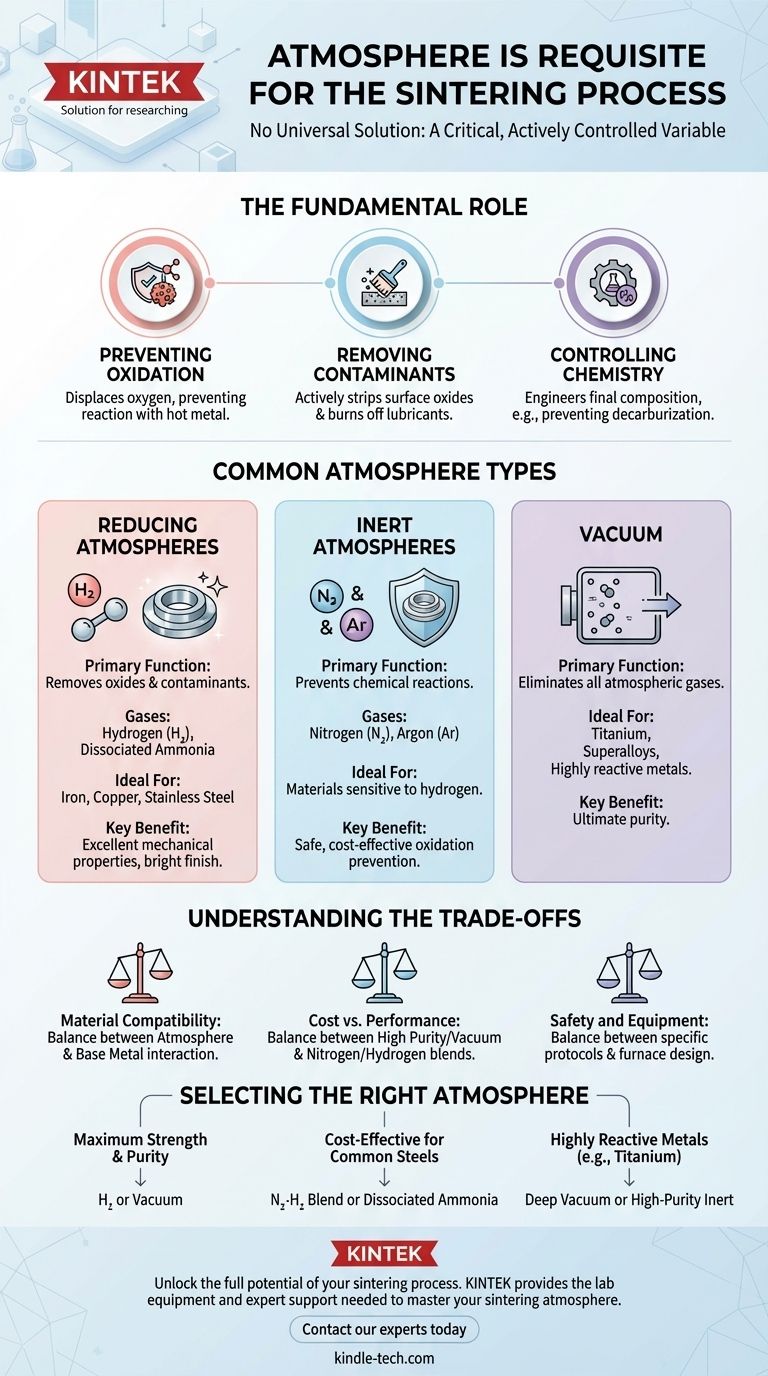
There is no single, universal atmosphere for sintering. Instead, the atmosphere is a critical, actively controlled variable selected based on the specific powdered material being used and the desired properties of the final component. The choice ranges from chemically reactive gases like hydrogen to inert environments or even a vacuum, each serving a distinct purpose in the high-temperature process.
The primary role of a sintering atmosphere is not merely to surround the part, but to actively control chemical reactions at the particle surfaces. A carefully chosen atmosphere prevents destructive oxidation and removes contaminants, ensuring the atomic bonds that give the final part its strength can form correctly.
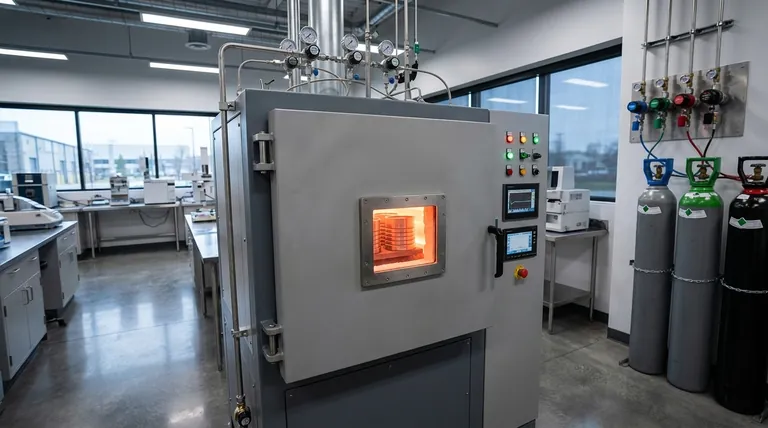

The Fundamental Role of the Sintering Atmosphere
Sintering transforms a collection of loose particles into a solid mass using heat below the material's melting point. At these high temperatures, the surfaces of the metal particles are highly reactive. The surrounding atmosphere dictates the success or failure of this transformation.
Preventing Oxidation
The most critical function of a sintering atmosphere is to prevent oxygen from reacting with the hot metal. Just as iron rusts in the open air, most metal powders will rapidly form performance-degrading oxides at sintering temperatures, which inhibit proper bonding between particles.
A controlled atmosphere displaces the oxygen, protecting the material.
Removing Surface Contaminants
Many metal powders have a thin layer of existing oxide on their surface before they even enter the furnace. A reducing atmosphere, such as one containing hydrogen, actively strips these oxides away, presenting clean, pure metallic surfaces that can bond effectively.
This cleaning action also helps burn off residual lubricants used during the initial powder compaction stage.
Controlling Material Chemistry
For certain alloys, like steel, the atmosphere can be used to control the final chemical composition. It can be engineered to prevent the loss of carbon (decarburization) from the steel's surface, which is essential for maintaining the material's hardness and wear resistance.
Common Types of Sintering Atmospheres
The choice of atmosphere is a deliberate engineering decision based on the material being processed, the desired outcome, and operational costs.
Reducing Atmospheres
Atmospheres containing hydrogen (H₂) are highly effective for many common metals like iron, copper, and stainless steel. High-purity hydrogen provides the best possible reducing conditions, leading to clean parts with excellent mechanical properties and a bright surface finish.
A common, cost-effective alternative is dissociated ammonia, which breaks down into a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen.
Inert Atmospheres
Gases like nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar) are used when the primary goal is simply to prevent any chemical reaction. They displace oxygen without actively reacting with the metal powder. This is crucial for materials that might have a negative reaction to hydrogen.
Vacuum
Sintering in a vacuum is the ultimate way to remove all atmospheric contaminants. By pumping out nearly all the gas from the furnace chamber, there is nothing left to react with the hot material. This method is often required for highly reactive metals such as titanium or certain superalloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an atmosphere involves balancing performance requirements with practical constraints. Simply choosing the most reactive atmosphere is not always the best approach.
Material Compatibility
The primary consideration is how the atmosphere interacts with the base metal. For example, while hydrogen is an excellent reducing agent for steel, it can cause embrittlement in certain other metals. The atmosphere must be chemically compatible with the material.
Cost vs. Performance
High-purity gases and high-vacuum furnaces represent a significant operational cost. For less demanding applications, a nitrogen-based atmosphere or a less pure hydrogen blend might provide perfectly adequate results for a fraction of the price.
Safety and Equipment
Different atmospheres carry different safety protocols. Hydrogen is flammable, while inert gases like nitrogen pose an asphyxiation risk in enclosed spaces. Furthermore, the furnace itself must be designed to safely contain the specific gas pressure or vacuum level required.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Application
The optimal choice depends entirely on your end goal. The atmosphere is not an afterthought; it is an essential ingredient in the process.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and purity: A high-purity hydrogen atmosphere or a vacuum is the superior choice for thoroughly removing oxides and ensuring the strongest possible bonds between particles.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective processing of common steels: A nitrogen-hydrogen blend or dissociated ammonia provides a good balance of reducing potential and operational cost for reliable results.
- If your primary focus is working with highly reactive metals like titanium: A deep vacuum or a high-purity inert gas like argon is non-negotiable to prevent any chemical contamination or reaction.
Ultimately, treating the atmosphere as a critical process ingredient, not just a background condition, is the key to successful and repeatable sintering.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Primary Function | Ideal For Materials | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing (e.g., Hydrogen) | Removes oxides and contaminants | Iron, Copper, Stainless Steel | Excellent mechanical properties, bright finish |
| Inert (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) | Prevents chemical reactions | Materials sensitive to hydrogen | Safe, cost-effective oxidation prevention |
| Vacuum | Eliminates all atmospheric gases | Titanium, Superalloys | Ultimate purity for highly reactive metals |
Unlock the full potential of your sintering process. The right atmosphere is critical for achieving the strength, purity, and performance your materials demand. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and expert support needed to master your sintering atmosphere. Whether you're working with common steels or advanced alloys, our solutions are tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you optimize your sintering results and enhance your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization



















