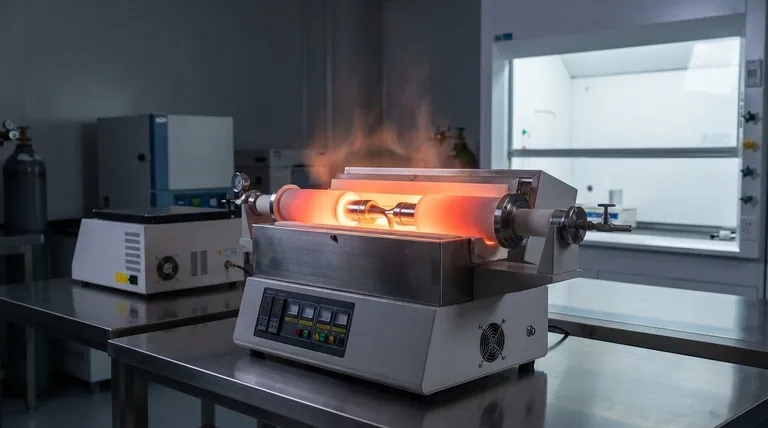
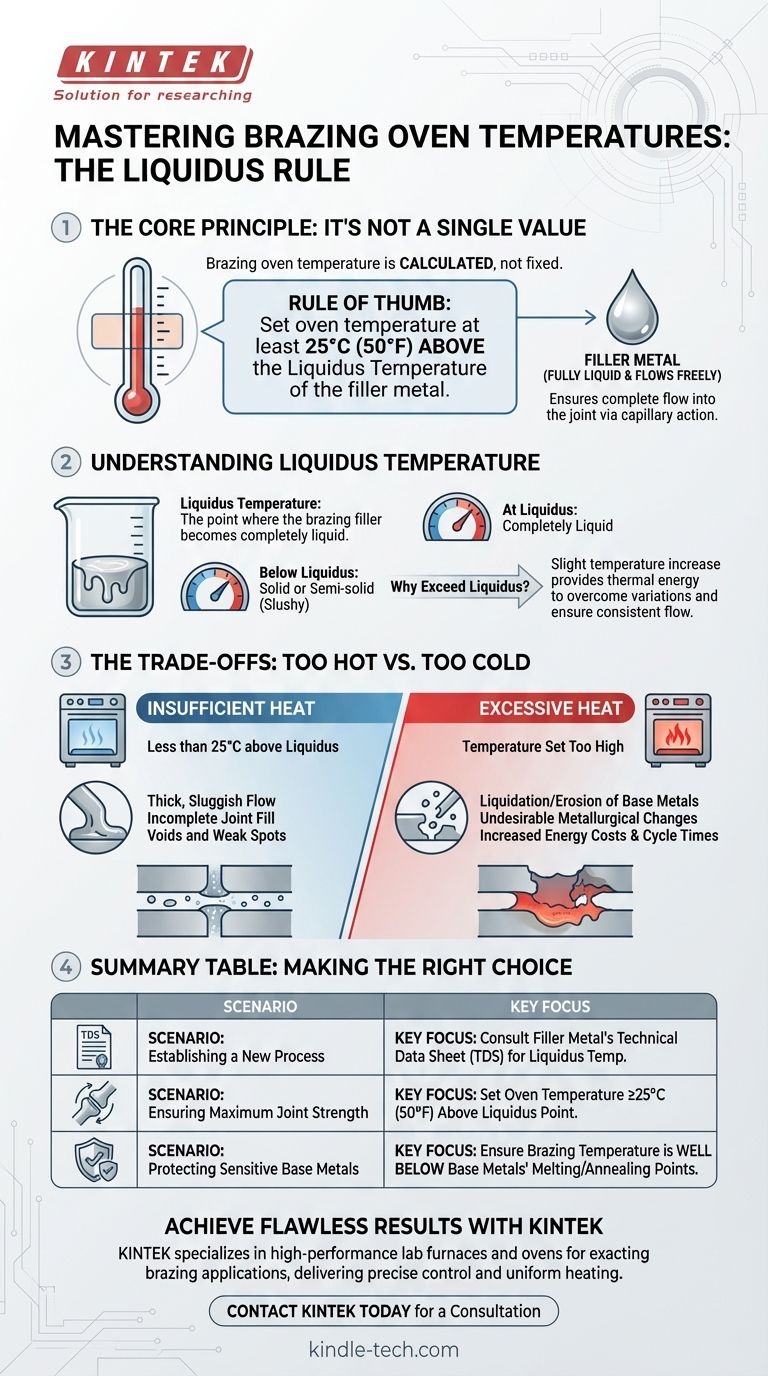
The temperature of a brazing oven is not a single, fixed value. Instead, it is precisely calculated based on the specific filler metal being used. The standard industry practice is to set the oven to a temperature that is at least 25°C (50°F) above the liquidus temperature of that filler metal.
The core principle is that the brazing oven's temperature must be hot enough to make the filler metal fully liquid and flow freely, but not so hot that it damages the base metals being joined. The right temperature is a function of your materials, not a generic setting.

The Core Principle: Liquidus Temperature is Key
To understand brazing temperatures, you must first understand the concept of "liquidus." This single property dictates the entire thermal profile of your process.
What is 'Liquidus'?
The liquidus temperature is the point at which a metal alloy, in this case, the brazing filler, becomes completely liquid. Below this temperature, the alloy will be either solid or in a semi-solid, slushy state.
Why You Must Exceed the Liquidus Temperature
Simply reaching the liquidus temperature is not enough. The oven must be hotter to ensure the filler metal flows smoothly and completely into the joint through capillary action.
This slight temperature increase provides the necessary thermal energy to overcome any minor temperature variations across the parts, ensuring a consistent and strong bond.
The 25°C (50°F) Rule of Thumb
The guideline to set the furnace at least 25°C (50°F) above the liquidus point provides a critical safety margin. It guarantees the filler becomes fully molten and fluid enough to penetrate the entire joint interface without requiring excessive heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Too Hot vs. Too Cold
Setting the correct temperature is a balancing act. Deviating in either direction can lead to joint failure, just for different reasons.
The Dangers of Insufficient Heat
If the oven temperature is too low (i.e., less than 25°C above liquidus), the filler metal may not become fully liquid. This results in a thick, sluggish flow.
This poor flow prevents the filler from completely filling the joint, creating voids and weak spots that will compromise the structural integrity of the final assembly.
The Risks of Excessive Heat
Setting the temperature too high is equally problematic. Overheating can lead to the liquidation or erosion of the base metals, damaging the parts you are trying to join.
Excess heat can also cause undesirable metallurgical changes in the base metals, such as excessive grain growth, which can make them brittle. It also needlessly increases energy costs and cycle times.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine the correct brazing temperature, you must move from general rules to the specific details of your project. The answer lies in the technical data for your chosen materials.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new process: Begin by consulting the Technical Data Sheet (TDS) for your specific brazing filler metal to find its exact liquidus temperature.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum joint strength: Set your oven temperature at least 25°C (50°F) above that documented liquidus point to guarantee complete, fluid flow.
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive base metals: Always verify that your final brazing temperature is well below the melting point or annealing temperature of the components being joined.
Ultimately, mastering your brazing temperature is the first step toward creating consistently strong and reliable joints.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Scenario | Key Temperature Focus |
|---|---|
| Establishing a New Process | Consult the filler metal's Technical Data Sheet (TDS) for its liquidus temperature. |
| Ensuring Maximum Joint Strength | Set oven temperature at least 25°C (50°F) above the liquidus point. |
| Protecting Sensitive Base Metals | Ensure brazing temperature is below the base metals' melting/annealing points. |
Achieve flawless brazing results every time.
Mastering the precise temperature profile is critical for creating strong, reliable bonds without damaging your components. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and ovens, including models designed for exacting brazing applications. Our equipment delivers the precise temperature control and uniform heating you need to consistently exceed your filler metal's liquidus point for perfect joint integrity.
Let our experts help you select the ideal brazing oven for your specific materials and process requirements. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and ensure your brazing process is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What are the tubes in a furnace called? Understanding the Role of the Working Tube
















