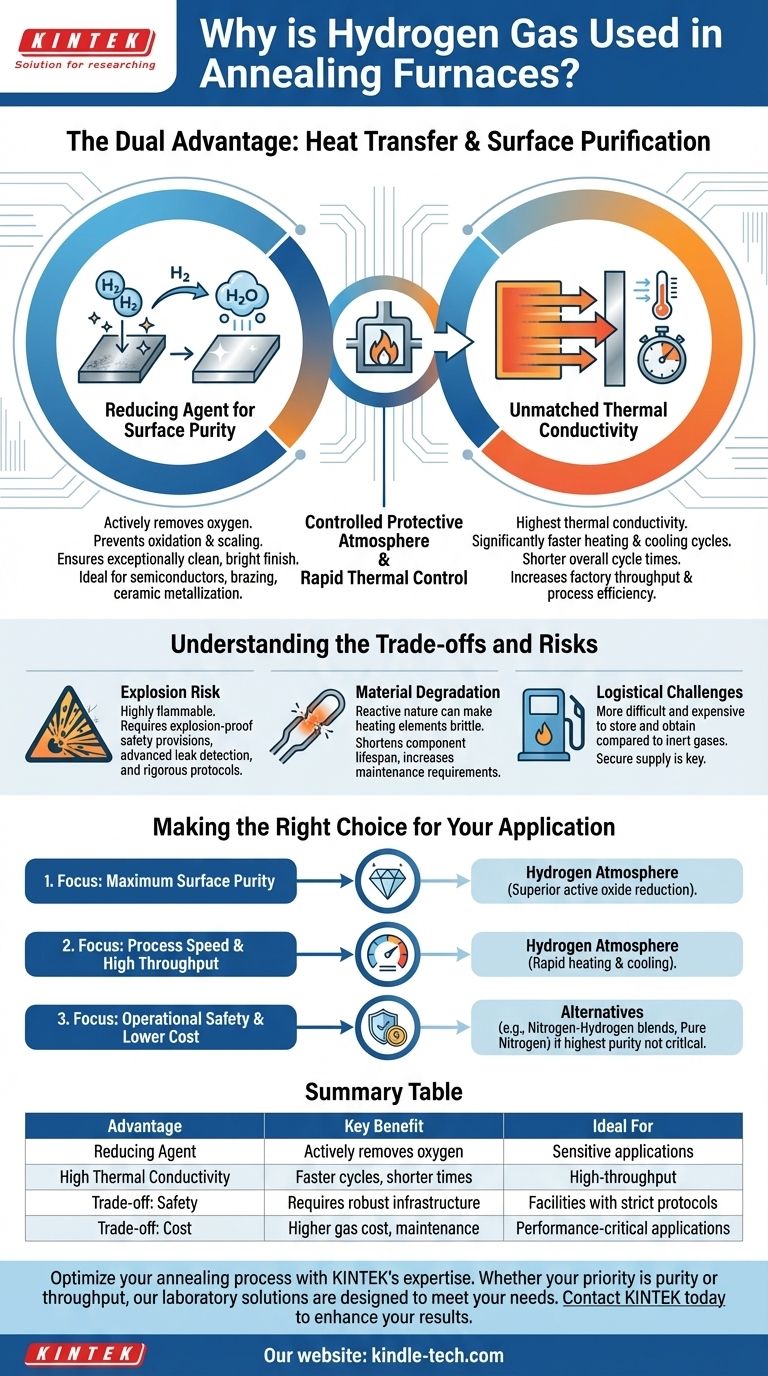
Hydrogen gas is used in annealing furnaces for two primary technical advantages: its exceptional ability to transfer heat and its powerful role as a reducing agent to prevent oxidation. It creates a highly controlled "protective atmosphere" that actively removes oxygen, ensuring the metal's surface remains pure and free from defects during high-temperature processing. Simultaneously, its high thermal conductivity allows for significantly faster heating and cooling cycles, improving process efficiency.
While other gases can provide a protective atmosphere, hydrogen offers a unique combination of active surface purification and rapid thermal control. This makes it ideal for high-performance applications where material integrity and process speed are critical, despite its significant safety and operational challenges.

The Dual Role of Hydrogen in High-Temperature Processing
To understand why hydrogen is chosen, it’s essential to look beyond its role as a simple "filler" gas. It performs two active functions that directly impact the quality of the final product and the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
A Powerful Reducing Agent for Surface Purity
The primary purpose of an annealing atmosphere is to prevent the hot metal surface from reacting with oxygen, which causes scaling and discoloration.
While inert gases like argon simply displace oxygen, hydrogen actively works to remove it. It acts as a reducing agent, meaning it chemically bonds with any oxygen present to form water vapor (H₂O), which is then flushed from the furnace.
This process ensures an exceptionally clean, bright finish on the metal part, which is critical for applications like ceramic metallization, semiconductor processing, and brazing.
Unmatched Thermal Conductivity for Process Efficiency
Hydrogen has the highest thermal conductivity of any gas. This physical property has a direct and significant impact on furnace cycle times.
Because heat is transferred to and from the workpiece much more rapidly in a hydrogen atmosphere, both the heating and cooling phases of the annealing process are accelerated.
This results in shorter overall cycle times, which increases factory throughput and allows for more precise control over the material's final microstructure and properties.
The Operating Environment of a Hydrogen Furnace
Hydrogen annealing furnaces are sophisticated pieces of equipment designed for high precision and control.
They often operate at very high temperatures, sometimes up to 1600°C, with tight temperature uniformity and control (often within ±1°C).
To manage reactivity and cost, a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen is often used as the protective atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The performance benefits of hydrogen come with significant challenges. Its use is a calculated decision that requires acknowledging and mitigating substantial risks.
The Inherent Risk of Explosion
Hydrogen is highly flammable and can form an explosive mixture with air over a wide range of concentrations.
Any leak from the furnace or its supply lines poses a severe safety hazard. For this reason, hydrogen furnaces must be equipped with explosion-proof safety provisions, advanced leak detection systems, and rigorous operational protocols.
Material and Equipment Degradation
The highly reactive nature of hydrogen can be detrimental to the furnace components themselves.
Heating elements, particularly resistors, can become brittle over time when exposed to a reducing hydrogen atmosphere. This phenomenon shortens the lifespan of critical components and increases maintenance requirements and costs.
Logistical and Supply Challenges
Hydrogen is more difficult and expensive to obtain and store in large quantities compared to inert gases like nitrogen or argon.
Managing a secure and sufficient supply of hydrogen is a key logistical consideration for any facility operating these furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right annealing atmosphere depends entirely on the technical requirements of your product and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface purity and a bright finish: Hydrogen's ability to actively reduce oxides is superior to inert gas atmospheres, making it the preferred choice for sensitive electronics or medical-grade components.
- If your primary focus is process speed and high throughput: The rapid heating and cooling enabled by hydrogen's thermal conductivity can dramatically shorten cycle times compared to vacuum or inert gas furnaces.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and lower cost: The significant risks and infrastructure requirements for hydrogen may lead you to consider alternatives like nitrogen-hydrogen blends, cracked ammonia, or pure nitrogen, especially if the absolute highest purity is not a strict requirement.
Ultimately, the decision to use a hydrogen annealing furnace is a strategic one, balancing its unparalleled performance benefits against its demanding operational and safety requirements.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing Agent | Actively removes oxygen, prevents oxidation and scaling | Sensitive applications (semiconductors, medical devices, brazing) |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Faster heating and cooling, shorter cycle times | High-throughput manufacturing |
| Trade-off: Safety | Highly flammable; requires explosion-proof systems and protocols | Facilities with robust safety infrastructure |
| Trade-off: Cost | Higher gas cost and potential for equipment degradation | Applications where performance outweighs operational expense |
Optimize your annealing process with KINTEK's expertise.
Choosing the right furnace atmosphere is critical for achieving your desired material properties and production efficiency. Whether your priority is ultimate surface purity for sensitive components or maximizing throughput, KINTEK's laboratory equipment solutions are designed to meet your specific thermal processing challenges.
Our team can help you select the right system—from hydrogen to inert gas atmospheres—ensuring safety, performance, and reliability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's annealing needs and discover how our equipment can enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing environments? Key Insights for Chemical Reactions
- What would be an advantage of biomass over the use of coal? A Cleaner, Carbon-Neutral Energy Source
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is the sputtering voltage of a magnetron? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What is the significance of using a tube furnace with vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Master Ceramic Synthesis














