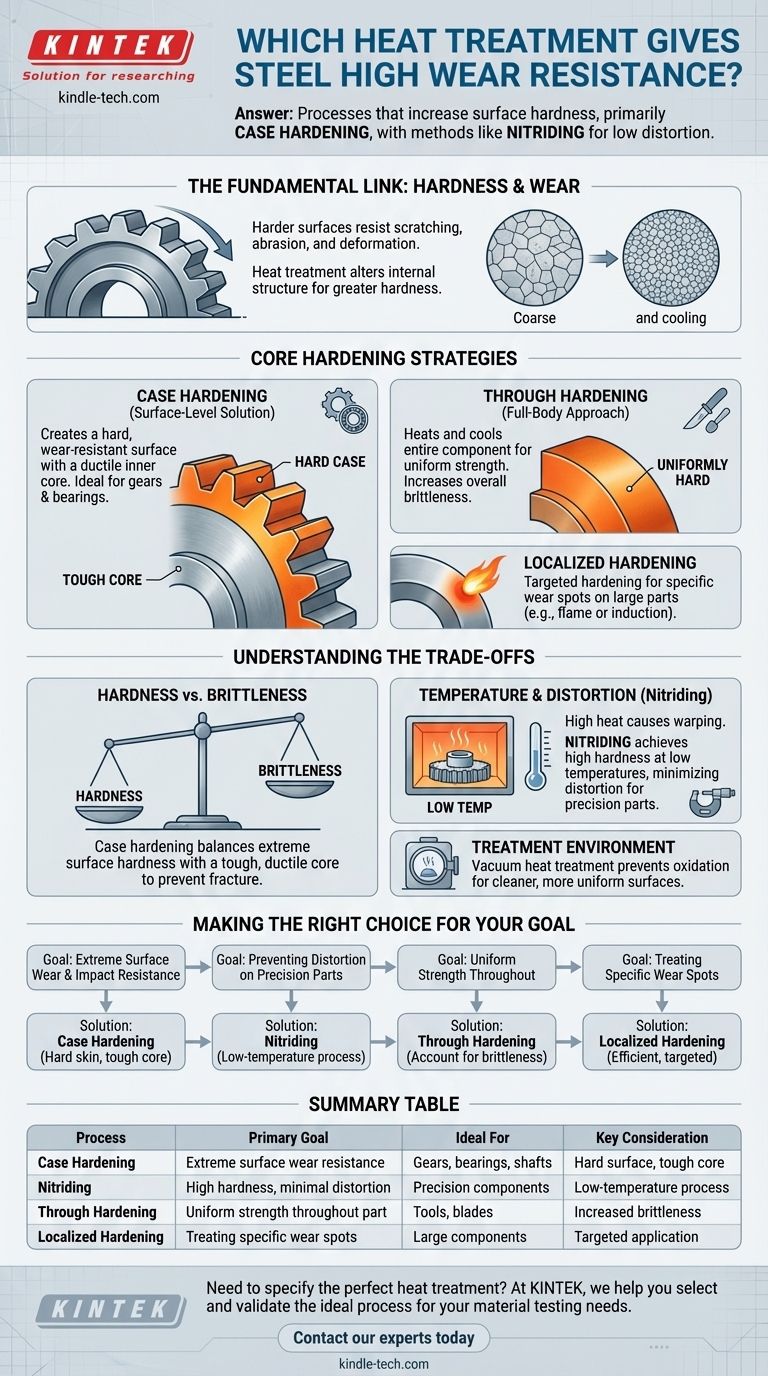
To give steel a high resistance against wear, you use heat treatment processes that increase surface hardness. The primary category for this is case hardening, which hardens only the outer layer of the component. Specific methods like nitriding are particularly effective as they achieve high hardness at low temperatures, minimizing part distortion.
The most effective strategy for wear resistance is not to harden the entire steel component, but to create an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer "case" while leaving the inner "core" tough and ductile. This provides the ideal combination of surface durability and overall structural integrity.

Why Hardness Dictates Wear Resistance
The Fundamental Link
Wear is the gradual removal of material from a surface due to mechanical action. A harder surface is inherently more resistant to being scratched, abraded, or deformed by friction and contact with other objects.
Heat treatment fundamentally alters the internal crystalline structure of the steel. By controlling heating and cooling cycles, you can create a microstructure that is denser and more resistant to deformation, directly increasing its hardness.
The Two Core Hardening Strategies
The primary decision in heat treatment for wear resistance is choosing between hardening just the surface or the entire part.
Case Hardening: The Surface-Level Solution
Case hardening creates a hard, wear-resistant surface layer (the "case") on a component while the material deeper inside (the "core") remains softer and tougher. This is the most common and effective approach for improving wear resistance.
This dual-property structure is ideal for parts like gears or bearings, which need to resist surface wear while also absorbing shock without fracturing.
Through Hardening: A Full-Body Approach
Through hardening heats and cools the entire component to make it uniformly hard all the way through. While this increases overall strength, it can also make the part more brittle and susceptible to cracking under impact.
This method is generally used when the entire component is subjected to high stress, not just surface wear.
Localized Hardening: A Targeted Method
For very large components or specific wear spots, localized hardening can be used. Techniques like flame or induction hardening apply intense heat to a very specific area, hardening it without affecting the rest of the part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right process requires understanding the balance between desired properties and potential downsides.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
The most critical trade-off is between hardness and brittleness. An extremely hard material often loses its ability to flex or deform under load, making it brittle.
Case hardening masterfully solves this problem. It provides extreme hardness where it's needed—on the surface—while the ductile core prevents catastrophic failure.
The Impact of Temperature and Distortion
High-temperature heat treatments can cause parts to warp, bend, or change dimensions. This is a significant problem for precision-engineered components.
Processes like nitriding are highly valued because they are performed at relatively low temperatures. This significantly reduces the risk of thermal distortion, ensuring the part maintains its precise shape and tolerances.
The Role of the Treatment Environment
The environment in which heat treatment occurs is also critical. Vacuum heat treatment, for example, is not a hardening process itself but a method for enhancing it.
By performing the treatment in a vacuum, you prevent surface oxidation and contamination, resulting in a cleaner, more uniform, and ultimately harder surface. This controlled environment optimizes the results of the hardening process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is extreme surface wear and impact resistance: Case hardening is the definitive solution, providing a hard skin over a tough core.
- If your primary focus is preventing distortion on a precision part: A low-temperature case hardening process like nitriding is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is uniform strength throughout the entire component: Through hardening is the correct approach, but you must account for the increase in brittleness.
- If your primary focus is treating a specific wear spot on a large part: Localized methods like flame or induction hardening are the most efficient.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heat treatment allows you to engineer the precise surface properties your steel component needs to perform its function reliably.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Ideal For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Hardening | Extreme surface wear resistance | Gears, bearings, shafts | Hard surface, tough core |
| Nitriding | High hardness, minimal distortion | Precision components | Low-temperature process |
| Through Hardening | Uniform strength throughout part | Tools, blades | Increased brittleness |
| Localized Hardening | Treating specific wear spots | Large components | Targeted application |
Need to specify the perfect heat treatment for your steel components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables for material testing and analysis. Our expertise helps you select and validate the ideal heat treatment process to achieve the precise hardness and wear resistance your application demands.
Let us help you enhance your component's durability and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and how our solutions can support your material science goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















