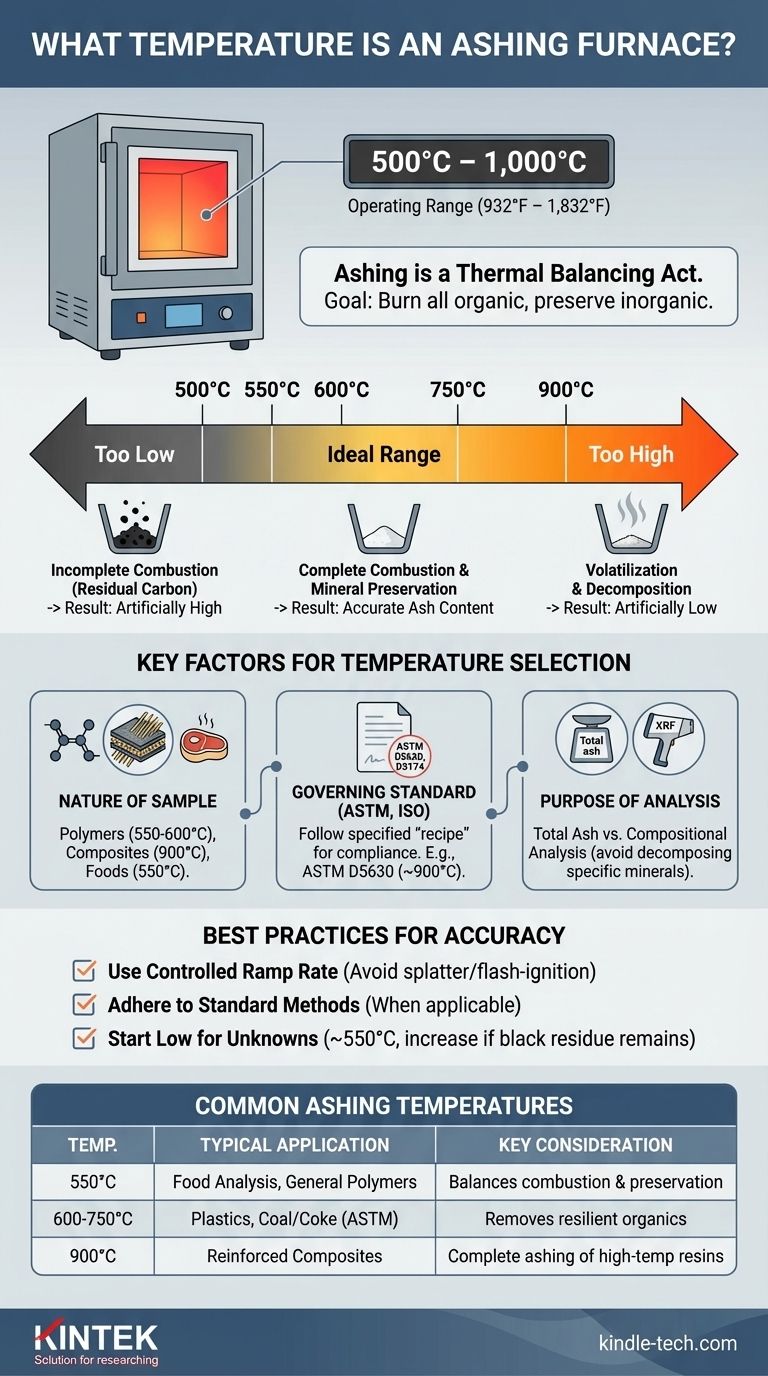
An ashing furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, typically operates within a temperature range of 500°C to 1,000°C (932°F to 1,832°F). The exact temperature is not a single value but is critically dependent on the specific material being analyzed and the official standard method being followed, with common setpoints including 550°C, 600°C, and 900°C.
Ashing is a thermal balancing act. The goal is to set a temperature high enough to completely burn away all organic material, but not so high that it causes the inorganic ash you are trying to measure to decompose or vaporize.

What is Ashing and Why is Temperature Critical?
Ashing is a fundamental analytical technique used to determine the amount of inorganic, non-combustible material in a sample. The temperature you choose directly dictates the accuracy and validity of your result.
The Goal: Isolating Inorganic Content
The core principle of ashing is thermal decomposition. By heating a sample in the presence of air, you initiate combustion. The high heat breaks down and burns off all the organic compounds—primarily carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen—as gases like CO2 and H2O.
What remains is the ash: a residue of the inorganic materials like minerals, fillers (e.g., glass fiber, talc in plastics), or salts that do not burn. The weight of this ash is then used to calculate the percentage of inorganic content in the original sample.
The Thermal Balancing Act
The selected temperature must be precise. It needs to be sufficiently high to ensure every last bit of organic matter is converted to gas. Any residual carbon will be weighed with the ash, leading to an artificially high and incorrect result.
However, if the temperature is too high, it can cause some of the inorganic components themselves to become volatile or decompose. This leads to a loss of mass, resulting in an artificially low and incorrect ash content measurement.
Key Factors That Determine Ashing Temperature
You cannot choose an ashing temperature without first considering the context of your analysis. Three factors are paramount: the sample, the standard, and the goal.
The Nature of Your Sample
Different materials require different temperatures for complete and accurate ashing.
- Polymers: Standard plastics like polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP) are often ashed at lower temperatures, around 550°C to 600°C.
- Reinforced Composites: Plastics containing resilient fillers like glass fiber or certain minerals may require higher temperatures, such as 900°C, to ensure all polymer resin is eliminated.
- Foods and Organics: Many food analysis procedures specify 550°C. This is hot enough to burn off carbohydrates and proteins without vaporizing volatile mineral salts.
The Governing Standard Method (ASTM, ISO)
For quality control and regulatory compliance, most industries rely on standardized test methods. These documents provide a non-negotiable "recipe" for the procedure.
For example, ASTM D5630 specifies ashing protocols for plastics, often using temperatures around 900°C. ASTM D3174 is used for determining the ash content in coal and coke, specifying temperatures around 750°C or 950°C depending on the method. Always defer to the official standard if one applies to your work.
The Purpose of the Analysis
If your only goal is to measure the total ash percentage, your main concern is ensuring complete combustion without volatilization.
However, if you plan to perform a compositional analysis on the resulting ash (e.g., using X-ray fluorescence), your temperature choice is even more constrained. You must avoid temperatures that could change the chemical state of the minerals you intend to analyze.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Common Ashing Pitfalls
Mistakes in ashing almost always trace back to an incorrect temperature setting or heating profile.
The Problem with Too Low a Temperature
If the temperature is not high enough, combustion will be incomplete. You will be left with unburnt carbon in your crucible, which typically looks like black or grey specks.
This residual carbon adds weight, making your final ash content measurement inaccurately high.
The Danger of Too High a Temperature
This is a more subtle but equally serious error. Certain inorganic compounds, like some chlorides and carbonates, can decompose or vaporize at very high temperatures.
For instance, calcium carbonate (CaCO3) can decompose into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide gas above ~825°C. This loss of CO2 gas from the ash leads to a final weight that is inaccurately low.
The Importance of Ramp Rate
The speed at which the furnace heats up (ramp rate) is also critical. If you heat the sample too quickly, it can flash-ignite or splatter, physically ejecting material from the crucible.
This loss of material, whether organic or inorganic, will lead to an invalid result. A slow, controlled ramp rate allows for gentle decomposition and ensures all material remains in the crucible for an accurate final weighing.
Selecting the Correct Temperature for Your Application
To ensure accurate and repeatable results, you must approach temperature selection methodically. Use these guidelines to make the right choice.
- If you are following a standard method (e.g., ASTM, ISO): Adhere strictly to the specified temperature, ramp rate, and dwell time, as these have been validated for that specific material.
- If you are analyzing common polymers or organic materials: Start with a widely accepted temperature like 550°C and check the resulting ash for a clean, white/light-colored appearance.
- If you are developing a new method or analyzing an unknown material: Begin with a lower temperature (~550°C) and inspect the ash for unburnt carbon. If black residue is present, repeat the test on a new sample at a slightly higher temperature (e.g., increase by 50°C) until the ash is consistently free of carbon.
- If you are concerned about losing volatile mineral components: Research the decomposition temperatures of the expected inorganic compounds in your sample and deliberately choose an ashing temperature well below that threshold.
By understanding these principles, you can move from simply following a procedure to truly controlling your analytical outcome.
Summary Table:
| Common Ashing Temperature | Typical Application | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 550°C | Food Analysis, General Polymers | Balances complete combustion with mineral preservation |
| 600°C - 750°C | Plastics, Coal/Coke (per ASTM) | Ensures removal of resilient organic material |
| 900°C | Reinforced Composites, Glass-filled Plastics | Required for complete ashing of high-temperature resins |
Achieve precise and reliable ashing results with KINTEK.
Selecting the correct furnace temperature is critical for accurate ash content measurement. Whether you are analyzing polymers, composites, or food products, our expert team and high-quality lab equipment are here to support your specific application needs.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable ashing furnaces and consumables for laboratories, ensuring you get valid results every time.
Contact our experts today to discuss your ashing requirements and find the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What type of insulation is used in a muffle furnace? Essential Materials for High-Temperature Performance
- What is a muffle furnace used in determination of? Precise Ash Content and Material Composition
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of muffle furnace? Achieve Absolute Purity and Control in Your Lab
- What is the working principle of laboratory muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What are the lab safety rules for heating substances? Essential Protocols to Prevent Accidents



















