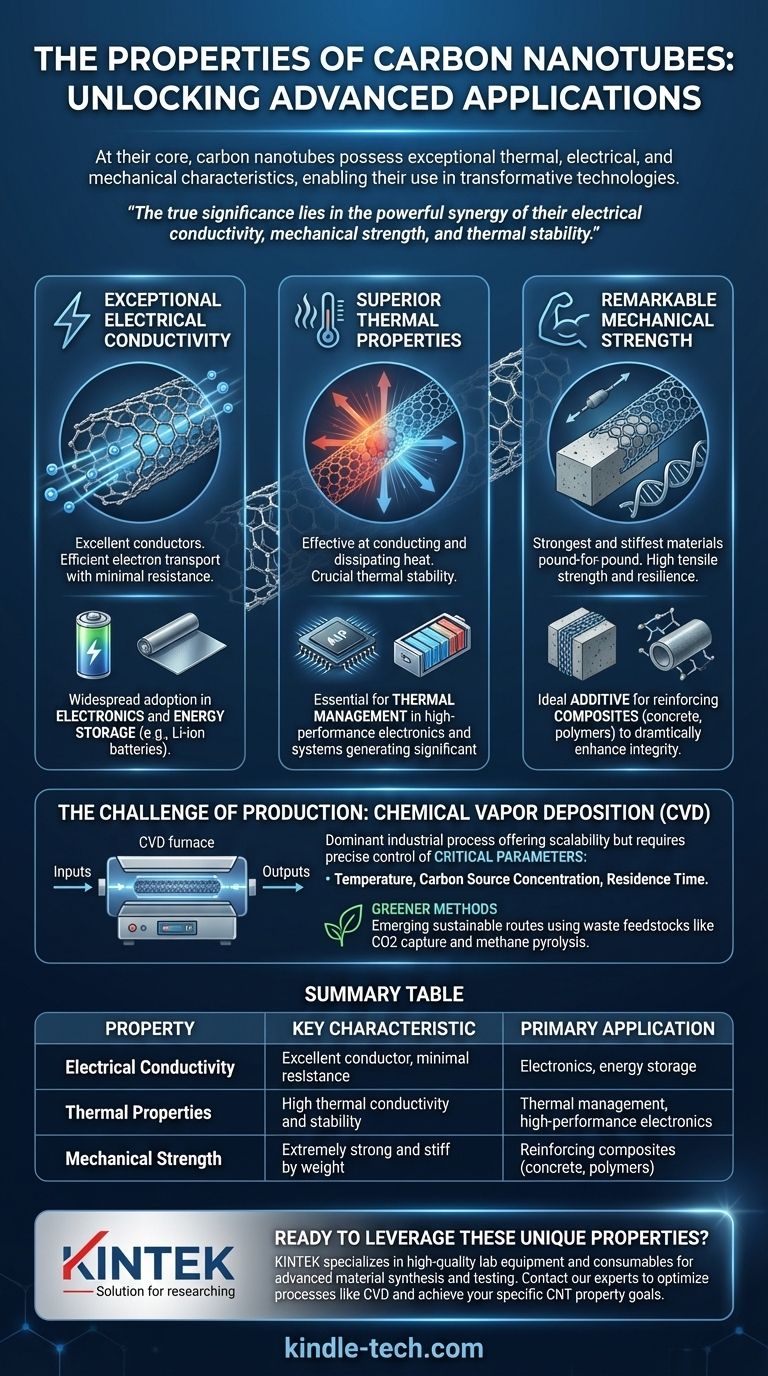
At their core, carbon nanotubes are defined by a unique combination of exceptional properties. They possess remarkable thermal, electrical, and mechanical characteristics that distinguish them from other materials and make them highly valuable for a wide range of advanced applications.
The true significance of carbon nanotubes lies not in any single attribute, but in the powerful synergy of their electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and thermal stability. This trifecta is what enables their use in transformative technologies, from next-generation batteries to reinforced composite materials.

The Defining Properties of Carbon Nanotubes
To understand the value of carbon nanotubes (CNTs), we must first examine their three primary characteristics. These properties are a direct result of their unique, cylindrical nanostructure.
Exceptional Electrical Conductivity
Carbon nanotubes are excellent conductors of electricity. This property is a key reason for their widespread adoption in the electronics and energy storage sectors.
Their high conductivity allows them to efficiently transport electrons with minimal resistance, making them a superior alternative to traditional conductive materials in many contexts.
Superior Thermal Properties
CNTs also exhibit unique thermal properties, meaning they are very effective at conducting and dissipating heat.
This thermal stability is critical for applications where temperature management is essential, such as in high-performance electronics or advanced battery systems that generate significant heat during operation.
Remarkable Mechanical Strength
On a pound-for-pound basis, carbon nanotubes are one of the strongest and stiffest materials ever discovered. They possess incredible tensile strength and resilience.
This makes them an ideal additive for reinforcing other materials. For example, when integrated into composites like concrete or polymers, they can dramatically enhance durability and structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Challenge of Production
While their properties are impressive, the practical application of carbon nanotubes is heavily influenced by the complexities of their synthesis. The method of production directly impacts the quality and cost of the final material.
The Dominance of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Although methods like laser ablation and arc discharge exist, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the dominant commercial process for producing CNTs today. This industrial method offers scalability but requires precise control.
Critical Synthesis Parameters
The quality and yield of CNTs are highly sensitive to manufacturing conditions. Key parameters such as temperature, carbon source concentration, and residence time must be carefully managed to ensure consistent and efficient production.
The Push for Greener Methods
There is a significant focus on developing more sustainable synthesis routes. Emerging methods include using waste feedstocks, such as carbon dioxide captured via electrolysis or methane from pyrolysis, to create CNTs. These "green" technologies are promising but still evolving.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific property you intend to leverage will determine how you approach using carbon nanotubes in your work.
- If your primary focus is improving electrical performance: Leverage CNTs as conductive additives in systems like lithium-ion batteries or conductive films.
- If your primary focus is enhancing material strength: Use CNTs as a reinforcing agent in composites, such as concrete or advanced polymers.
- If your primary focus is thermal management: Explore their use in applications like heat sinks for electronics or in thermally stable components.
By understanding these fundamental properties, you can effectively deploy carbon nanotubes to solve specific engineering and scientific challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent conductor with minimal resistance | Electronics, energy storage (batteries) |
| Thermal Properties | High thermal conductivity and stability | Thermal management, high-performance electronics |
| Mechanical Strength | Extremely strong and stiff on a weight basis | Reinforcing composites (concrete, polymers) |
Ready to leverage the unique properties of carbon nanotubes in your research or product development? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced material synthesis and testing. Our expertise can help you optimize processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) to achieve the specific CNT properties you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals in nanotechnology and material science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a BN inner liner in a graphite mold during Flash Sintering? Master Precise Current Control
- Why is Boron Nitride used in RRDE? Enhance Precision with Superior Insulating and Protective Material
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential Components for Extreme Heat & Electrical Insulation
- What is a ceramic tube? A Guide to Extreme Environment Performance
- What is the function of the ceramic tube in a DBD plasma jet? Enhancing Stability for Delicate Material Treatment



















