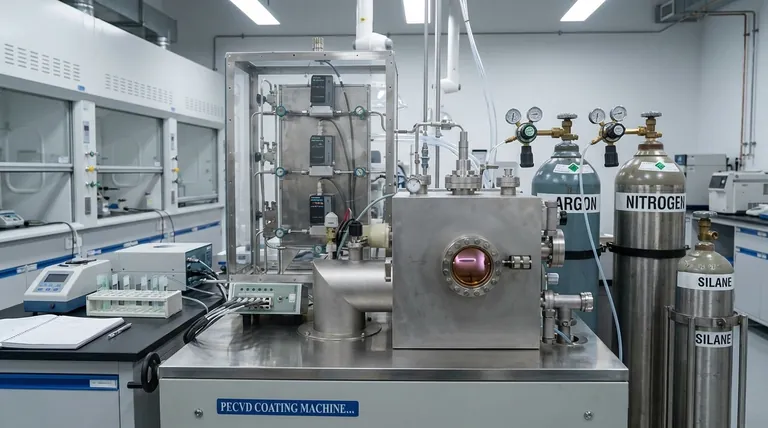
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the process relies on a precise mixture of gases, not a single substance. This mixture is composed of two primary categories: reactant gases, also known as precursors, which contain the elements that will form the solid film, and carrier or diluent gases, which are inert and used to transport the reactants and control the reaction environment.
The core principle to understand is that the choice of gas is fundamental to the entire process. The reactant gases determine what material is deposited, while the inert gases provide control over how that material is deposited by managing concentration, flow, and reaction rates.
The Two Fundamental Roles of Gases in CVD
To understand the process, you must recognize that different gases perform distinct and critical jobs inside the reaction chamber. The entire deposition is a carefully choreographed interaction between these gas types.
Reactant Gases (Precursors): The Building Blocks
Reactant gases are the most critical component, as they are the source of the material you intend to deposit. These gaseous molecules contain the atomic elements that will form the final, solid thin film on the substrate.
They are specifically chosen based on the desired coating. For example, depositing silicon requires a silicon-containing precursor gas, while depositing titanium nitride requires both titanium- and nitrogen-containing precursors.
These gases are designed to decompose or react when they come into contact with the heated substrate, leaving behind the solid material and releasing other elements as gaseous byproducts.
Carrier and Diluent Gases: The Process Controllers
These are chemically inert gases, such as argon or nitrogen, that do not participate in the primary chemical reaction. They serve two vital functions.
First, they act as the carrier, physically transporting the reactant gas molecules from the gas source into the reaction chamber and to the surface of the substrate.
Second, they act as a diluent, allowing technicians to precisely control the concentration of the reactant gases. This is critical for managing the deposition rate and ensuring a uniform, high-quality film.
Reaction Byproducts: The Exhaust
The chemical reactions that form the film also create unwanted gaseous byproducts. These leftover gases are desorbed from the substrate surface and must be continuously evacuated from the chamber.
Proper removal of byproducts is essential to prevent them from interfering with the deposition process or being incorporated as impurities into the growing film.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Selection Criteria
Choosing the right gases is not a simple task. It involves balancing the desired outcome with significant practical and safety considerations. Ignoring these factors can lead to poor results or hazardous conditions.
The Critical Nature of Precursor Selection
Safety is a primary concern. Many highly effective precursor gases are also highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive. The potential byproducts of the reaction can also be hazardous.
Therefore, the selection process must include a thorough risk assessment and the implementation of appropriate handling and abatement systems.
Purity and Contamination
The purity of both the reactant and carrier gases is paramount. Even trace amounts of contaminants, like water or oxygen, can be incorporated into the film.
These impurities can drastically alter the film's electrical, optical, or mechanical properties, leading to device failure or poor performance.
Balancing Flow Rates
The ratio of reactant gas to diluent gas is a critical process parameter that directly influences film quality.
If the reactant concentration is too high, reactions can occur in the gas phase before reaching the substrate, creating particles that result in a rough or powdery coating. If it's too low, the deposition rate will be impractically slow.
Matching Gases to Your Deposition Goal
Your specific objective dictates how you should prioritize your gas selection and control strategy.
- If your primary focus is material composition: Your choice of reactant gases (precursors) is the most critical decision, as they directly supply the elements for the film.
- If your primary focus is film quality and uniformity: The flow rates and ratios of carrier and diluent gases are paramount for controlling reaction kinetics and ensuring even deposition.
- If your primary focus is process safety and stability: The potential toxicity and reactivity of both the precursor gases and their byproducts must be carefully evaluated and managed.
Ultimately, mastering the gas mixture is the key to controlling the outcome and quality of any CVD process.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Function | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Reactant Gases (Precursors) | Supply elements to form the solid film | Silane (SiH₄), Titanium Tetrachloride (TiCl₄) |
| Carrier/Diluent Gases | Transport reactants & control concentration | Argon (Ar), Nitrogen (N₂), Hydrogen (H₂) |
| Reaction Byproducts | Waste gases to be evacuated from the chamber | Hydrogen Chloride (HCl), Methane (CH₄) |
Optimize Your CVD Process with KINTEK's Expertise
Choosing the right gas mixture is critical for achieving high-quality, uniform thin films. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored for precise Chemical Vapor Deposition. Our solutions help you manage precursor delivery, gas flow rates, and safety protocols effectively.
Whether you are depositing silicon, titanium nitride, or other advanced materials, we can support your laboratory needs with equipment designed for stability and purity.
Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your CVD process and ensure optimal deposition results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















