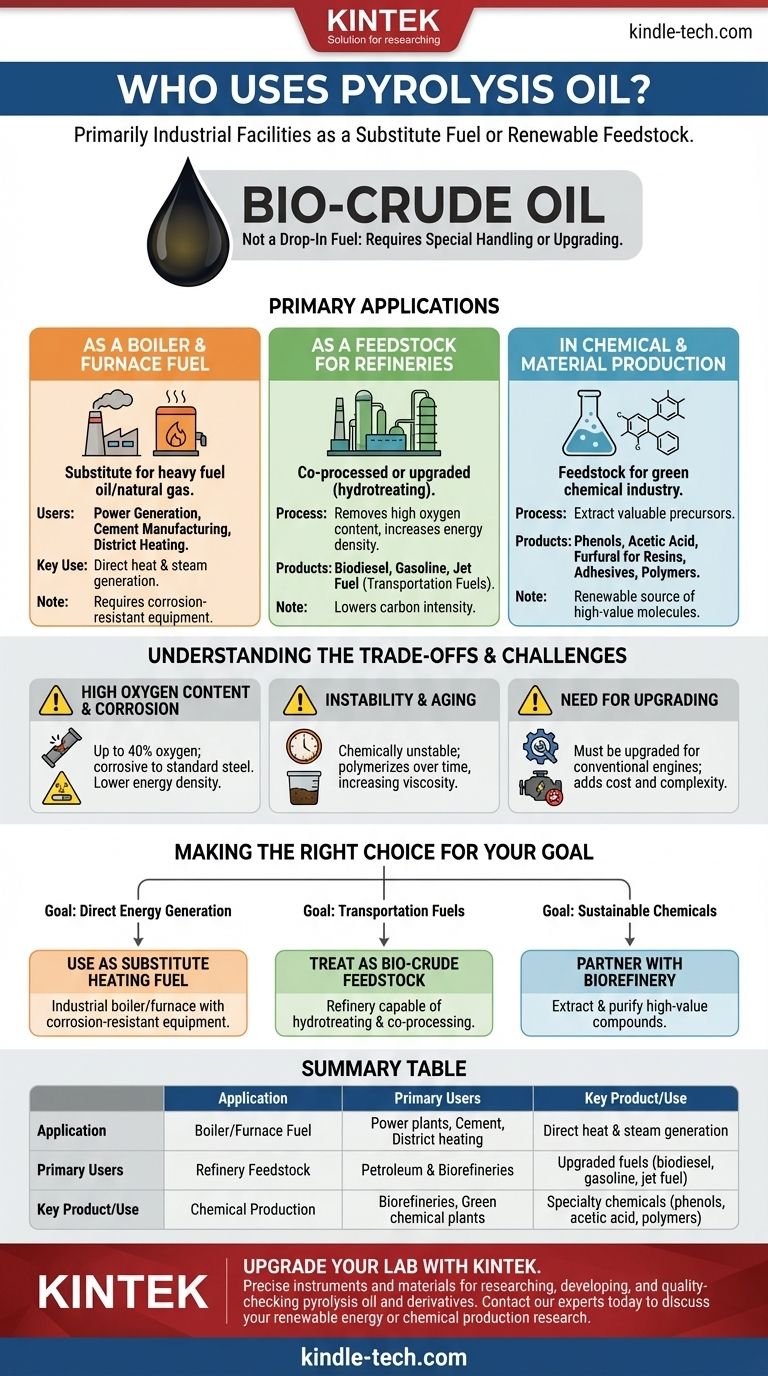
In short, pyrolysis oil is primarily used by industrial facilities as a substitute fuel for boilers and furnaces. It also serves as a renewable feedstock for refineries and chemical plants that can upgrade it into higher-value products like transportation fuels and specialty chemicals.
Pyrolysis oil should not be viewed as a ready-to-use "drop-in" fuel. Think of it as a synthetic bio-crude oil—a valuable intermediate product that requires specific equipment to burn directly or further processing to unlock its full potential.

The Primary Applications for Pyrolysis Oil
Pyrolysis oil's unique chemical makeup dictates who can use it and for what purpose. Its applications fall into three main categories, ranging from direct use to complex upgrading.
As a Boiler and Furnace Fuel
The most straightforward use for pyrolysis oil is as a substitute for heavy fuel oil or natural gas in large industrial boilers, kilns, and furnaces.
Industries like power generation, cement manufacturing, and district heating can burn the oil directly to produce heat and steam. This application is attractive because it requires the least amount of pre-processing.
However, due to the oil's properties, the combustion equipment often needs to be made of corrosion-resistant materials or be specifically designed to handle this type of fuel.
As a Feedstock for Refineries
A more advanced use is sending pyrolysis oil to a petroleum refinery or a dedicated biorefinery.
Here, the bio-crude is co-processed alongside traditional crude oil or upgraded through a process called hydrotreating. This process uses hydrogen to remove the high oxygen content, stabilizing the oil and increasing its energy density.
The upgraded oil can then be refined into conventional transportation fuels like biodiesel, gasoline, and jet fuel, helping to lower the carbon intensity of the final product.
In Chemical and Material Production
The complex mixture of organic compounds in pyrolysis oil makes it a potential feedstock for the "green" chemical industry.
Specialized biorefineries can extract valuable chemical precursors like phenols, acetic acid, and furfural. These components are building blocks for producing resins, adhesives, food flavorings, and specialty polymers.
This application treats pyrolysis oil not as a fuel, but as a renewable source of high-value molecules, contributing to a circular economy.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Isn't It Everywhere?
While promising, pyrolysis oil has significant technical challenges that limit its widespread adoption as a simple drop-in fuel. Understanding these limitations is key to understanding its user base.
The Challenge of High Oxygen Content
Pyrolysis oil can contain up to 40% oxygen by weight. This makes the oil acidic and highly corrosive to the standard steel pipes, pumps, and storage tanks used for conventional fuels.
This high oxygen content also means it has a lower energy density than fossil fuels, so you need more of it to produce the same amount of energy.
Instability and Aging
The oil is a complex, reactive mixture that is chemically unstable. Over time, it can undergo polymerization, causing its viscosity to increase until it becomes a thick, unusable sludge.
This instability complicates long-term storage and transportation, requiring users to either consume it quickly or invest in stabilization techniques.
The Need for Upgrading
Because of its corrosivity and instability, pyrolysis oil cannot be used in conventional engines (like those in cars or trucks). To create a high-grade transportation fuel, it must be upgraded.
This upgrading step adds significant cost and complexity, which is why its primary users are large industrial players with the capital and infrastructure to handle or process it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal user for pyrolysis oil depends entirely on the end goal and the available infrastructure.
- If your primary focus is direct energy generation: Your best option is to use it as a substitute heating fuel in an industrial boiler or furnace that is properly equipped to handle corrosive fuels.
- If your primary focus is producing transportation fuels: The oil must be treated as a bio-crude feedstock for a refinery capable of hydrotreating and co-processing.
- If your primary focus is creating sustainable chemicals: The most effective path is to partner with a biorefinery that can extract and purify high-value chemical compounds from the oil.
Ultimately, pyrolysis oil serves a narrow but critical set of industrial users who see its value as a renewable intermediate step toward energy and material production.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Users | Key Product/Use |
|---|---|---|
| Boiler/Furnace Fuel | Power plants, Cement manufacturers, District heating systems | Direct heat and steam generation |
| Refinery Feedstock | Petroleum refineries, Biorefineries | Upgraded transportation fuels (biodiesel, gasoline, jet fuel) |
| Chemical Production | Biorefineries, Green chemical plants | Specialty chemicals (phenols, acetic acid, polymers) |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities in biofuel and chemical analysis with KINTEK.
As a leading supplier of lab equipment and consumables, we provide the precise instruments and materials needed to research, develop, and quality-check pyrolysis oil and its derivatives. Whether you are optimizing pyrolysis processes, analyzing fuel properties, or developing new green chemicals, KINTEK supports your innovation with reliable solutions.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can enhance your renewable energy or chemical production research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- What is titanium used for in manufacturing? Leveraging High-Performance Properties for Critical Applications
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- What products are manufactured with titanium? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Materials
- Why is platinum unreactive? The Atomic Secrets Behind Its Remarkable Stability

