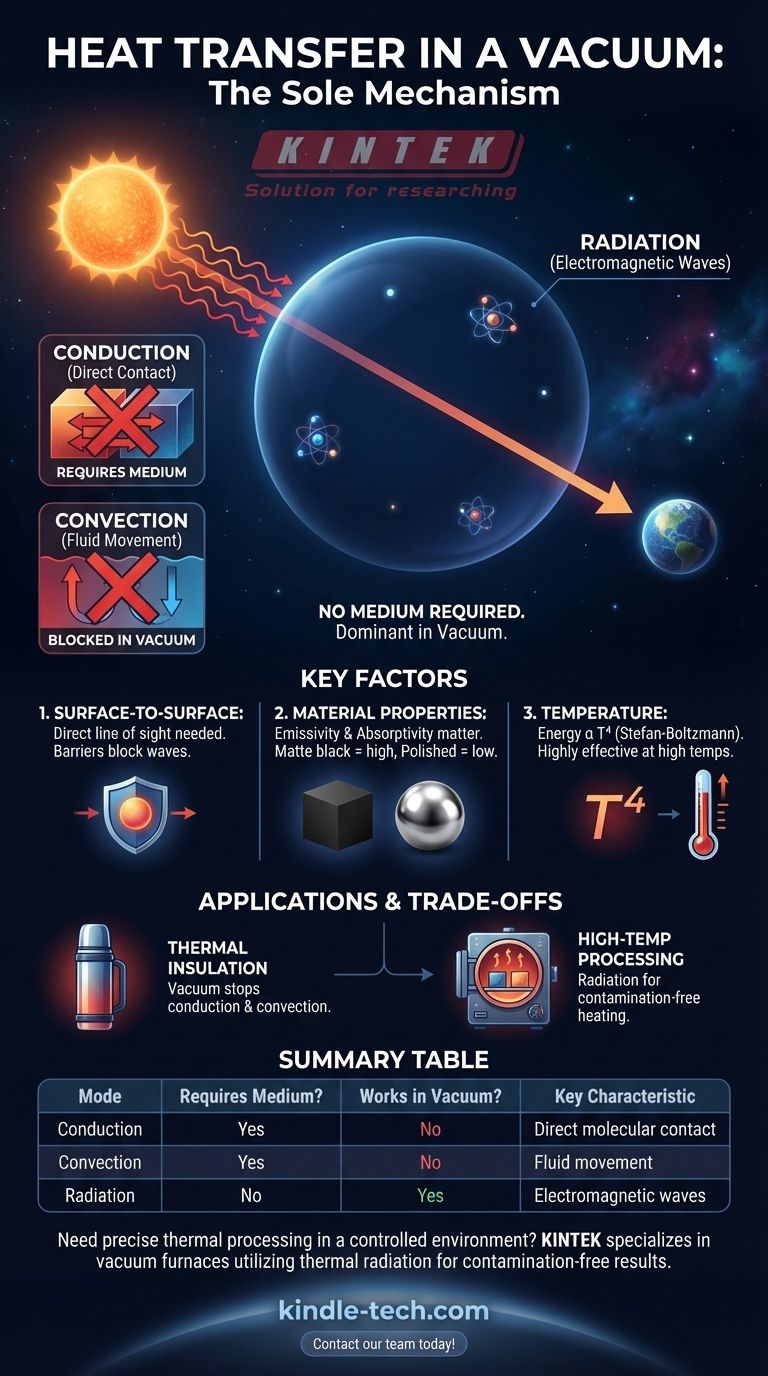
Contrary to what intuition might suggest, yes, heat transfer absolutely occurs in a vacuum. While the familiar methods of conduction and convection require a medium, a vacuum environment completely stops them. The sole mechanism for heat transfer in a vacuum is thermal radiation, the same process by which the sun warms the Earth across the vast emptiness of space.
In the absence of matter, two of the three heat transfer methods are nullified. This leaves thermal radiation—the transfer of energy via electromagnetic waves—as the only way for heat to travel across the empty space between objects.

The Three Modes of Heat Transfer: A Quick Refresher
To understand why a vacuum is unique, we must first distinguish between the three fundamental types of heat transfer.
Conduction (Direct Contact)
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct molecular collision. When you touch a hot pan, the heat transfers directly to your hand through conduction.
This process requires a physical medium—a solid, liquid, or gas—for the energy to pass through. Without matter, there can be no conduction.
Convection (Fluid Movement)
Convection is the transfer of heat through the bulk movement of fluids (liquids or gases). Hot, less dense fluid rises, and cooler, denser fluid sinks, creating a convection current.
This is how a radiator warms a room or water boils in a pot. Like conduction, it is entirely dependent on a medium to transport the heat.
Radiation (Electromagnetic Waves)
Radiation is the transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared spectrum. Unlike the other two methods, it requires no medium whatsoever.
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero emits thermal radiation. This is how you can feel the warmth of a campfire even when you are several feet away, with no air current blowing towards you.
How Radiation Dominates in a Vacuum
With conduction and convection eliminated, radiation becomes the only game in town. This has profound implications in both nature and technology.
The Role of Electromagnetic Waves
An object's heat is a representation of the kinetic energy of its atoms. These vibrating atoms emit electromagnetic waves that travel outwards at the speed of light.
When these waves strike another object, they transfer their energy, causing the atoms in the receiving object to vibrate more intensely, which we perceive as an increase in temperature.
The Sun: The Ultimate Example
The 93 million miles between the Sun and Earth is an almost perfect vacuum. The immense energy that sustains life on our planet travels this entire distance exclusively through thermal radiation.
This process demonstrates the incredible power of radiation to transfer vast amounts of energy without any intervening matter.
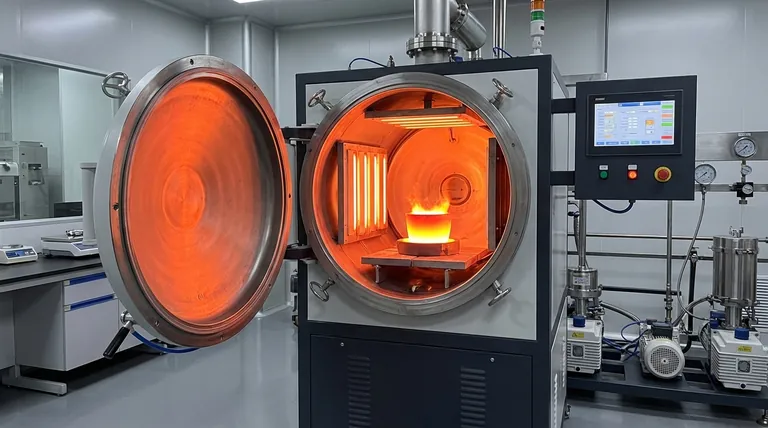
Practical Applications: Vacuum Furnaces
In industrial processes like vacuum induction sintering, materials are heated to extreme temperatures inside a vacuum chamber. This is done to prevent contamination or unwanted chemical reactions with gases in the air.
Heat is transferred from the heating elements to the material purely by radiation. Engineers must carefully design these systems based on the material's radiative properties to ensure uniform and effective heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Factors
Relying solely on radiation is not without its challenges and requires careful consideration of several factors.
It's a Surface-to-Surface Phenomenon
Radiative heat transfer requires a direct line of sight between the hot object and the cold object. Any physical barrier will block the electromagnetic waves, creating a "shadow."
This is why a space station's sun-facing side can become incredibly hot while its shaded side becomes intensely cold.
Material Properties Are Critical
How well an object radiates or absorbs heat is determined by its surface properties, specifically its emissivity and absorptivity.
A matte black surface is an excellent emitter and absorber of radiation. In contrast, a polished, mirror-like surface is a poor emitter and reflects most incoming radiation. This is why emergency space blankets are shiny—to reflect body heat back to the person.
The Impact of Temperature
The amount of energy transferred via radiation is extremely sensitive to temperature. Specifically, the energy radiated is proportional to the fourth power of the object's absolute temperature (the Stefan-Boltzmann law).
This means that radiation is a relatively slow method of heat transfer at low temperatures but becomes incredibly effective and dominant at very high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how heat behaves in a vacuum allows you to either harness it for a specific purpose or create a powerful barrier against it.
- If your primary focus is thermal insulation: A vacuum is one of the most effective insulators possible, as it completely stops heat transfer from conduction and convection. This is the principle behind a Thermos or Dewar flask.
- If your primary focus is processing materials at high temperatures without contamination: A vacuum is ideal, as radiation becomes an efficient transfer mechanism while eliminating unwanted chemical reactions from the air.
Ultimately, mastering thermal radiation is the key to controlling temperature in the unique environment of a vacuum.
Summary Table:
| Mode of Heat Transfer | Requires a Medium? | Works in a Vacuum? | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Yes | No | Transfer through direct molecular contact. |
| Convection | Yes | No | Transfer through the movement of fluids (liquids/gases). |
| Radiation | No | Yes | Transfer via electromagnetic waves (e.g., sunlight). |
Need precise thermal processing in a controlled environment? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment like vacuum furnaces that leverage thermal radiation for contamination-free heating. Our solutions are designed for materials that require high-temperature processing without the interference of air. Let our experts help you achieve perfect results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a constant temperature stirring reactor necessary for castor oil transesterification? Optimize Biodiesel Yields
- Why is specialized heating equipment necessary for TiC-steel debinding? Ensure Purity Before Sintering
- What is the requirement of heat treatment? Unlock Your Material's Full Potential
- Why is a vacuum drying oven recommended for processing wet gels of Erbium-doped titanium dioxide? | KINTEK
- Which type of furnace can create high temperature? Choose Between Tube and Box Furnaces
- What type of heating sources are used in brazing? Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Application
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum furnace play in treating the C/SiC pre-coating? Optimize Your Cf/SiC Composites
- What is the primary function of a vacuum drying oven for NH4H2PO4-coated NCM811? Optimize Your Battery Precursor Prep



















