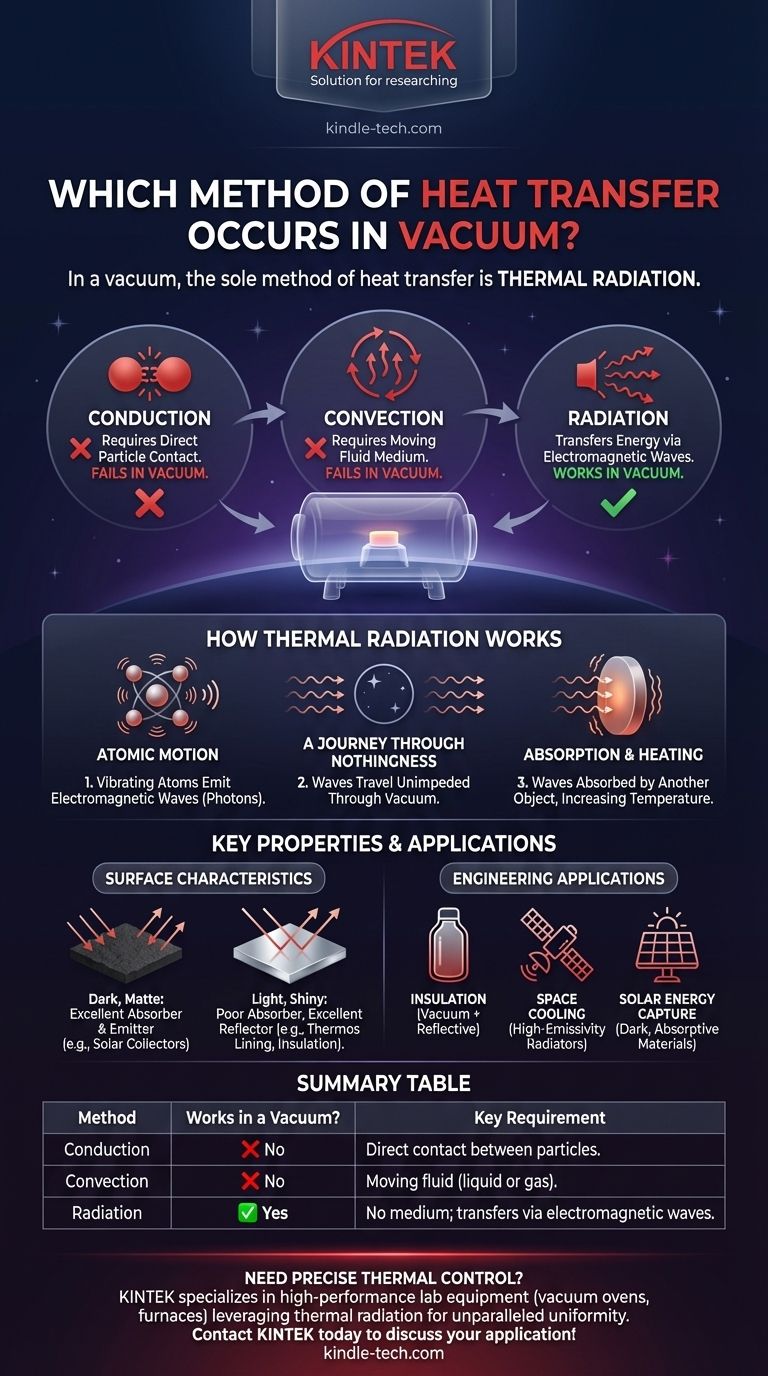
In a vacuum, the sole method of heat transfer is thermal radiation. This is because the other two primary methods of heat transfer—conduction and convection—require a medium of particles (atoms or molecules) to carry the thermal energy. Since a vacuum is, by definition, a space devoid of matter, radiation is the only process that can move heat across it.
While conduction and convection rely on particle interactions to transfer heat, thermal radiation moves energy via electromagnetic waves. This fundamental difference is why radiation is the only way heat can travel through the empty expanse of space or a man-made vacuum.

The Three Modes of Heat Transfer: A Quick Review
To understand why radiation is unique, it's helpful to quickly review all three mechanisms of heat transfer.
Conduction: The Molecular Chain Reaction
Conduction is heat transfer through direct contact. When a hot object touches a colder one, the faster-vibrating atoms in the hot object collide with the slower-vibrating atoms in the cold object, transferring kinetic energy. This is why a metal spoon heats up when left in a hot cup of coffee.
Convection: The Moving Fluid
Convection occurs when a fluid (a liquid or gas) moves, carrying thermal energy with it. Warmer, less dense fluid rises, and cooler, denser fluid sinks, creating a convection current. This is the principle behind boiling water or a room heater warming the air.
Why Conduction and Convection Fail in a Vacuum
Both conduction and convection depend entirely on the presence of atoms or molecules. Without a medium, there are no particles to collide (for conduction) or flow (for convection). A vacuum creates a physical barrier that stops these two processes completely.
How Thermal Radiation Works
Thermal radiation is fundamentally different. It does not rely on matter to propagate; it is a form of pure energy transport.
From Atomic Motion to Light Waves
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C or 0 Kelvin) has atoms in constant motion. This vibration causes the charged particles within those atoms to accelerate, which in turn emits electromagnetic waves, also known as photons.
These waves carry energy away from the object. This is not just a process for extremely hot objects; everything radiates energy, including ice cubes, planets, and the human body.
A Journey Through Nothingness
Once emitted, these electromagnetic waves travel outwards at the speed of light. They can pass through a vacuum unimpeded, just as starlight travels across the vast emptiness of space to reach our eyes.
Absorption and Heating
When these electromagnetic waves strike another object, their energy can be absorbed. This absorbed energy increases the kinetic energy of the receiving object's atoms, causing them to vibrate faster. We perceive this increase in atomic vibration as a rise in temperature. This is how the Earth is warmed by the Sun, despite the vacuum of space between them.
Key Properties of Thermal Radiation
Understanding radiation involves more than just knowing it works in a vacuum. Its behavior is governed by specific properties.
Surface Characteristics are Critical
The effectiveness of radiation depends heavily on an object's surface.
- Dark, matte surfaces are excellent absorbers and emitters of thermal radiation.
- Light, shiny surfaces are poor absorbers and emitters; they reflect most radiation instead. This is why a thermos has a silvered inner lining—to reflect heat back to the hot liquid (or away from the cold liquid), minimizing radiative heat transfer.
Temperature Dictates Intensity and Wavelength
The hotter an object is, the more thermal energy it radiates. Furthermore, the type of radiation changes with temperature. A lukewarm object primarily emits low-energy infrared waves (invisible to us), while a red-hot piece of iron emits higher-energy visible light.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling heat transfer is a core engineering challenge. Understanding radiation is key to designing effective systems.
- If your primary focus is insulation: Use a vacuum to eliminate conduction and convection, and a reflective surface to minimize heat transfer by radiation, as seen in a Dewar flask (thermos).
- If your primary focus is cooling an object in space: Design it with high-emissivity surfaces (like black radiator panels) that can efficiently radiate excess heat away into space.
- If your primary focus is capturing solar energy: Use dark, highly absorptive materials to maximize the amount of energy absorbed from the sun's radiation.
By understanding how energy moves through nothingness, you can engineer solutions that function effectively in any environment, from your daily coffee to deep space exploration.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Method | Works in a Vacuum? | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | ❌ No | Requires direct contact between particles. |
| Convection | ❌ No | Requires a moving fluid (liquid or gas). |
| Radiation | ✅ Yes | Requires no medium; transfers energy via electromagnetic waves. |
Need precise thermal control for your laboratory processes?
Understanding heat transfer is fundamental to applications like vacuum drying, heat treatment, and materials research. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum ovens and furnaces, designed to leverage thermal radiation for unparalleled temperature uniformity and process control.
Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your specific needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum quenching? Achieve Maximum Hardness with a Clean, Oxidation-Free Finish
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature annealing furnace in Ni-30Cr research? Master Alloy Homogenization
- What industries use annealing? A Guide to Its Critical Role in Manufacturing
- What are the different types of industrial furnaces? Find the Right Heating Solution for Your Process
- Why is a high-temperature furnace used for solution treatment of AFA steel? Optimize Your sCO2 Exposure Experiments
- What role does a high-temperature furnace play in Inconel 718 homogenization? Ensure Microstructural Precision
- What is sintering with hydrogen? Achieve Superior Strength and Purity in Metal Parts
- What are the safety precautions while brazing? Essential Steps to Protect Yourself and Your Workspace



















