In short, different coatings are applied to carbide tool inserts to dramatically enhance their performance by providing properties the underlying carbide substrate lacks. These coatings act as a specialized shield, tailored to combat the specific challenges of a machining operation, primarily by increasing surface hardness for wear resistance, acting as a thermal barrier against intense heat, and reducing friction.
The core reason for the variety of coatings is that there is no single "best" solution. The choice of coating is a strategic trade-off, balancing hardness, heat resistance, and lubricity to precisely match the demands of the material being cut and the type of machining being performed.

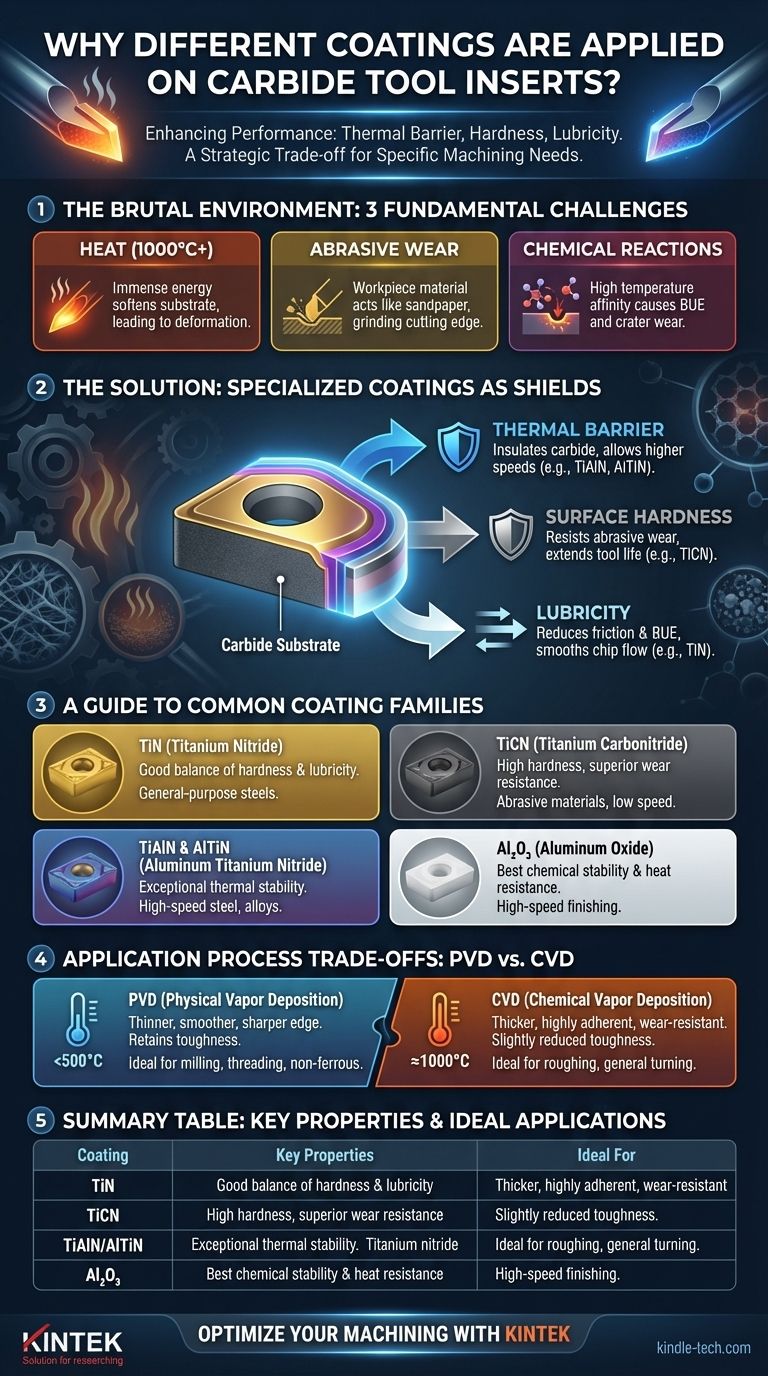
The Fundamental Challenges in Machining
To understand why coatings are essential, we must first recognize the brutal environment a cutting edge endures. The carbide insert is in a constant battle against three primary forces that seek to destroy it.
The Battle Against Heat
The energy required to shear metal generates immense heat, often exceeding 1,000°C (1,800°F) at the tool tip. This extreme temperature can soften the carbide substrate, causing it to deform plastically and rapidly lose its cutting edge.
Resisting Abrasive Wear
The workpiece material, especially alloys containing hard carbides or abrasive elements like sand in castings, acts like sandpaper against the tool. This abrasive wear grinds down the cutting edge, leading to poor surface finish and dimensional inaccuracy.
Preventing Chemical Reactions
At high temperatures, a chemical affinity can develop between the tool and the workpiece. This can cause workpiece material to weld to the tool tip (known as a built-up edge or BUE) or cause elements to diffuse from the tool, weakening it in a process called crater wear.
How Coatings Function as a Solution
Coatings are microscopically thin layers—typically 1 to 15 microns—that are vapor-deposited onto the carbide. Each type of coating provides a specific combination of benefits to counteract the challenges of machining.
Thermal Barrier: Insulating the Carbide
Many modern coatings, particularly those containing aluminum (like TiAlN and AlTiN), form a stable, insulating layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) at high cutting temperatures. This layer acts as a thermal barrier, slowing the transfer of heat into the carbide substrate and allowing the tool to maintain its hardness at much higher cutting speeds.
Surface Hardness: A Shield Against Abrasion
Coatings are significantly harder than the carbide itself. A coating like Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) provides exceptional surface hardness, creating a shield that directly resists the abrasive wear from the workpiece material, dramatically extending tool life.
Lubricity: Reducing Friction and Built-Up Edge
A smooth, lubricious coating reduces the coefficient of friction between the tool and the chip. This allows the chip to slide more easily across the tool face, which reduces heat generation and prevents workpiece material from sticking to the edge (built-up edge), a common problem when machining gummy materials like aluminum and stainless steel.
A Guide to Common Coating Families
The "different" coatings exist because each is engineered to prioritize certain benefits, making them suitable for different applications.
TiN (Titanium Nitride)
This is the classic, general-purpose gold-colored coating. It offers a good balance of increased hardness and lubricity, serving as an excellent baseline improvement over uncoated carbide for a wide range of applications in steels.
TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride)
By adding carbon, TiCN becomes significantly harder and more wear-resistant than TiN. Its primary advantage is superior performance in abrasive materials like cast iron or when cutting at lower speeds where heat is less of a concern than abrasion.
TiAlN & AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride)
These are the workhorses of modern high-performance machining. The aluminum content allows them to form a protective aluminum oxide layer at high temperatures, giving them exceptional thermal stability. This makes them ideal for high-speed cutting of steels, stainless steels, and high-temp alloys. AlTiN, with a higher aluminum content, generally offers better performance at even higher temperatures.
Al₂O₃ (Aluminum Oxide)
Applied as a thick layer via a high-temperature process, Al₂O₃ offers the best chemical stability and heat resistance. It excels in high-speed finishing of steels and cast iron, where maintaining a clean cutting edge under intense heat is critical. It is often used as the outermost layer in a multi-layer coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. CVD
The method used to apply the coating is just as important as the coating material itself. This choice represents a key engineering trade-off.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
This high-temperature process (around 1,000°C) creates thick, highly adherent, and very wear-resistant coatings. It is excellent for roughing and general turning of steel and cast iron. However, the high heat can slightly reduce the toughness of the carbide, and the thicker coating can round the cutting edge, making it less suitable for applications requiring extreme sharpness.
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)
This is a lower-temperature process (below 500°C). It produces a thinner, smoother coating while preserving the inherent toughness and sharpness of the carbide substrate. PVD is the preferred choice for milling (where toughness is key due to interrupted cuts), threading, and machining non-ferrous materials like aluminum that require a very sharp edge to prevent built-up edge.
Selecting the Right Coating for Your Application
Choosing a coating is not about finding the "best" one, but the most appropriate one. Base your decision on the material you are cutting and your primary performance goal.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose machining of steels: Start with a versatile PVD TiAlN coating for a great balance of wear resistance and toughness.
- If your primary focus is cutting abrasive materials like cast iron: A hard CVD coating with TiCN or Al₂O₃ layers provides the necessary abrasive wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is maximum speed and productivity in hard steels or alloys: An AlTiN or multi-layer CVD coating with a thick Al₂O₃ top layer is engineered for this high-heat environment.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality finish on aluminum or stainless steel: A very sharp edge with a smooth, thin PVD coating (like TiN) or even an uncoated polished insert is ideal to prevent material adhesion.
Ultimately, selecting the correct coating transforms a cutting tool from a piece of carbide into a highly specialized solution engineered for a specific task.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Key Properties | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| TiN (Titanium Nitride) | Good hardness, lubricity | General-purpose steel machining |
| TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride) | High hardness, wear resistance | Abrasive materials (e.g., cast iron) |
| TiAlN/AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride) | Excellent thermal stability, heat resistance | High-speed cutting of steels, stainless steels |
| Al₂O₃ (Aluminum Oxide) | Superior chemical stability, heat resistance | High-speed finishing of steels, cast iron |
Ready to optimize your machining process with the right tool coating? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including cutting tools engineered for superior durability and efficiency. Our expertise helps you select the ideal coating for your specific material and application, maximizing tool life and productivity. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory or production needs and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production



















