In short, hydrogen is used in sintering because it acts as a powerful chemical cleaning agent at high temperatures. It actively removes surface oxides from metal powders, prevents new oxidation from occurring, and strips away other impurities. This chemical reduction process is critical for allowing the metal particles to properly fuse, resulting in finished parts with superior strength, density, and a clean, bright surface.
The crucial insight is that a hydrogen atmosphere is not passive. It is an active chemical reactant that purifies the metal during the sintering process, directly improving the final part's mechanical properties and metallurgical quality in a way inert gases cannot.

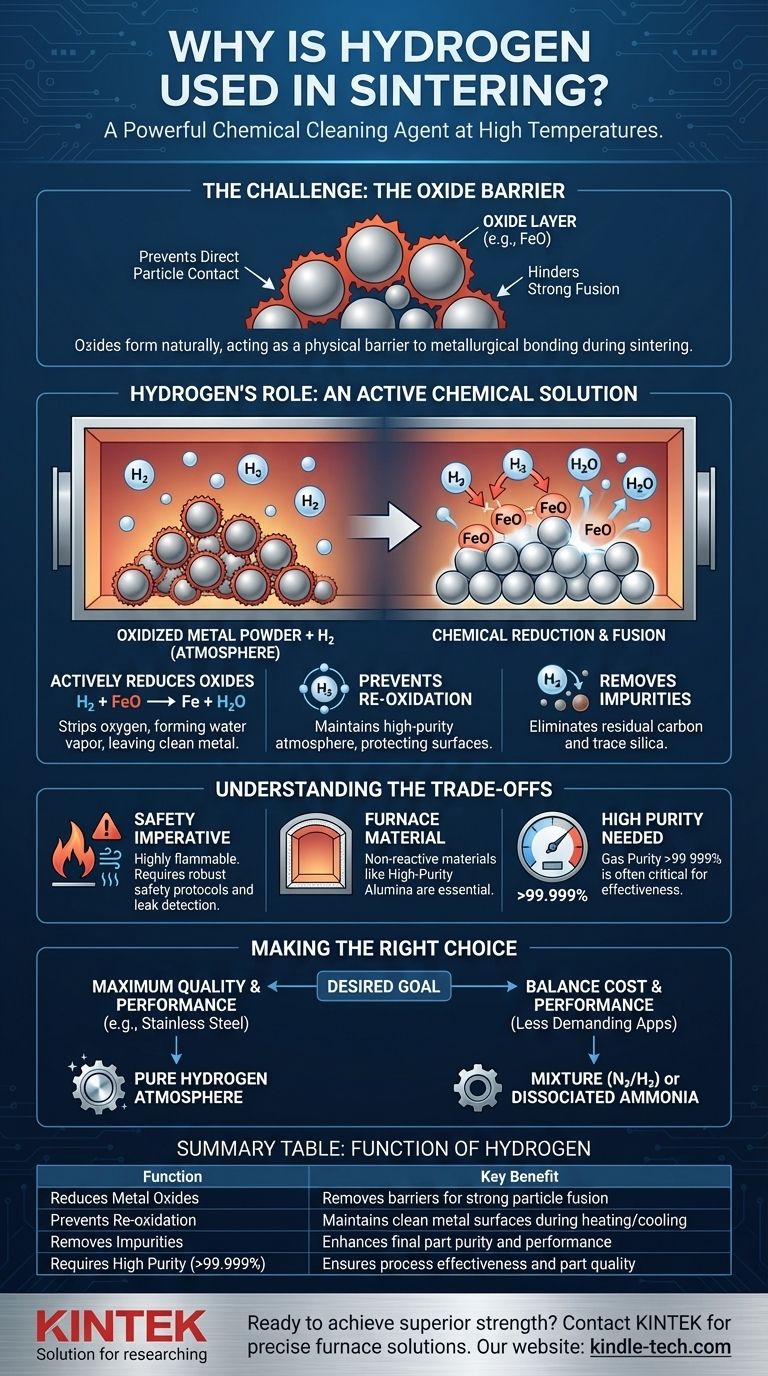
The Challenge: Why Atmosphere is Critical in Sintering
To understand hydrogen's role, we must first understand the fundamental challenge of sintering.
The Goal of Sintering
Sintering is a thermal process used to bond metal powders into a solid mass. The material is heated to a high temperature, but crucially, below its melting point. Through heat and pressure, the individual particles fuse together, increasing the object's density and strength.
This technique is vital for working with metals that have extremely high melting points and for creating complex shapes in processes like metal 3D printing.
The Problem: The Oxide Barrier
Nearly all metal powders are covered in a microscopically thin layer of oxide. This layer forms naturally when the metal is exposed to oxygen in the air.
During sintering, this oxide layer acts as a physical barrier. It prevents the clean, metallic surfaces of the powder particles from making direct contact and forming strong metallurgical bonds. Heating the part in open air would only worsen the problem, creating even more oxide and preventing fusion entirely.
Hydrogen's Role: An Active Chemical Solution
A controlled atmosphere is necessary to overcome the oxide barrier. While inert gases like argon can prevent further oxidation, hydrogen goes a step further by actively reversing it.
Actively Reducing Oxides
Hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent. At the high temperatures of a sintering furnace, hydrogen gas (H₂) reacts with metal oxides (like iron oxide, FeO).
This chemical reaction strips the oxygen atom from the metal, forming water vapor (H₂O) and leaving behind a pure, clean metal surface. The water vapor is then safely flushed from the furnace.
Preventing Re-Oxidation
By maintaining a high-purity hydrogen atmosphere, any stray oxygen that enters the furnace or is released from the material will preferentially react with the abundant hydrogen. This prevents the clean metal surfaces from re-oxidizing during the critical heating and cooling phases.
Removing Other Impurities
Hydrogen's benefits extend beyond just oxides. It can also help strip other unwanted contaminants from the alloy, such as residual carbon from binding agents or trace amounts of silica. This further enhances the purity and performance of the final component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using hydrogen offers significant advantages, but it also introduces specific engineering and safety requirements that must be managed.
The Safety Imperative
Hydrogen is highly flammable and can be explosive when mixed with air. Operating a hydrogen sintering furnace demands robust safety protocols, specialized leak detection systems, and carefully engineered ventilation to mitigate risk.
Furnace Material Compatibility
The materials used to construct the furnace itself become critical. The refractory linings inside the furnace must be non-reactive with hydrogen at high temperatures. High-purity alumina is often required, as common silica-based materials can be degraded by the hydrogen atmosphere, compromising the furnace and contaminating the parts.
The Need for High Purity
The effectiveness of the process is directly tied to the purity of the hydrogen gas. Any contaminants in the gas supply can introduce impurities or reduce its effectiveness as a reducing agent. This is why high-purity hydrogen (>99.999%) is often specified for demanding applications like sintering stainless steel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use hydrogen depends on the material being processed and the desired quality of the final part.
- If your primary focus is maximum quality and performance: For materials like stainless steel or other sensitive alloys where strength, density, and surface finish are paramount, a pure hydrogen atmosphere is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and performance: For less-demanding applications, a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen (N₂/H₂) or dissociated ammonia can provide sufficient reducing potential while mitigating some of the costs and safety overhead of pure hydrogen.
Ultimately, using hydrogen transforms the sintering atmosphere from a simple shield into an active tool for engineering a superior material.
Summary Table:
| Function of Hydrogen | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Reduces Metal Oxides | Removes surface barriers for strong particle fusion |
| Prevents Re-oxidation | Maintains clean metal surfaces during heating/cooling |
| Removes Impurities | Enhances final part purity and performance |
| Requires High Purity (>99.999%) | Ensures process effectiveness and part quality |
Ready to achieve superior strength and metallurgical quality in your sintered parts? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise furnace solutions and expertise needed to harness the power of hydrogen sintering. Our high-purity systems are engineered for safety and performance, ensuring your materials meet the highest standards. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how we can enhance your sintering process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What happens during the annealing process? A Guide to Controlled Softening and Stress Relief
- What is an integral quench furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Sealed Atmosphere Heat Treating
- Why are atmosphere control and temperature precision critical for single-crystal cathode synthesis?
- Which type of furnace is used in annealing process? Choose the Right Controlled Atmosphere Furnace
- What roles do temperature-controlled furnaces and inert gas play in hot-dip aluminizing? Master Coating Precision
- What gases are used in a furnace? A Guide to Fuel vs. Process Atmospheres
- Why is reducing atmosphere significant? Unlock the Power to Reverse Oxidation and Create Pure Materials
- How does an atmosphere furnace influence copper hollow fiber membranes? Stabilize Pore Structure during Sintering



















