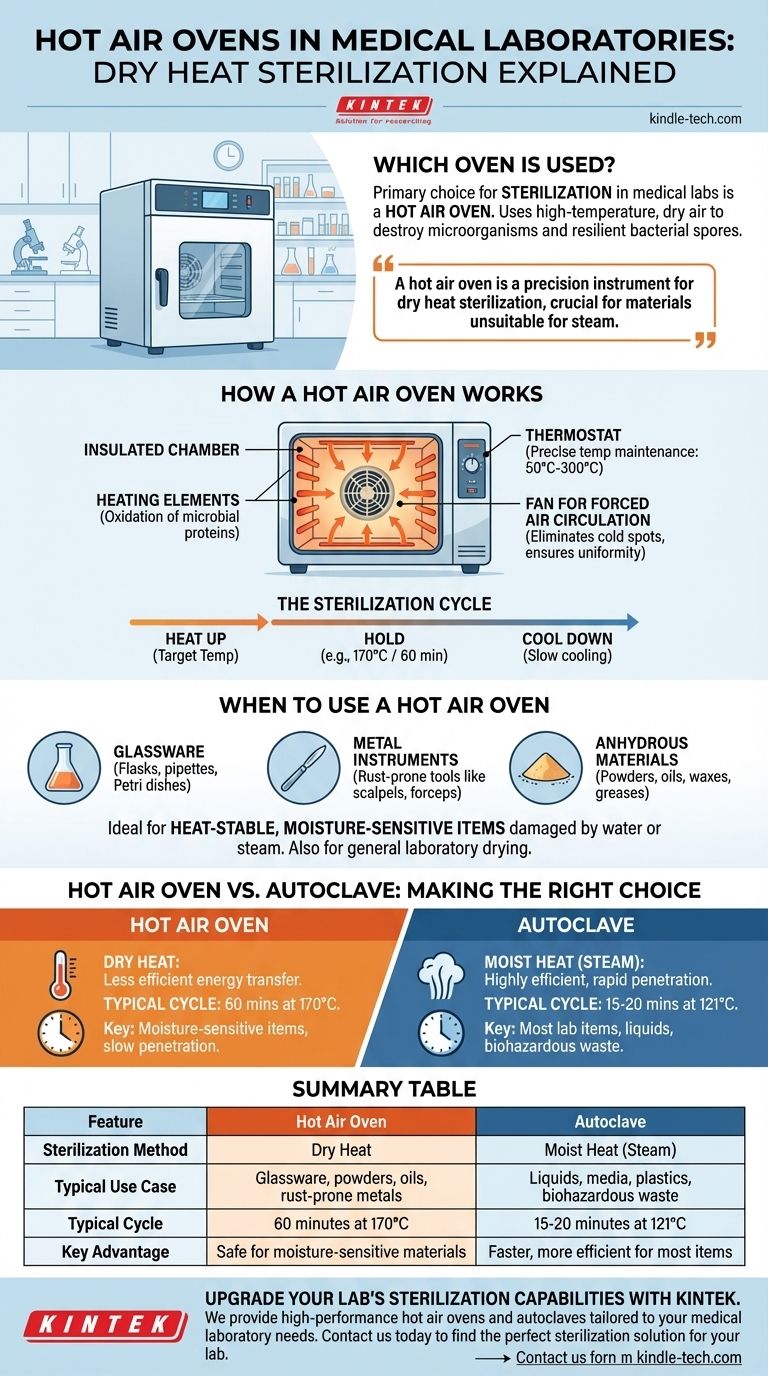
In a medical laboratory, the primary type of oven used for sterilization is a hot air oven. This specialized equipment uses high-temperature, dry air to destroy all forms of microbial life, including resilient bacterial spores. It is essential for sterilizing materials that can withstand high heat but would be damaged by the moisture present in other methods, like steam autoclaving.
A hot air oven is not just a simple heater; it's a precision instrument for dry heat sterilization. Its critical role is to process materials unsuitable for steam, such as anhydrous oils, powders, and certain glassware, by using prolonged, high-temperature exposure to achieve sterility.

How a Hot Air Oven Works
A hot air oven is more than its name suggests. It's an insulated chamber designed to deliver and maintain precise, uniform temperatures, typically between 50°C and 300°C.
The Principle of Dry Heat Sterilization
The oven kills microorganisms through a process of oxidation. The extreme, dry heat essentially causes the slow charring of microbial proteins and components, leading to cell death. This method requires higher temperatures and longer exposure times compared to moist heat sterilization.
Key Components for Uniformity
To be effective, a hot air oven must have several key features. A thermostat maintains a constant, precise temperature. Most modern units also include a fan for forced air circulation, which eliminates cold spots inside the chamber and ensures every item receives the same amount of heat.
The Sterilization Cycle
A typical cycle involves heating the chamber to the target temperature (e.g., 170°C / 340°F), holding it there for a specified time (e.g., 60 minutes), and then allowing the contents to cool slowly before removal. Proper loading is crucial to allow air to circulate freely around every object.
When to Use a Hot Air Oven
The choice between a hot air oven and another sterilization method, like an autoclave, depends entirely on the material being processed.
Heat-Stable, Moisture-Sensitive Items
This is the primary application. A hot air oven is the correct tool for sterilizing materials that are either damaged by water or cannot be penetrated by steam.
Common examples include:
- Glassware: Flasks, pipettes, and Petri dishes.
- Metal Instruments: Forceps, scalpels, and scissors that are prone to rusting.
- Anhydrous Materials: Powders, oils, waxes, and greases that steam cannot penetrate.
General Laboratory Drying
Beyond sterilization, these ovens are frequently used for routine drying of washed glassware or for removing moisture from chemical samples in a controlled environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hot Air Oven vs. Autoclave
While both are used for sterilization, they are not interchangeable. An autoclave, which uses high-pressure steam, is the most common and efficient method for general sterilization in a medical lab.
Time and Temperature Requirements
Dry heat is less efficient at transferring energy than moist heat. Consequently, a hot air oven requires much higher temperatures and longer cycles. For example, sterilization might take 60 minutes at 170°C in an oven, while an autoclave can achieve it in just 15-20 minutes at 121°C.
Material Compatibility is Crucial
The autoclave is the workhorse for most items, including surgical instruments, liquids (media), and biohazardous waste. A hot air oven is reserved for the specific items that steam would damage or fail to sterilize. It cannot be used for plastics that would melt, liquids that would evaporate, or fabrics.
Penetration Power
The pressurized steam in an autoclave rapidly penetrates materials, ensuring thorough sterilization. Dry heat penetrates much more slowly, which is why proper loading and longer cycle times are absolutely critical for success.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct method is fundamental to laboratory safety and the validity of your results.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing most laboratory items, including liquids, media, plastics, or biohazardous waste: The autoclave is the faster, more efficient, and appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing anhydrous materials like oils, powders, glassware, or rust-prone metal instruments: The hot air oven is the only correct tool for effective dry heat sterilization.
Ultimately, understanding the unique function of the hot air oven is key to maintaining a safe and sterile laboratory environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Air Oven | Autoclave |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization Method | Dry Heat | Moist Heat (Steam) |
| Typical Use Case | Glassware, powders, oils, rust-prone metals | Liquids, media, plastics, biohazardous waste |
| Typical Cycle | 60 minutes at 170°C | 15-20 minutes at 121°C |
| Key Advantage | Safe for moisture-sensitive materials | Faster, more efficient for most items |
Upgrade your lab's sterilization capabilities with KINTEK.
Choosing the right equipment is critical for laboratory safety and efficiency. Whether you need a reliable hot air oven for dry heat sterilization or an autoclave for steam-based processes, KINTEK provides high-performance lab equipment tailored to your needs.
We specialize in supplying medical laboratories with durable, precise ovens that ensure uniform heating and consistent results for sterilizing glassware, powders, and metal instruments.
Contact us today to find the perfect sterilization solution for your lab → #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is the use of autoclave in medical? The Critical Role of Sterilization in Patient Safety
- What are the sizes of autoclaves? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- How does the lab autoclave work? Achieve Complete Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization



















