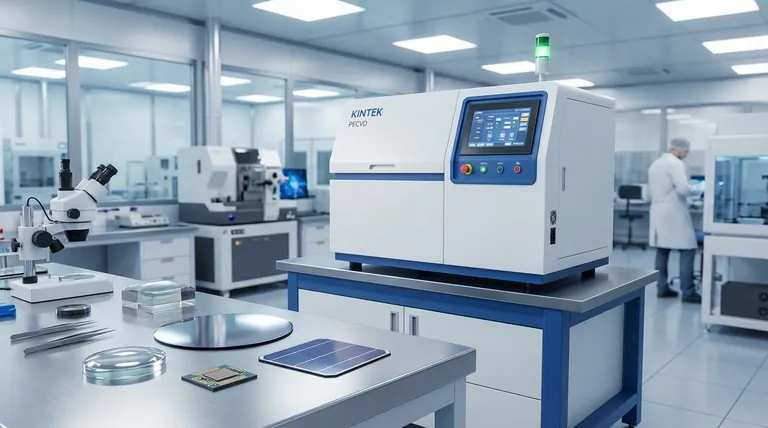
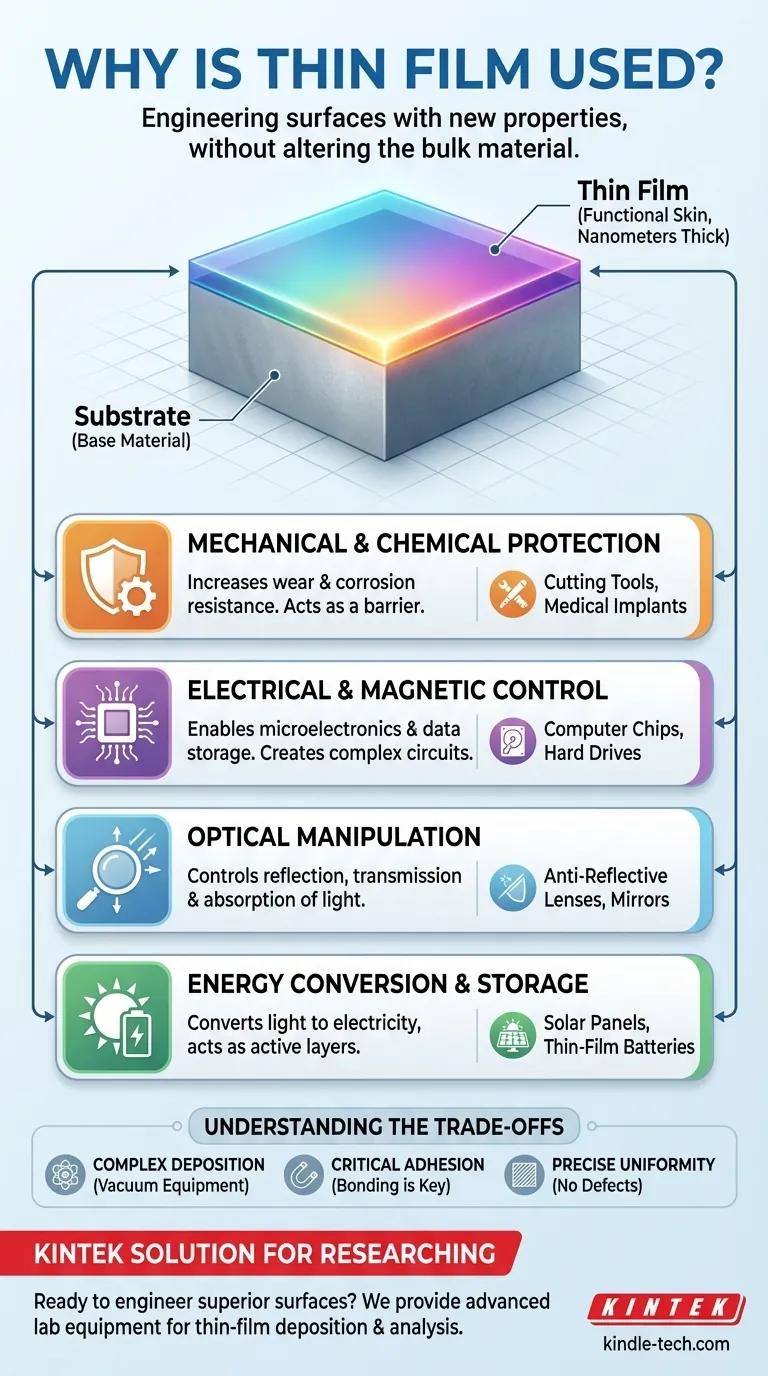
In short, thin films are used to add new properties to the surface of a material. These engineered layers are applied to a base material, known as a substrate, to enhance its performance or grant it entirely new capabilities—such as making it more durable, electrically conductive, or able to interact with light in specific ways.
The core reason for using thin films is to strategically engineer the surface of an object without altering its bulk properties. This allows for the creation of high-performance products by combining the cost-effectiveness or structural integrity of a base material with the specialized functions of a microscopic surface layer.

The Core Principle: Engineering a Surface
Think of a thin film not as a standalone object, but as a functional "skin" applied to a larger structure. This approach is fundamental to modern materials science and engineering.
Substrate and Film: A Symbiotic Relationship
A substrate is the base material, chosen for its structural properties, cost, or other core attributes. The thin film is the meticulously deposited layer, often only nanometers or micrometers thick, that provides a specialized surface function.
This combination allows engineers to create materials that are, for example, as strong as steel but also highly reflective, or as flexible as plastic but also capable of generating electricity from light.
Why Not Make the Whole Object from the Film Material?
In many cases, the material used for the thin film is expensive, rare, or lacks the necessary structural strength for the application. Applying it as a thin layer is far more efficient and economical than constructing the entire device from that material.
Key Functional Benefits of Thin Films
The versatility of thin films comes from the wide range of properties they can introduce. These functions can be grouped into several key categories.
Enhancing Mechanical and Chemical Properties
One of the most common uses for thin films is protection. They act as a barrier between the substrate and the environment.
This includes providing superior resistance to wear and corrosion, which is critical for extending the life of cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants. They also increase durability and can improve the adhesion of subsequent layers.
Modifying Electrical and Magnetic Behavior
Thin films are the building blocks of the digital world. Layers of conductive, insulating, and semi-conductive materials are deposited to create complex circuits.
These films are essential for microelectronic devices like the transistors in computer processors, magnetic storage media like hard drives, and components for advanced thin-film batteries.
Manipulating Light and Optics
Thin films give us precise control over how light reflects, transmits, or is absorbed by a surface.
This is the principle behind anti-reflective coatings on eyeglass lenses and camera lenses, the reflective layers on household mirrors, and specialized optical filters used in scientific instruments. They are also used for simple cosmetic improvements to enhance a product's appearance.
Enabling Energy Conversion and Storage
Thin films are critical for renewable energy technologies. They are the active layers in many photovoltaic cells (solar panels), responsible for converting light energy into electrical power.
They also play a key role in the development of next-generation thin-film batteries and other energy storage devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the application of thin films is a highly technical process with specific challenges.
The Complexity of Deposition
Applying a thin film is not like painting. It requires sophisticated vacuum process equipment that uses methods like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This machinery is complex and represents a significant investment.
The Critical Need for Adhesion
A thin film is only effective if it bonds perfectly to the substrate. If adhesion fails, the film can peel or flake off, completely negating its benefits. Ensuring a clean surface and the right process parameters is crucial.
The Challenge of Uniformity
For applications in optics or microelectronics, the film must be perfectly uniform in thickness and free of microscopic defects or pinholes. Achieving this level of precision across a large surface area is a significant engineering challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The reason for using a thin film depends entirely on the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is protection and durability: Thin films are used as hard, corrosion-resistant coatings to dramatically extend the lifespan of tools and components.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronic or optical functionality: Thin films are the fundamental building blocks used to create everything from computer chips to anti-reflection lenses.
- If your primary focus is energy conversion or storage: Thin films are the active layers essential for creating modern solar cells and next-generation batteries.
Ultimately, thin-film technology allows us to create materials with capabilities that far exceed what any single substance could provide on its own.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical/Chemical Protection | Increases wear & corrosion resistance | Cutting tools, medical implants |
| Electrical/Magnetic Control | Enables microelectronics & data storage | Computer chips, hard drives |
| Optical Manipulation | Controls reflection, transmission, absorption | Anti-reflective lenses, mirrors |
| Energy Conversion & Storage | Converts light to electricity, stores energy | Solar panels, thin-film batteries |
Ready to engineer superior surface properties for your products? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for thin-film deposition and analysis. Our solutions help you develop durable coatings, sophisticated electronics, and efficient energy devices. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's thin-film innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















