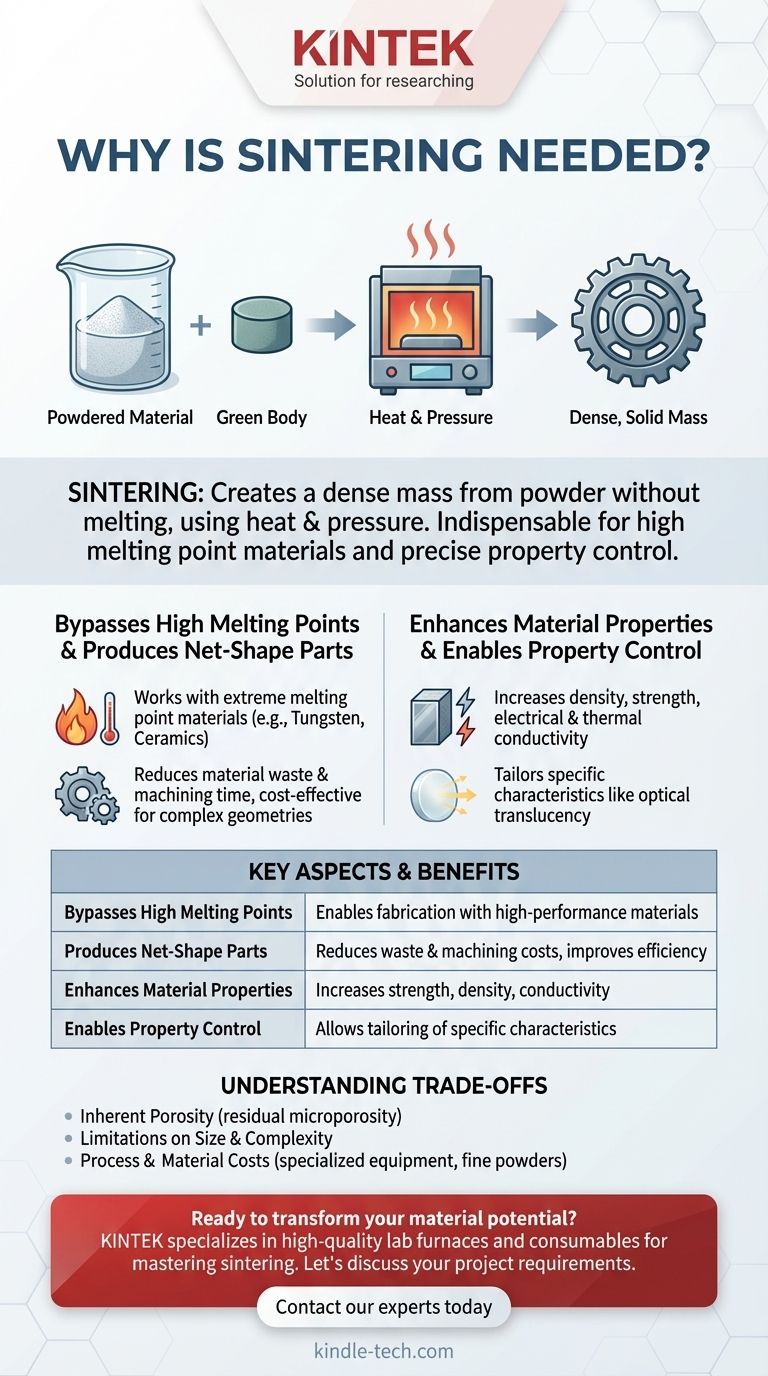
At its core, sintering is necessary to create a dense, solid mass from a powdered material without having to melt it. This process uses heat and pressure to bond particles together at an atomic level, making it an indispensable technique for working with materials that have extremely high melting points or for creating components with precisely controlled properties.
Sintering is not just an alternative to melting; it is a strategic manufacturing process for creating high-performance, net-shape parts that are often stronger, more efficient, and more cost-effective than what traditional casting or machining can produce.

The Fundamental Principle: Strength Without Melting
The primary reason sintering exists is to overcome the limitations of melting and casting. It opens up a new world of material possibilities by fundamentally changing how we form solid objects.
How Sintering Works
The process begins with a fine powder, which is often compacted into a desired shape (a "green body"). This object is then heated in a furnace to a temperature below its melting point. At this elevated temperature, the atoms at the contact points of the particles diffuse across the boundaries, fusing the individual particles into a solid, coherent piece.
The Problem with High Melting Points
For many advanced materials, such as tungsten (melting point 3,422°C) or certain ceramics, reaching melting temperature is either prohibitively expensive or technically impractical. Sintering bypasses this problem entirely. It allows us to form durable, functional components like turbine blades or electrical contacts from these materials using significantly less energy.
Creating Net-Shape Components
Sintering excels at producing "net-shape" or "near-net-shape" objects. This means the part comes out of the furnace very close to its final dimensions. This drastically reduces or eliminates the need for secondary machining, minimizing material waste, saving time, and lowering overall production costs for complex parts like gears, sprockets, and bearings.
Precision Control Over Material Properties
Beyond simply forming a shape, sintering is a tool for engineering a material's final characteristics. The process offers a level of control that is difficult to achieve with other methods.
Reducing Porosity for Increased Density and Strength
A block of loose powder is mostly empty space. The sintering process systematically eliminates these porous voids between particles. As the material becomes denser, its mechanical strength, integrity, and durability increase dramatically.
Enhancing Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
The gaps between unsintered particles act as insulators, impeding the flow of heat and electricity. By fusing these particles together, sintering creates a continuous pathway. This directly improves the thermal and electrical conductivity of the material, a critical requirement for electrical contacts and heat management components.
Achieving Unique Properties
Sintering allows for a high degree of uniformity and purity in the final product. For certain materials, like specific ceramics, controlling the density and eliminating internal voids through sintering is the key to achieving optical translucency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to applying it correctly.
Inherent Porosity
Although sintering reduces porosity, it rarely eliminates it completely. Residual microporosity can sometimes make a sintered part less strong than a component forged or cast from a fully molten state. For applications where absolute maximum strength is the only concern, other methods might be superior.
Limitations on Size and Complexity
Achieving uniform density and temperature throughout a very large or an extraordinarily complex part can be challenging. This can place practical limits on the size of components that can be effectively sintered.
Process and Material Costs
While often cost-effective for mass production, the specialized furnaces and tooling for sintering represent a significant capital investment. Furthermore, producing the high-purity, fine-grain metal or ceramic powders used as starting materials can be an expensive process itself.
When to Choose Sintering for Your Project
Your specific goal will determine if sintering is the right approach.
- If your primary focus is high performance with difficult materials: Sintering is often the only viable method for creating strong, functional components from metals and ceramics with extreme melting points.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex parts: Sintering enables the creation of net-shape components, which can drastically reduce the waste and machining time associated with traditional manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is developing materials with tailored properties: Sintering provides precise control over density and microstructure, allowing you to engineer materials for specific characteristics like strength, conductivity, or even translucency.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful and precise method to transform powdered potential into solid-state performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Bypasses High Melting Points | Enables fabrication of components from materials like tungsten and ceramics. |
| Produces Net-Shape Parts | Reduces material waste and machining costs for complex geometries. |
| Enhances Material Properties | Increases density, strength, and electrical/thermal conductivity. |
| Enables Property Control | Allows for tailoring characteristics like translucency in ceramics. |
Ready to transform your material potential into high-performance components?
Sintering is a precise process that requires reliable equipment to ensure consistent results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and consumables, providing the tools you need to master sintering for R&D or production.
Whether you're working with advanced metals, ceramics, or developing new materials, our solutions help you achieve the density, strength, and properties you require. Let's discuss your project requirements and find the perfect sintering solution for your lab.
Contact our experts today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance



















