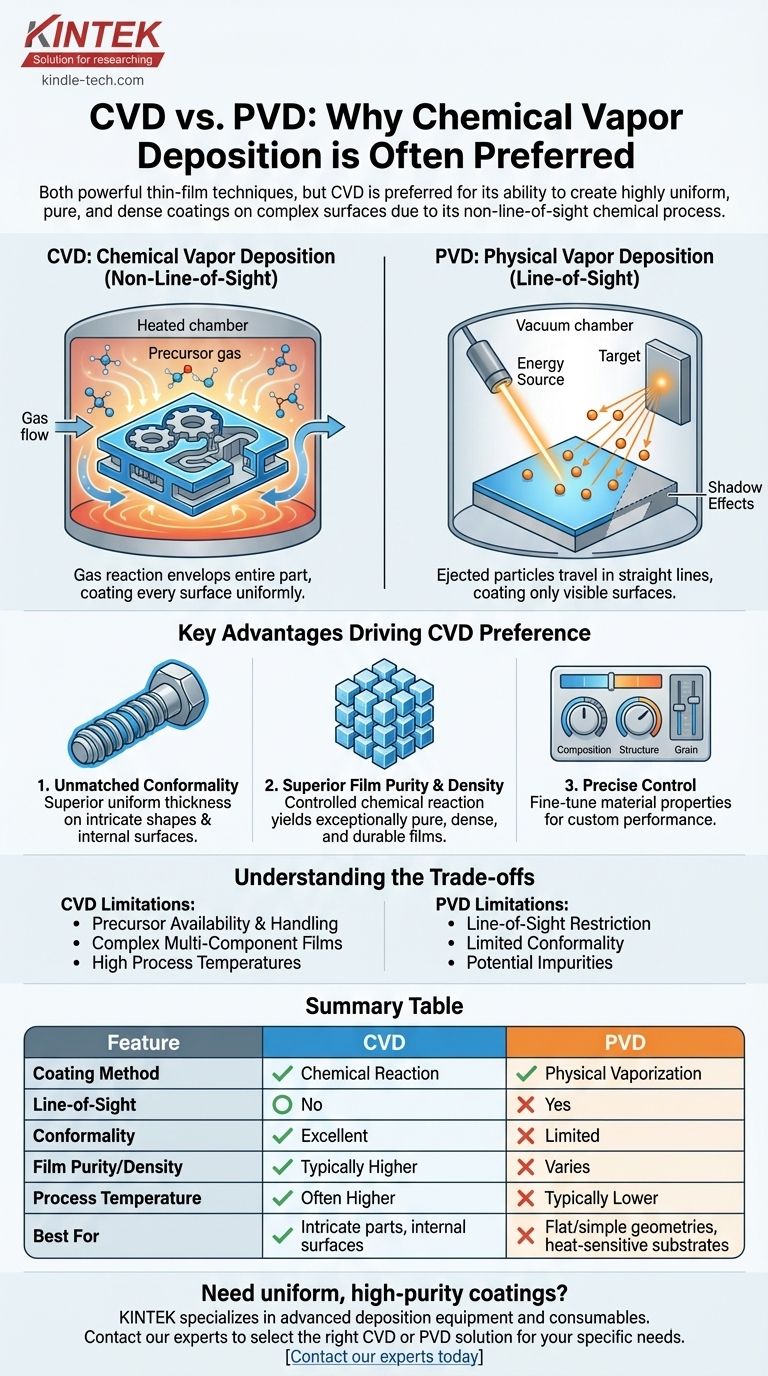
While both are powerful thin-film deposition techniques, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is often preferred over Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) for its unique ability to create highly uniform, pure, and dense coatings on complex, non-line-of-sight surfaces. This is because CVD relies on a chemical reaction from a gas that envelops the part, whereas PVD is fundamentally a line-of-sight process, similar to spray painting.
The choice between CVD and PVD is not about which is universally "better," but which is right for the specific geometry and material requirements of the task. The core reason CVD is often preferred is its non-line-of-sight nature, which enables superior film quality and uniformity on intricate components that are impossible to coat evenly with PVD.

The Fundamental Difference: Gas vs. Line-of-Sight
To understand the preference for CVD, you must first grasp the core difference in how each process works. This distinction is the root of nearly all their respective advantages and disadvantages.
How CVD Works: Precursor Gases and Surface Reactions
In Chemical Vapor Deposition, volatile precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber containing the object to be coated (the substrate).
These gases decompose or react on the heated surface of the substrate, chemically bonding to it and building up a solid film layer by layer. Because the gas flows around and envelops the entire substrate, every surface—including internal channels and complex 3D shapes—is exposed to the precursors.
How PVD Works: The "Spray Paint" Analogy
Physical Vapor Deposition works by physically bombarding a solid source material (the "target") with energy, causing atoms or molecules to be ejected.
These ejected particles travel in a straight line through a vacuum and condense onto the substrate. This is a line-of-sight process. Any surface not in the direct path of the ejected particles will not be coated, creating a "shadow" effect on complex parts.
Key Advantages Driving CVD Preference
The chemical, non-line-of-sight nature of CVD gives it several critical advantages that make it the superior choice for many advanced applications.
Unmatched Conformality on Complex Geometries
This is the most significant advantage of CVD. Since the precursor gas can penetrate and surround intricate shapes, it produces a highly conformal coating of uniform thickness.
This "wrap-around" capability is essential for coating components like engine parts, medical implants, or complex microelectronic structures where complete and even coverage is non-negotiable. PVD simply cannot achieve this.
Superior Film Purity and Density
The CVD process builds films through a controlled chemical reaction, which can result in exceptionally pure and dense coatings.
The process parameters—such as gas composition, temperature, and pressure—can be finely tuned to minimize impurities and create a tightly packed crystal structure. This leads to films with excellent durability, corrosion resistance, and electrical properties.
Precise Control Over Film Properties
CVD offers a high degree of control over the final film. By adjusting the deposition parameters, engineers can precisely manage the material's chemical composition, crystal structure, and grain size.
This allows for the creation of custom-engineered coatings tailored to specific performance requirements, such as hardness, abrasion resistance, or optical transparency.
Wide Versatility of Materials
The chemical basis of CVD allows for the deposition of an incredibly wide range of materials. This includes metals, multi-component alloys, ceramics, and other compound layers that can be difficult or impossible to deposit using PVD methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technology is without its drawbacks. Acknowledging the limitations of CVD is crucial for making an objective decision.
The Challenge of Precursor Chemicals
CVD is entirely dependent on the availability of suitable precursor gases. For some materials, it can be difficult to find precursors that are volatile, non-toxic, and stable enough for a reliable industrial process.
Complexity in Multi-Component Films
While versatile, creating films from multiple materials can be complex. Different precursors may have varying vapor pressures or reaction rates, making it challenging to achieve a homogenous composition throughout the film.
Higher Process Temperatures
Many CVD processes require high substrate temperatures to initiate the necessary chemical reactions. This can limit the types of materials that can be coated, as some substrates may not be able to withstand the heat without being damaged.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use CVD over PVD depends on your primary goal and the constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D shapes or internal surfaces: CVD is the definitive choice due to its superior conformality.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and density for a critical application: CVD's controlled chemical reaction process often provides a significant advantage.
- If you are depositing on a temperature-sensitive substrate or need a simpler, lower-cost process for a flat surface: PVD may be a more practical and effective solution.
Selecting the right deposition method begins with a clear understanding of your component's geometry and the final film properties you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Method | Chemical reaction from gas phase | Physical vaporization & condensation |
| Line-of-Sight? | No - gas surrounds entire part | Yes - limited to direct paths |
| Conformality | Excellent on complex geometries | Limited on hidden surfaces |
| Film Purity/Density | Typically higher | Varies by method |
| Process Temperature | Often higher | Typically lower |
| Best For | Intricate parts, internal surfaces | Flat/simple geometries, heat-sensitive substrates |
Need to coat complex components with uniform, high-purity films? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced deposition processes. Our expertise can help you select the right CVD or PVD solution for your specific application—ensuring optimal film quality, durability, and performance for your laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















