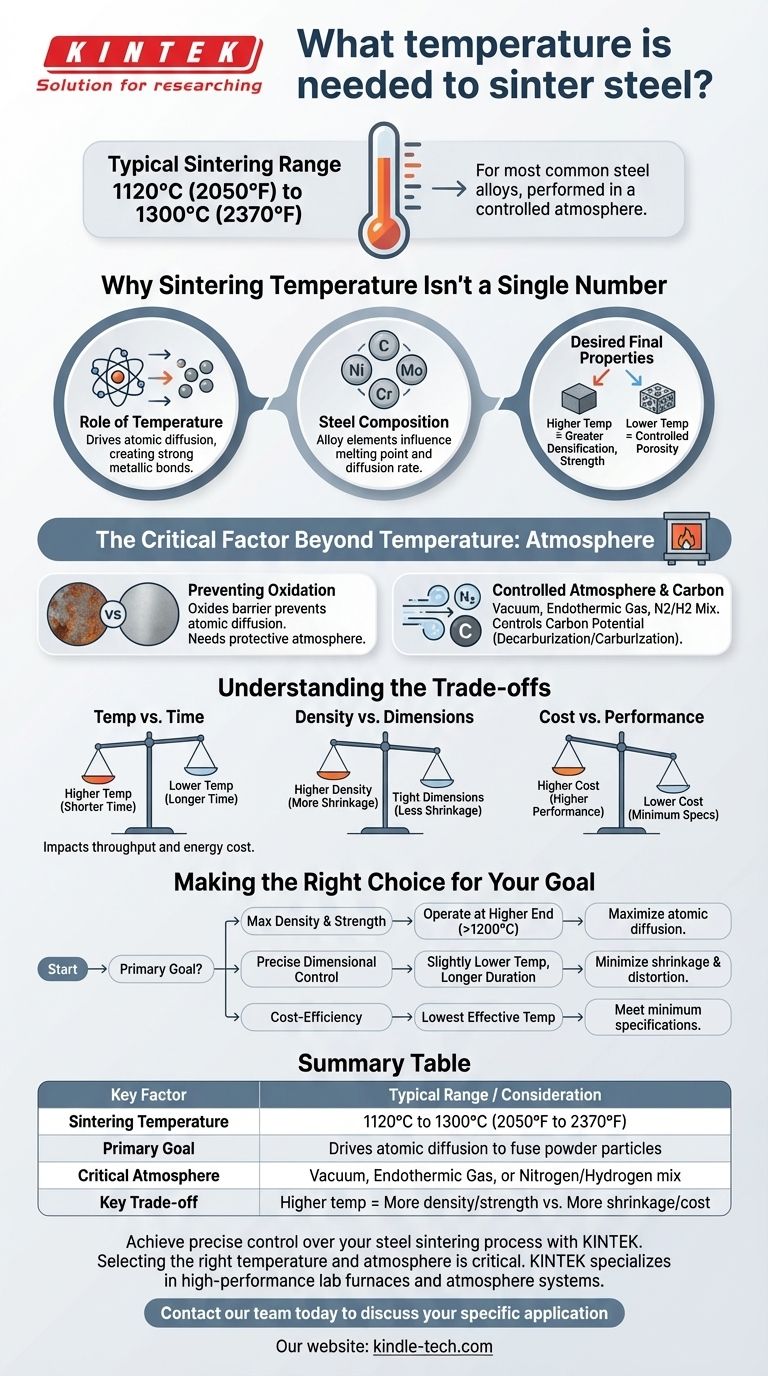
For most common steel alloys, the necessary sintering temperature falls within a range of 1120°C to 1300°C (approximately 2050°F to 2370°F). This process is performed in a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation and ensure the metal powder particles fuse together correctly.
The specific temperature for sintering steel is not a single value but a critical process variable that must be adjusted based on the steel's specific alloy composition, the desired final density, and the mechanical properties required for the part.

Why Sintering Temperature Isn't a Single Number
Successfully sintering a steel component requires understanding the interplay between heat, material science, and the desired outcome. The temperature is a tool to achieve a specific goal, not the goal itself.
The Role of Temperature in Sintering
The primary purpose of heat in sintering is to provide enough thermal energy to drive atomic diffusion. This process allows atoms to move between the surfaces of individual powder particles, creating strong metallic bonds that fuse the loose powder into a solid, coherent mass.
Impact of Steel Composition
Different steel alloys contain various elements like carbon, nickel, molybdenum, or chromium. These elements directly influence the material's melting point and the rate of diffusion, thus dictating the ideal sintering temperature. For example, alloys with a lower melting point will naturally require a lower sintering temperature.
Desired Final Properties
The final temperature directly impacts the part's characteristics. Higher temperatures generally promote greater densification, leading to increased strength and hardness. However, this also causes more shrinkage and can risk distortion. Lower temperatures may be used if some level of porosity is acceptable or desired, such as in self-lubricating bearings.
The Critical Factor Beyond Temperature: Atmosphere
Simply heating steel powder in the air will not work. The atmosphere inside the furnace is as critical as the temperature itself.
Preventing Oxidation
At high temperatures, the iron in steel reacts aggressively with oxygen, forming oxides (rust) on the particle surfaces. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the atomic diffusion necessary for proper bonding.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
To prevent oxidation, sintering is performed in a vacuum or, more commonly, a protective atmosphere. This often consists of an endothermic gas or a blend of nitrogen and hydrogen, which removes oxygen and protects the part's surface.
Controlling Carbon Content
For carbon steels, the furnace atmosphere must also have the correct carbon potential. An incorrect atmosphere can either strip carbon from the steel (decarburization), making it weaker, or add excess carbon (carburization), making it brittle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering temperature involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" setting, only the optimal one for a specific application.
Temperature vs. Time
A similar level of sintering can often be achieved by using a lower temperature for a longer period or a higher temperature for a shorter time. This trade-off impacts furnace throughput, energy consumption, and overall operational cost.
Density vs. Dimensional Control
Pushing for the highest possible density with very high temperatures increases part shrinkage. This can make holding tight dimensional tolerances on the final component more challenging and may require secondary sizing operations.
Cost vs. Performance
Higher temperatures demand more energy and may require more expensive furnace materials and maintenance. This increased cost must be justified by the performance requirements of the final part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sintering temperature requires defining your primary objective for the finished component.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength: Operate at the higher end of the material's recommended sintering range, often above 1200°C, to maximize atomic diffusion.
- If your primary focus is maintaining precise dimensional control: Consider using a slightly lower temperature for a longer duration to minimize shrinkage and potential distortion.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for non-critical parts: Sinter at the lowest effective temperature that reliably meets the minimum performance and density specifications for the application.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is about precisely controlling these variables to consistently produce parts that meet their engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Typical Range / Consideration |
|---|---|
| Sintering Temperature | 1120°C to 1300°C (2050°F to 2370°F) |
| Primary Goal | Drives atomic diffusion to fuse powder particles |
| Critical Atmosphere | Vacuum, Endothermic Gas, or Nitrogen/Hydrogen mix |
| Key Trade-off | Higher temperature = More density/strength vs. More shrinkage/cost |
Achieve precise control over your steel sintering process with KINTEK.
Selecting the right temperature and atmosphere is critical for achieving the desired density, strength, and dimensional accuracy in your sintered steel components. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and atmosphere systems designed for the exacting demands of metal powder sintering.
Our experts can help you optimize your sintering parameters to balance performance, cost, and throughput. Whether you need maximum strength or tight dimensional control, we have the equipment and knowledge to support your goals.
Ready to enhance your sintering results? Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and discover the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What are the tubes in a furnace called? Understanding the Role of the Working Tube
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness



















