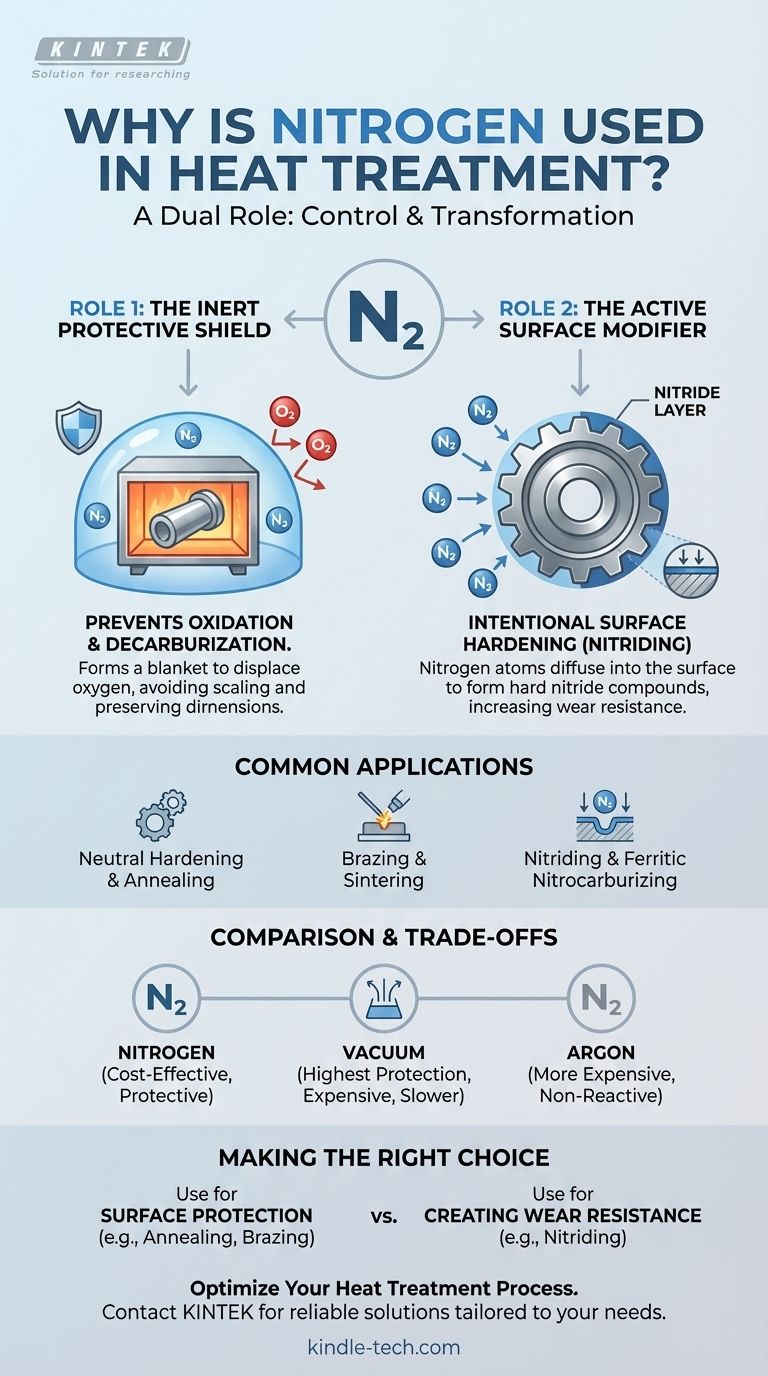
At its core, nitrogen's role in heat treatment is one of control. It is used for two distinct and almost opposite purposes. First, as an inert gas, it creates a protective atmosphere that shields metal from oxygen and other reactive elements at high temperatures, preventing unwanted effects like scaling and decarburization. Second, as an active chemical, it is used in processes like nitriding to intentionally diffuse into a metal's surface, forming a hard, wear-resistant case.
In the high-temperature environment of a furnace, metal is highly vulnerable to unwanted chemical reactions. Nitrogen provides a cost-effective and versatile solution, allowing operators to either completely prevent these reactions or to force a specific, beneficial reaction for surface hardening.

The Dual Nature of Nitrogen in Heat Treatment
To understand why nitrogen is so widely used, you must first recognize its two primary functions. It can be either a passive shield or an active ingredient, depending on the process parameters.
Role 1: The Inert Protective Shield
At the high temperatures required for heat treating, steel and other metals readily react with oxygen in the air. This process, called oxidation, forms a brittle layer of scale on the surface.
This oxidation can ruin a part’s surface finish, alter its precise dimensions, and compromise its metallurgical properties.
By flooding the furnace with nitrogen, you displace the oxygen. Because nitrogen gas (N₂) is relatively inert (non-reactive) under many heat treat conditions, it forms a protective blanket around the workpiece, preventing these unwanted reactions from occurring.
Role 2: The Active Surface Modifier
In a completely different application, nitrogen is used as an active agent for case hardening in a process called nitriding.
Here, the conditions are intentionally set so that nitrogen atoms break free and diffuse directly into the surface of the steel.
These nitrogen atoms combine with iron and other alloying elements to form extremely hard nitride compounds. This creates a hard, wear-resistant "case" on the component's surface while the core remains tough and ductile.
Common Applications and Processes
Nitrogen's dual nature makes it essential for a wide range of heat treatment applications.
Neutral Hardening and Annealing
In processes like neutral hardening, annealing, or stress relieving, the goal is to alter the bulk properties of the metal without changing its surface chemistry.
A nitrogen atmosphere is ideal for this. It prevents both oxidation (adding oxygen) and decarburization (losing carbon), ensuring the part's surface remains clean and its composition unchanged.
Brazing and Sintering
For brazing (joining metals with a filler material) and sintering (fusing metal powders), nitrogen often serves as a carrier gas.
It provides a base protective atmosphere while carrying smaller amounts of active gases, like hydrogen, which help clean the metal surfaces and promote proper bonding.
Nitriding and Ferritic Nitrocarburizing
These are the primary processes where nitrogen is used as an active element. By precisely controlling the temperature and atmosphere composition, manufacturers can achieve a very hard surface with excellent wear and corrosion resistance.
This is highly desirable for components like gears, crankshafts, and tooling that experience significant friction and wear.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While nitrogen is a versatile workhorse, it is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Nitrogen vs. Other Atmospheres
Compared to simply using air, a nitrogen atmosphere adds cost but provides critical protection against oxidation.
Compared to a vacuum, nitrogen is generally cheaper and allows for faster processing cycles. However, a vacuum provides the highest level of protection and is necessary for extremely reactive metals like titanium or niobium.
Compared to other inert gases like argon, nitrogen is far more economical. Argon is only used when there is a risk of nitrogen reacting with the specific metal being treated, even in a protective role.
The Risk of Unwanted Nitriding
Even when used as a "protective" atmosphere, nitrogen can sometimes become reactive at very high temperatures, especially with certain high-chromium stainless steels.
This can lead to unintended nitriding, which may cause surface embrittlement or other negative effects. This is why precise microprocessor-based control of temperature and gas flow is critical in modern furnaces to ensure the nitrogen behaves as intended.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision to use nitrogen and how you use it depends entirely on whether you need to protect the surface or fundamentally change it.
- If your primary focus is surface protection and cleanliness: Use a high-purity nitrogen atmosphere to displace oxygen during processes like annealing, neutral hardening, or brazing.
- If your primary focus is creating a hard, wear-resistant surface: Use a nitriding process where a nitrogen-rich atmosphere is specifically designed to react with the steel's surface.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general-purpose protection: Nitrogen is almost always the most economical and effective choice over either a full vacuum or more expensive inert gases like argon.
By understanding nitrogen's dual capabilities, you can leverage it as a precise tool to achieve consistent, high-quality results in your heat treatment operations.
Summary Table:
| Nitrogen's Role | Primary Function | Key Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Shield | Prevents oxidation & decarburization | Neutral hardening, annealing, brazing |
| Active Agent | Creates hard, wear-resistant surface | Nitriding, ferritic nitrocarburizing |
Ready to Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process with Nitrogen?
Whether you need to protect your metal parts from oxidation during annealing or create a hard, wear-resistant surface through nitriding, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to help. As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, we provide reliable solutions tailored to your laboratory's specific heat treatment needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our nitrogen atmosphere systems can enhance your results, improve efficiency, and ensure consistent, high-quality outcomes for your critical components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using an atmosphere-controlled heating furnace for Cu reduction? Achieve Active Catalytic States
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab



















