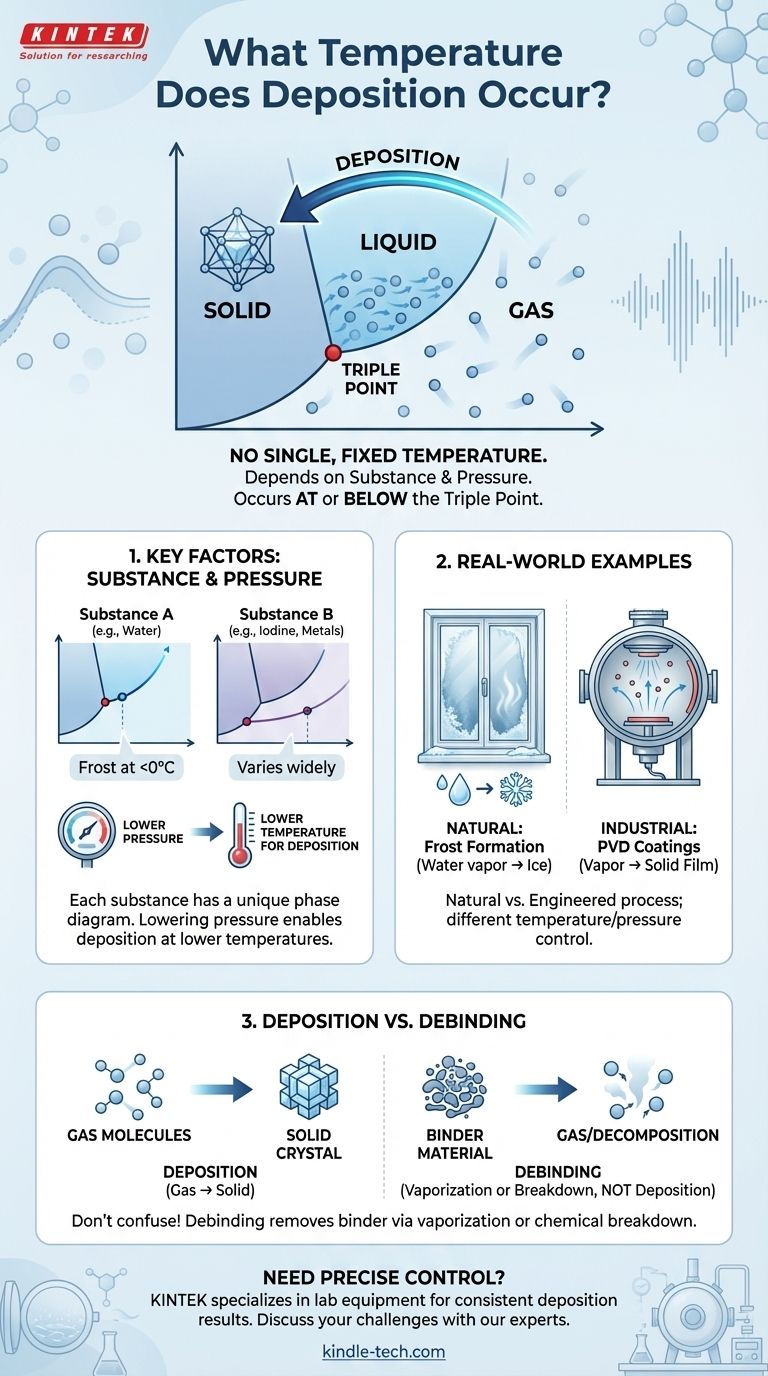
Deposition does not occur at a single, fixed temperature. Instead, the specific temperature for deposition—the process where a gas turns directly into a solid—is entirely dependent on the substance in question and the surrounding pressure. This phase transition happens at or below a substance's "triple point," the unique condition where its solid, liquid, and gas phases can coexist in equilibrium.
The critical takeaway is that "deposition temperature" is not a universal constant but a variable point on a substance's phase diagram. It is defined by the specific relationship between temperature and pressure that allows a material to bypass its liquid state.

What is Deposition? A First-Principles Look
To understand why there's no single answer, we need to look at the physics of phase changes. Deposition is fundamentally linked to a substance's unique energetic properties.
From Gas Directly to Solid
Deposition is a thermodynamic process where gas molecules lose enough thermal energy to lock directly into a solid crystal structure, skipping the liquid phase entirely.
This process is the direct reverse of sublimation, where a solid turns directly into a gas (like dry ice, which is solid carbon dioxide, turning into vapor).
The Role of the "Triple Point"
Every substance has a phase diagram that maps its physical state (solid, liquid, gas) across a range of temperatures and pressures.
The triple point is a specific temperature and pressure on this diagram where all three phases coexist. Deposition can only occur at temperature and pressure combinations below this triple point.
Everyday Example: Frost on a Window
The most common example of deposition is the formation of frost. On a cold night, water vapor (a gas) in the air comes into contact with a surface, like a window pane, that is below the freezing point of water.
If the conditions are right (below water's triple point), the water vapor molecules transition directly into solid ice crystals without first becoming liquid water droplets.
Key Factors That Determine Deposition Temperature
Since there is no universal temperature, you must consider two primary factors for any specific application.
The Substance Itself
Every substance has a unique molecular structure and bonding energy, resulting in a different phase diagram. The deposition conditions for water are vastly different from those for iodine or the metals used in industrial coatings.
The Critical Role of Pressure
Pressure is equally important as temperature. Lowering the pressure generally makes it easier for a substance to remain in a gaseous state at lower temperatures.
In controlled environments like a vacuum chamber, manipulating the pressure allows engineers to induce deposition at specific, targeted temperatures that might be impossible under normal atmospheric conditions.
Clarifying Common Misconceptions
It's easy to confuse deposition with other thermal processes that occur in industrial settings. Understanding the distinction is key to process control.
Deposition vs. Debinding
The reference to a debinding process finishing at 600°C describes a fundamentally different mechanism. Debinding is the thermal removal of a "binder" material used to hold particles together in a preliminary part.
This process works by vaporization (liquid to gas) or thermal decomposition (breaking down the binder's molecules), not deposition. The 600°C figure is specific to the binder's chemical properties, not a gas-to-solid phase transition.
Deposition in Industrial Applications
In manufacturing, processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are used to apply thin film coatings to tools, optics, and semiconductors.
Here, a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum, transported as a gas, and then allowed to deposit onto a cooler target surface. The "deposition temperature" in this context is a carefully engineered process variable, not a natural property.
Finding the Right Temperature for Your Goal
To determine the relevant temperature for deposition, you must first define your context.
- If your primary focus is understanding a natural phenomenon (like frost): You must reference the phase diagram for that specific substance (e.g., water) and consider the ambient temperature and partial pressure.
- If your primary focus is controlling an industrial process (like PVD): The deposition temperature is an engineered parameter that depends on the coating material, the substrate, and the desired film properties, which are found in process documentation.
- If your primary focus is differentiating from other thermal processes: Remember that deposition is a specific phase change (gas to solid), while processes like debinding involve removing material through vaporization or chemical breakdown under a different set of thermal rules.
Ultimately, determining the deposition temperature requires shifting from seeking a single number to understanding the interplay between a specific substance, its temperature, and its pressure.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Why It Matters for Deposition Temperature |
|---|---|
| Substance | Each material has a unique phase diagram and triple point. |
| Pressure | Lowering pressure allows deposition to occur at lower temperatures. |
| Process Goal | Industrial PVD and natural frost formation have different requirements. |
Need precise control over deposition temperatures for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including vacuum chambers and thermal systems, that enable accurate temperature and pressure control for consistent deposition results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific material science or thin-film coating challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















