Factors Influencing Temperature Control Accuracy
Temperature Sensors
High-precision temperature sensors, such as thermocouples and Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), play a pivotal role in enhancing the accuracy of temperature sensing and feedback within muffle furnaces. These sensors are designed to measure temperature with a high degree of precision, often within fractions of a degree Celsius. The accuracy of these sensors directly influences the effectiveness of temperature control systems, ensuring that the desired temperature is maintained consistently.
In muffle furnaces, where precise temperature control is critical for various scientific and industrial applications, the use of advanced temperature sensors can significantly improve the reliability of experimental results. For instance, thermocouples, which are based on the Seebeck effect, can measure a wide range of temperatures and are known for their fast response times. On the other hand, RTDs, which rely on the resistance change of a material with temperature, offer higher accuracy and stability, making them suitable for applications requiring precise temperature measurements.
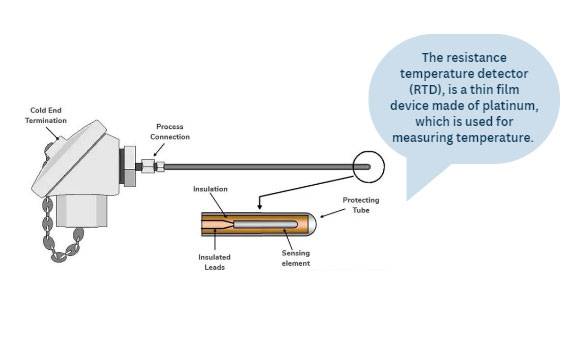
The integration of these high-precision sensors with advanced control systems, such as intelligent PID controllers, further amplifies their effectiveness. These controllers can automatically adjust control parameters based on real-time data from the sensors, optimizing temperature control to minimize deviations. This synergy ensures that the muffle furnace operates within the desired temperature range, contributing to better overall performance and more accurate experimental outcomes.
| Sensor Type | Accuracy | Response Time | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermocouples | ±1°C to ±5°C | Fast | -200°C to 1700°C |
| RTDs | ±0.1°C to ±0.5°C | Moderate | -200°C to 850°C |
In summary, the selection and implementation of high-precision temperature sensors are crucial for achieving optimal temperature control in muffle furnaces. Their ability to provide accurate and timely feedback enables more precise adjustments, ultimately leading to improved experimental accuracy and reliability.
Control Systems
Advanced control systems play a pivotal role in enhancing the precision of temperature control within high-temperature muffle furnaces. One of the most notable innovations in this domain is the integration of intelligent PID controllers. These sophisticated controllers are designed to dynamically adjust control parameters in real-time, ensuring optimal performance even under varying conditions such as thermal inertia and load changes.
The adaptive nature of intelligent PID controllers allows them to continuously monitor and adjust the heating process, thereby minimizing temperature deviations. This is achieved through algorithms that analyze feedback from temperature sensors, such as thermocouples or RTDs, and make instantaneous adjustments to maintain the desired temperature setpoint. This level of automation not only improves the accuracy of temperature control but also reduces the need for manual intervention, making the operation of the muffle furnace more efficient and reliable.
Moreover, the ability of these controllers to learn and adapt over time further enhances their effectiveness. By continuously optimizing control parameters based on historical data and current operating conditions, intelligent PID controllers can achieve temperature control accuracy that is superior to traditional systems. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in high-temperature environments where maintaining precise temperature control is critical for experimental success.
In summary, the deployment of advanced control systems, particularly intelligent PID controllers, significantly elevates the temperature control accuracy of high-temperature muffle furnaces. Their ability to automatically optimize control parameters in response to dynamic conditions ensures consistent and precise temperature management, ultimately contributing to more reliable and accurate experimental outcomes.
Heating Elements
Heating elements play a crucial role in maintaining temperature uniformity within high-temperature muffle furnaces. These elements convert electrical energy into heat through the process of Joule heating, where electric current encounters resistance, resulting in the heating of the element. Unlike the Peltier effect, this process is independent of the direction of current, ensuring consistent performance regardless of the current flow.
The choice of heating element material is paramount. Common materials include nichrome, a blend of 80% nickel and 20% chromium, which forms an adherent layer of chromium oxide upon initial heating. This protective layer prevents oxidation of the underlying material, thereby extending the element's lifespan. Other metals such as chromium, nickel, iron, tungsten, and molybdenum are also frequently used. The diameter or cross-section of the element determines its resistance; larger cross-sections lower resistance, making them suitable for high-temperature applications where larger diameters (typically between 1/4″ to 1/2″ or 6.35 to 12.7 mm) are necessary.
In specialized furnaces like endo carburizing and vacuum furnaces, particularly Low-Pressure Carburizing (LPC) systems, the design and selection of heating elements are critical. The portion of the element that passes through the insulation and steel structure to external connections must be meticulously designed to avoid common issues. Proper vetting and design considerations ensure that these elements can withstand the rigorous demands of such high-temperature environments, contributing to overall temperature control accuracy.
| Material | Composition | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nichrome | 80% Nickel, 20% Chromium | Common in toasters, hair dryers, industrial furnaces, floor heating, roof heating, pathway heating, dryers, etc. |
| Chromium | Chromium, Nickel, Iron, Tungsten, Molybdenum | High-temperature applications in specialized furnaces like endo carburizing and vacuum furnaces. |
The table above highlights the common materials used in heating elements and their typical applications, illustrating the diverse range of uses and the importance of material selection in achieving uniform and stable heating.
Insulation Materials and Furnace Structure
The selection of insulation materials and the design of the furnace structure play pivotal roles in ensuring uniform heat transfer and precise temperature control within high-voltage furnaces. These elements are meticulously chosen to withstand the extreme temperatures and harsh conditions inherent in such environments.

Insulation Materials
High-voltage furnaces often employ a combination of ceramic fiber and refractory materials for insulation. Ceramic fibers, such as alumina multi-fiber insulation, are favored for their high service temperatures and rapid heat and cold resistance. These fibers are typically used in layers, with an insulation layer thickness of up to 170mm, ensuring minimal heat loss and superior thermal insulation performance. The energy-saving effect of these materials can be as high as 80% compared to traditional electric furnaces.
Refractory materials, including alumina, magnesia, and zirconia, are also integral to the furnace lining. These materials are selected for their high melting points, resistance to thermal shock, and chemical corrosion. The furnace lining is often constructed using high-purity alumina fiber, vacuum-formed fiber materials, and light hollow aluminum oxide plates, which not only enhance the furnace's durability but also prevent cracking and slag falling.
Furnace Structure
The furnace structure, including the air ducts and furnace wall thickness, is designed to optimize heat transfer uniformity. A double furnace structure is commonly employed, which not only accelerates the heating process but also enhances the furnace's robustness and longevity. The outer shell of the furnace is typically welded from steel plates and profiles, equipped with detachable protective plates that undergo electrostatic spraying and paint baking, ensuring both durability and aesthetic appeal.
Energy Efficiency
The integration of these advanced insulation materials and a well-engineered furnace structure results in significant energy savings. The lightweight design and rapid temperature rise capabilities contribute to energy savings of over 50%, making these furnaces not only efficient but also environmentally friendly.
In summary, the careful selection of insulation materials and the meticulous design of the furnace structure are critical to achieving optimal heat transfer uniformity and precise temperature control in high-voltage furnaces. These elements work in tandem to enhance the overall performance and reliability of the furnace, ensuring accurate and consistent experimental results.
External Environmental Factors
Maintaining precise temperature control in high-temperature muffle furnaces is not solely dependent on internal mechanisms but also significantly influenced by external environmental factors. A stable power supply is paramount, as fluctuations in voltage can disrupt the delicate balance of heating elements and control systems, leading to temperature deviations. Ideally, a consistent power source ensures that the furnace operates smoothly, without sudden changes that could compromise accuracy.
The ambient temperature surrounding the furnace also plays a crucial role. Extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can affect the furnace's thermal equilibrium. For instance, a furnace operating in a very cold environment might require additional energy to reach and maintain the desired temperature, potentially leading to inefficiencies and inaccuracies. Conversely, excessive heat in the surroundings can cause the furnace to overcompensate, again resulting in unstable temperature control.
Minimizing external interference is another critical factor. This includes reducing vibrations, electromagnetic disturbances, and other environmental noises that could interfere with the furnace's operation. For example, vibrations can cause misalignment of heating elements, leading to uneven heating, while electromagnetic interference can disrupt the sensitive control systems, affecting their ability to accurately regulate temperature.
In summary, while internal components like temperature sensors, control systems, and heating elements are essential for achieving high temperature control accuracy, the external environment must also be carefully managed. Stable power supply, suitable ambient temperature, and minimal external interference collectively contribute to maintaining the precision and reliability required for high-temperature experiments.
Modern High Temperature Muffle Furnace Capabilities
Temperature Control Systems
Modern muffle furnaces are equipped with sophisticated PID intelligent temperature control systems that work in tandem with high-precision sensors to ensure real-time temperature monitoring and adjustment. These systems are designed to automatically optimize control parameters based on thermal inertia and load changes, which significantly enhances the accuracy of temperature control.
One of the key advantages of these advanced control systems is their ability to achieve temperature accuracy within a narrow margin, typically ±1°C or better. This level of precision is crucial for a wide range of high-temperature applications, from material science research to industrial processes. The integration of high-precision sensors, such as thermocouples or RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), further amplifies the effectiveness of these control systems by providing accurate temperature feedback.
To illustrate the impact of these control systems, consider the following table comparing traditional and modern temperature control methods:
| Feature | Traditional Control Systems | Modern PID Control Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Accuracy | ±5°C | ±1°C or better |
| Real-time Adjustment | Limited | Yes |
| Automatic Parameter Tuning | No | Yes |
| Sensor Integration | Basic | High-precision |
By leveraging these advanced technologies, modern muffle furnaces not only meet but often exceed the stringent requirements of high-temperature experiments, ensuring reliable and repeatable results.
Enhanced Insulation and Auxiliary Equipment
The integration of multi-layer insulation structures and temperature-evening fans plays a pivotal role in minimizing heat loss within high-temperature muffle furnaces. These insulation layers, often composed of materials like ceramic fibers or aerogels, significantly reduce thermal conductivity, thereby maintaining a stable internal temperature environment. Additionally, temperature-evening fans, strategically positioned within the furnace, facilitate the even distribution of heat by circulating the air, which helps in eliminating hotspots and ensuring a uniform temperature profile across the experimental chamber.
This dual approach not only enhances the overall efficiency of the furnace but also contributes to the accuracy and reliability of experimental results. By maintaining a consistent temperature, these enhancements mitigate the risk of thermal gradients, which can otherwise lead to inaccurate readings and compromised data integrity. The synergy between advanced insulation techniques and auxiliary equipment underscores the importance of meticulous design in achieving superior temperature control in high-temperature applications.
Future Prospects

Technological Advancements
Future advancements in temperature control technology are poised to revolutionize high-temperature muffle furnaces, offering researchers unprecedented precision and ease of use. These innovations will likely stem from several key areas:
-
Advanced Sensors and Feedback Mechanisms: The integration of next-generation temperature sensors, such as quantum dots or fiber optic sensors, could provide real-time, highly accurate temperature readings, reducing measurement errors significantly.
-
Intelligent Control Algorithms: The development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms could enable furnaces to predict and adjust for thermal fluctuations autonomously, optimizing control parameters in real-time for enhanced accuracy.
-
Enhanced Heating Elements: New materials, such as graphene-based heating elements, could offer superior thermal conductivity and stability, ensuring uniform heat distribution across the furnace chamber.
-
Smart Insulation and Structural Design: Innovations in insulation materials, like aerogels or phase-change materials, combined with intelligent structural designs, could minimize heat loss and ensure uniform temperature distribution, further refining control accuracy.
-
Integrated IoT Solutions: The incorporation of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies could allow for remote monitoring and control of muffle furnaces, enabling researchers to adjust settings and receive alerts from anywhere, enhancing both convenience and precision.
These technological leaps promise to not only improve the accuracy of temperature control but also to make high-temperature experiments more accessible and efficient, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries in various fields.
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
Related Articles
- Why Your High-Temperature Experiments Fail: The Furnace Flaw Most Labs Overlook
- Why Your Ashing Tests Fail: The Hidden Difference Between Muffle and Ashing Furnaces
- Why Your Furnace Experiments Fail: The Hidden Mismatch in Your Lab
- Muffle vs. Tube Furnace: How One Choice Prevents Costly Research Failures
- Why Your High-Temperature Experiments Fail: It's Not the Heat, It's the Furnace















