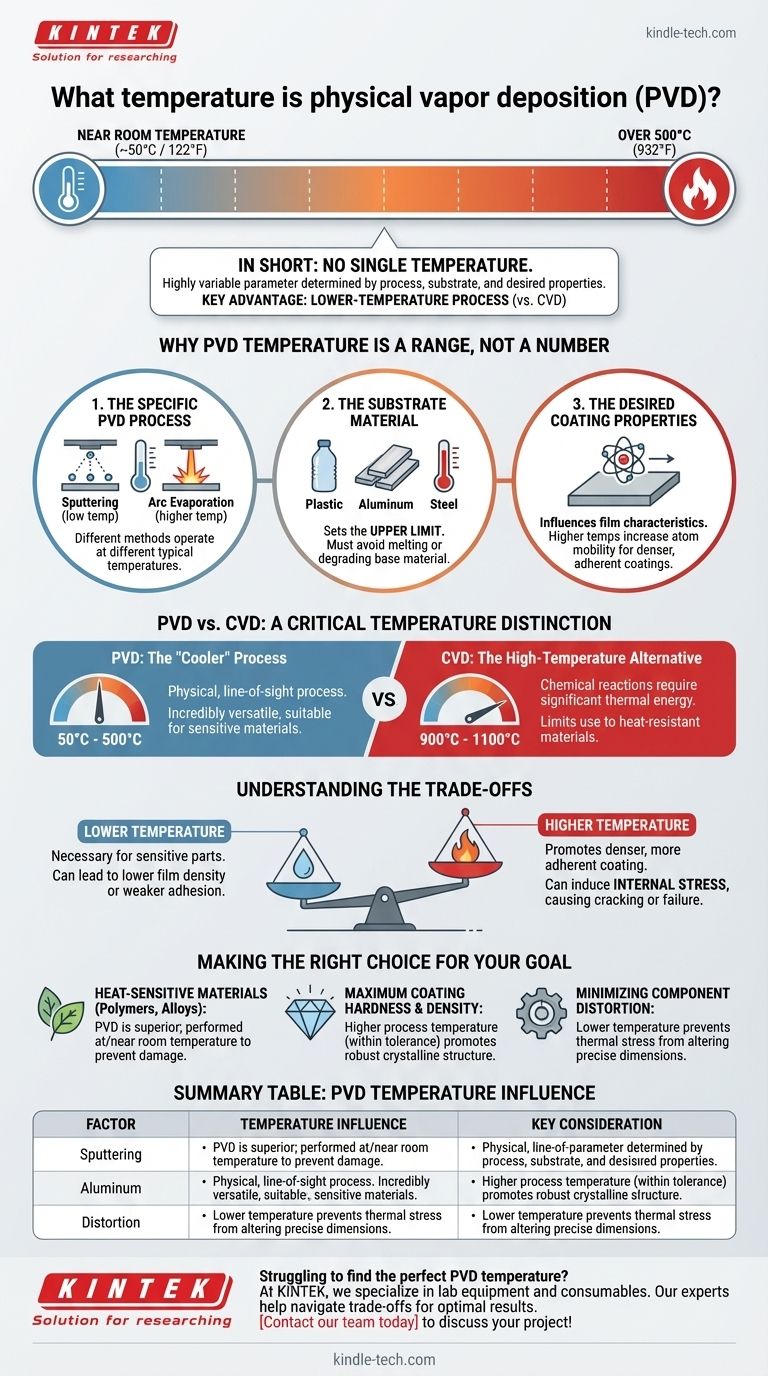
In short, there is no single temperature for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The process temperature is a highly variable parameter, typically ranging from near room temperature to over 500°C (932°F). The correct temperature is determined by the specific PVD technique used, the material being coated (the substrate), and the properties desired in the final coating.
The essential takeaway is that PVD is fundamentally a lower-temperature coating process compared to alternatives like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This variability and relatively low heat are its key advantages, allowing it to be used on a wide range of materials, including those sensitive to heat.
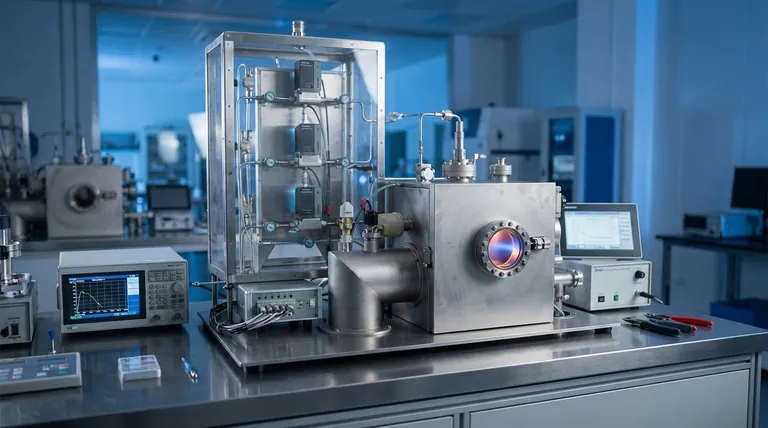

Why PVD Temperature is a Range, Not a Number
The operating temperature in a PVD process is not a fixed value but a critical parameter that is carefully controlled to achieve a specific outcome. Several factors dictate the final process temperature.
The Specific PVD Process
Different PVD methods operate at different typical temperatures. For example, some sputtering processes can be run at relatively low temperatures, while certain arc evaporation techniques used for hard coatings require higher temperatures to achieve the desired film structure.
The Substrate Material
This is often the most significant limiting factor. The process temperature must remain well below the point where the substrate material would melt, soften, or otherwise degrade. This is why PVD is ideal for coating temperature-sensitive materials like plastics, aluminum alloys, or pre-hardened steels that cannot be re-tempered.
The Desired Coating Properties
Temperature directly influences the characteristics of the deposited film. Higher temperatures generally increase the mobility of atoms on the substrate surface, which can lead to a denser, more adherent coating. However, this is not always the desired outcome.
PVD vs. CVD: A Critical Temperature Distinction
Understanding the context of PVD temperature is best done by comparing it to its main alternative, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
PVD: The "Cooler" Process
PVD is a "line-of-sight" physical process that deposits a thin film atom by atom. Its typical operating range of 50°C to 500°C is considered low in the world of industrial coatings, making it incredibly versatile.
CVD: The High-Temperature Alternative
CVD relies on chemical reactions on the substrate surface, which require significant thermal energy to initiate. Consequently, CVD processes often run at extremely high temperatures, frequently in the range of 900°C to 1100°C. This limits its use to materials that can withstand extreme heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right temperature involves balancing competing factors. This is where process engineering becomes critical.
Lower Temperature vs. Adhesion
While low temperatures are necessary for sensitive parts, they can sometimes result in lower film density or weaker adhesion compared to a hotter process. This can be mitigated by other techniques, such as ion bombardment, but it remains a primary consideration.
Higher Temperature vs. Internal Stress
Conversely, running the process too hot for a given substrate-coating combination can be detrimental. The mismatch in thermal expansion between the two materials as they cool can induce high levels of internal stress, potentially causing the coating to crack, peel, or fail prematurely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal PVD temperature is entirely dependent on your objective.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials (like polymers or certain alloys): PVD is the superior choice precisely because it can be performed at or near room temperature, preventing damage to the part.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum coating hardness and density: A higher process temperature, within the substrate's tolerance, is generally required to promote a more robust crystalline structure in the film.
- If your primary focus is minimizing component distortion: A lower temperature is essential to prevent thermal stress from altering the precise dimensions of your part.
Ultimately, viewing PVD temperature not as a static number but as a strategic tool is key to achieving a successful coating.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Temperature Influence | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| PVD Process Type | Defines the baseline range | Sputtering (lower temp) vs. Arc Evaporation (higher temp) |
| Substrate Material | Sets the upper limit | Must avoid melting, softening, or degrading the base material |
| Desired Coating | Optimizes film properties | Higher temps often increase density and adhesion |
Struggling to find the perfect PVD temperature for your specific substrate and coating goals?
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables for advanced coating applications. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature, adhesion, and material integrity to achieve optimal results for your laboratory's needs.
Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your PVD process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings



















