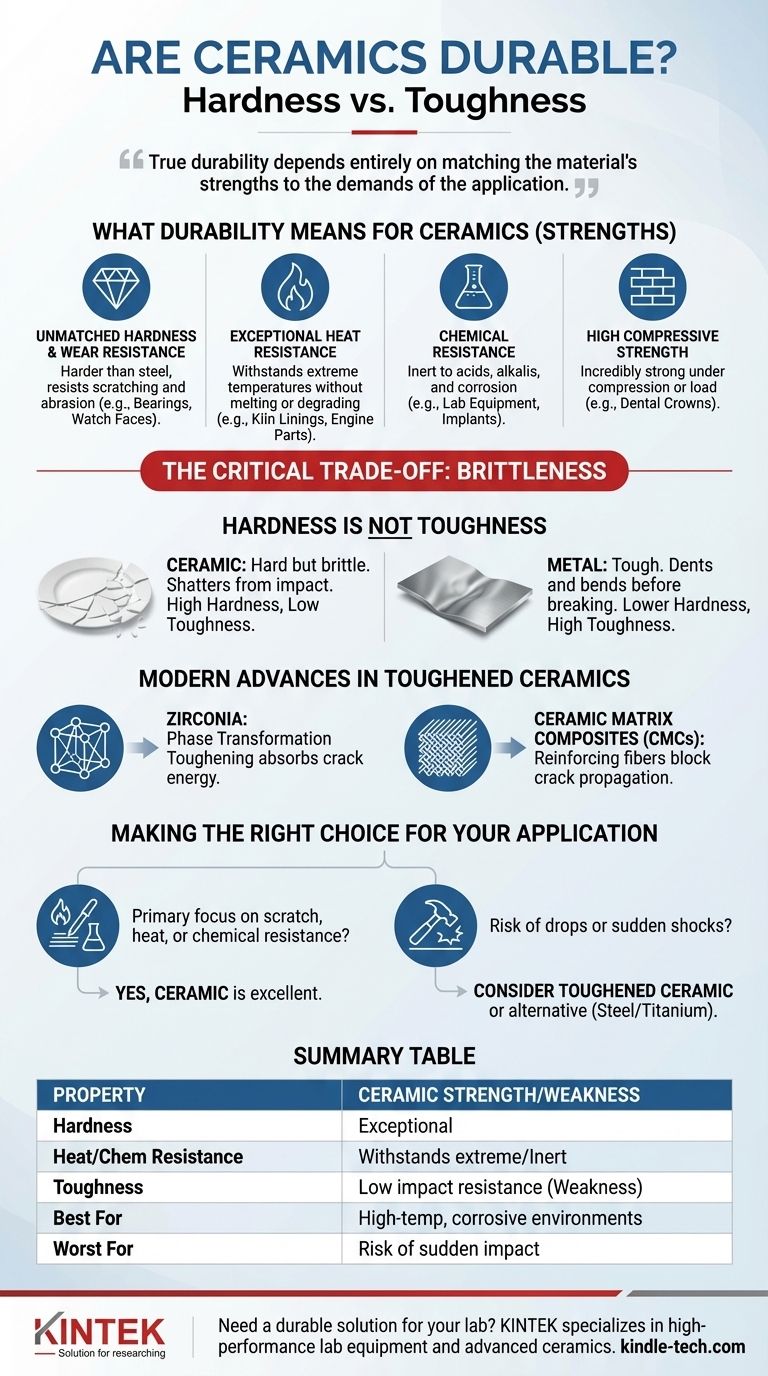
In many specific contexts, ceramics are among the most durable materials available. Their durability, however, is not universal. They are exceptionally hard and resistant to heat, wear, and chemical corrosion, but they are also inherently brittle, meaning they can be prone to shattering from a sudden impact. True durability depends entirely on matching the material's strengths to the demands of the application.
The core issue is the difference between hardness and toughness. Ceramics are extremely hard, resisting scratches and wear better than almost any metal. However, they lack toughness, the ability to absorb impact energy, which is why a ceramic plate shatters when dropped while a steel plate only dents.

What "Durability" Means for Ceramics
The term "durability" is not a single property but a collection of attributes. For ceramics, their strengths lie in resistance to gradual degradation, not sudden force.
Unmatched Hardness and Wear Resistance
Ceramics are defined by their extreme hardness. Materials like silicon carbide and aluminum oxide are harder than any steel, making them nearly impossible to scratch with everyday objects.
This property provides exceptional resistance to abrasion and wear. It is why ceramic coatings are used on high-end cookware, why ceramic bearings last longer in machinery, and why a sapphire crystal (a form of ceramic) is used on a premium watch face.
Exceptional Heat and Chemical Resistance
Ceramic materials are formed at very high temperatures, giving them incredible thermal stability. They do not melt, warp, or degrade when exposed to heat that would destroy metals and plastics.
This is why they are essential for applications like kiln linings, engine components, and the heat-shielding tiles on a spacecraft. They are also chemically inert, meaning they do not react with acids, alkalis, or other corrosive agents, making them ideal for laboratory equipment and medical implants.
High Compressive Strength
Ceramics are incredibly strong when being squeezed or compressed. A brick wall is a perfect example; it can support an immense load pressing down on it.
This same principle applies to advanced ceramics in dental crowns or hip replacements, which are designed to withstand the immense biting or compressive forces of the human body.
The Critical Trade-off: Brittleness
The immense strength of ceramics is tied directly to their greatest weakness: brittleness. This trade-off is the single most important factor to understand.
Hardness Is Not Toughness
Hardness is a material's ability to resist surface scratching and indentation. Toughness is its ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. Ceramics have high hardness but low toughness.
Think of a glass window. It is very hard—you can't easily scratch it with a key. But a small stone can cause it to shatter completely. This is a classic example of a hard but brittle material. Metals, in contrast, are tougher; they will dent and bend before they break.
The Nature of Brittle Fracture
The atoms in a ceramic are held in a rigid crystal structure by very strong ionic and covalent bonds. These bonds do not allow atoms to slide past one another to relieve stress, as they do in metals.
When a small crack forms in a ceramic—even a microscopic one—the stress concentrates at the tip of that crack. With nowhere else to go, the energy forces the crack to propagate almost instantly through the material, resulting in catastrophic failure.
The Risk of Sudden Impact
This brittleness makes ceramics vulnerable to sudden shocks. Dropping a ceramic knife on a tile floor will likely chip or shatter it, whereas a steel knife would be unharmed. Bumping a ceramic watch case hard against a door frame can cause it to crack.
Modern Advances in Toughened Ceramics
Material science has made significant strides in mitigating the inherent brittleness of ceramics for high-performance applications.
Zirconia and Transformation Toughening
Advanced ceramics like Zirconia are engineered to be significantly tougher than their traditional counterparts. They use a mechanism called "phase transformation toughening."
When a crack begins to form in zirconia, the stress from the crack tip triggers a change in the material's crystal structure. This change expands the material locally, effectively squeezing the crack shut and absorbing its energy, which stops it from spreading. This is why zirconia is used for durable dental implants and premium knives.
Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs)
Another strategy is to create composites by embedding reinforcing fibers (like silicon carbide or carbon) into a ceramic matrix.
If a crack forms in the ceramic, it cannot easily propagate because its path is blocked by these tough fibers, which absorb and dissipate the energy. CMCs are used in cutting-edge applications like jet engine turbines and high-performance vehicle brakes where failure is not an option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Whether ceramic is the right choice depends entirely on the forces it will encounter.
- If your primary focus is scratch resistance and longevity: For watch faces, cookware surfaces, or dental crowns that face abrasion but not sharp impacts, ceramic is an excellent and highly durable choice.
- If your application involves risk of drops or sudden shocks: For an all-purpose tool or a component subject to vibration, a traditional ceramic is likely a poor choice due to its brittleness. Consider a toughened ceramic like zirconia or a different material class like steel or titanium.
- If you need performance at extreme temperatures or in corrosive environments: For specialized industrial or engineering parts, advanced ceramics are not just a good choice—they are often the only viable one.
Understanding this fundamental balance between hardness and brittleness allows you to leverage the exceptional strengths of ceramic while avoiding its weaknesses.
Summary Table:
| Property | Ceramic Strength | Ceramic Weakness |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Exceptional scratch and wear resistance | - |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands extreme temperatures without degradation | - |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to acids, alkalis, and corrosive agents | - |
| Toughness | - | Low impact resistance; prone to shattering |
| Best For | High-temperature, corrosive, or abrasive environments | Applications with risk of sudden impact or shock |
Need a durable solution for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramics designed for extreme conditions. Whether you require materials for high-temperature furnaces, corrosion-resistant components, or wear-resistant parts, our expertise ensures you get the right ceramic solution for your specific application. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to enhance your laboratory's efficiency and reliability with KINTEK's precision equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- Is silicon carbide heat resistant? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Temperatures
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C



















