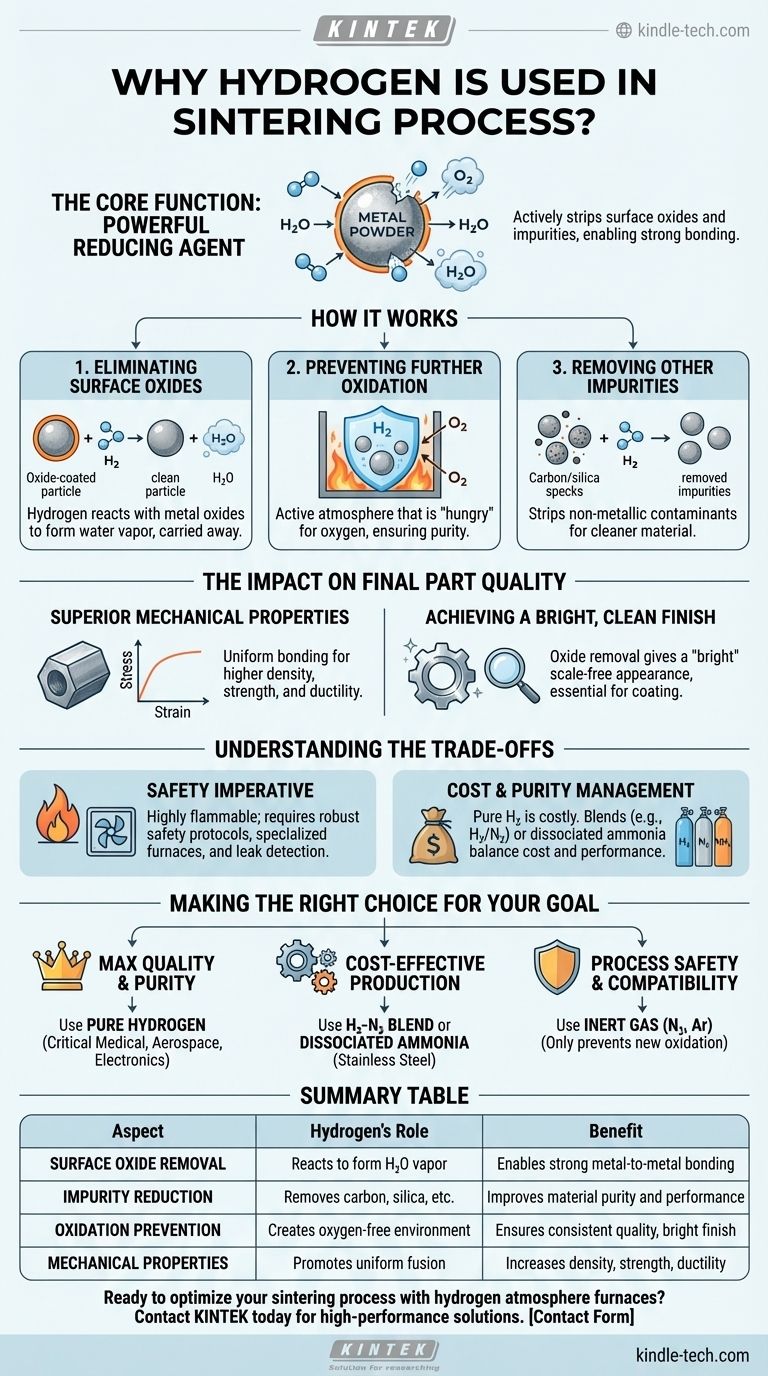
In short, hydrogen is used in sintering because it acts as a powerful reducing agent at high temperatures. It chemically strips away surface oxides and other impurities from the metal powders, creating exceptionally clean surfaces that can fuse together effectively. This process is critical for producing dense, high-strength parts with a bright, clean finish.
The core function of a hydrogen atmosphere is not merely to prevent oxidation, but to actively reverse it. This purification step is what allows individual metal particles to bond properly, unlocking the superior mechanical properties and surface quality expected from the sintering process.
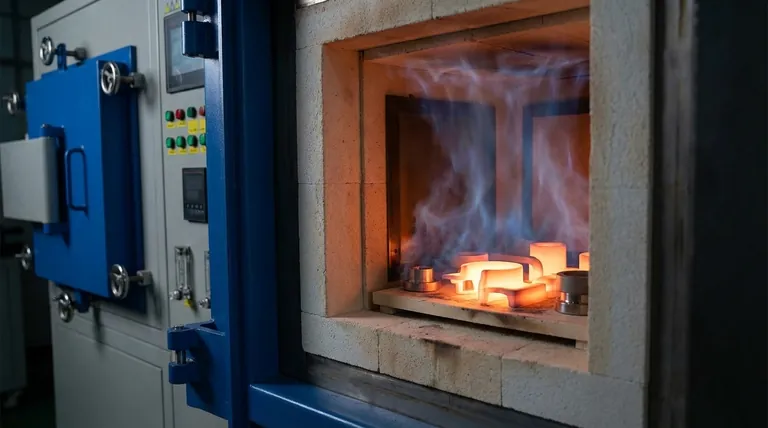

The Core Function: A Powerful Reducing Agent
Sintering involves heating compacted powder to just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse into a solid mass. The quality of this fusion depends entirely on the cleanliness of the particle surfaces.
Eliminating Surface Oxides
Nearly all metal powders have a thin, invisible layer of oxide on their surface from exposure to air. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the metal-to-metal contact needed for strong bonds to form during sintering. Hydrogen directly addresses this by reacting with the oxygen in the metal oxides to form water vapor (H₂O), which is then carried away.
Preventing Further Oxidation
At the high temperatures required for sintering, metals are extremely reactive and will rapidly re-oxidize if exposed to any trace amounts of oxygen. A continuous flow of hydrogen creates a furnace atmosphere that is not just inert, but actively "hungry" for oxygen, ensuring the parts remain pure and oxide-free throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Removing Other Impurities
Hydrogen's role as a purifier extends beyond just oxygen. For many alloys, it helps strip away other non-metallic impurities, such as residual carbon from binders used in the powder compaction stage or trace elements like silica. This leads to a cleaner, higher-performance final material.
The Impact on Final Part Quality
Using a hydrogen atmosphere directly translates to tangible improvements in the finished component. This is why it is essential for demanding applications, from stainless steel parts to tungsten carbides.
Superior Mechanical Properties
By ensuring atomically clean surfaces, hydrogen promotes more complete and uniform bonding between powder particles. This results in a final part with higher density, greater strength, and improved ductility compared to parts sintered in less effective atmospheres.
Achieving a Bright, Clean Finish
The removal of oxides is what gives hydrogen-sintered parts their characteristic "bright" appearance. This is not just cosmetic; a clean, scale-free surface is often a critical functional requirement, improving corrosion resistance and preparing the part for subsequent plating or coating operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, using hydrogen is a technical decision that comes with specific challenges and considerations that must be managed.
The Safety Imperative
Hydrogen is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Its use demands robust safety protocols, specialized furnace designs, proper ventilation, and leak detection systems. These necessary safety measures represent a significant investment in both equipment and operator training.
Cost and Purity Management
High-purity hydrogen can be more expensive than inert gases like nitrogen or argon. To balance cost and performance, many processes use a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen (e.g., 5% H₂ / 95% N₂). Another common alternative is dissociated ammonia, which breaks down at high temperatures to provide a ready-made mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace atmosphere depends on the material being processed and the desired outcome for the final part.
- If your primary focus is maximum quality and purity: Use a pure hydrogen atmosphere for critical components in the medical, aerospace, or electronics industries where performance is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of stainless steel: Use a hydrogen-nitrogen blend or dissociated ammonia to achieve excellent oxide reduction and carbon control at a lower operational cost.
- If your primary focus is process safety or material compatibility: Consider an inert atmosphere like pure nitrogen or argon, but understand that these will only prevent further oxidation and will not reduce existing oxides.
Ultimately, hydrogen's ability to actively purify the material during heating makes it an indispensable tool for advanced powder metallurgy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hydrogen's Role | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Oxide Removal | Reacts with oxides to form water vapor | Enables strong metal-to-metal bonding |
| Impurity Reduction | Removes carbon, silica, and other contaminants | Improves material purity and performance |
| Oxidation Prevention | Creates an oxygen-free environment during heating/cooling | Ensures consistent part quality and bright finish |
| Mechanical Properties | Promotes uniform particle fusion | Increases density, strength, and ductility |
Ready to optimize your sintering process with hydrogen atmosphere furnaces? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for laboratories seeking superior material purity and mechanical properties. Our expertise in sintering technology ensures you achieve dense, high-strength parts with bright, clean finishes. Contact us today to discuss how our hydrogen-compatible furnaces can enhance your powder metallurgy results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is hydrogen annealing? Achieve Superior Material Properties with Bright Annealing
- What is hydrogen atmosphere heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Purity & Brightness
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance



















