Yes, there are several distinct types of annealing. While they all follow the same fundamental principle of heating and controlled cooling, each type is a precise variation designed to achieve a specific outcome. These processes are used to soften metals, improve their workability, and relieve internal stresses introduced during manufacturing processes like forming, bending, or welding.
The key difference between the types of annealing is not the process itself, but the target temperature and rate of cooling. These variables are carefully controlled to manipulate the metal's internal crystal structure to produce the desired mechanical properties.

The Foundation: What Annealing Actually Does
Annealing is a heat treatment process that alters the microstructure of a material. This change is what modifies its mechanical properties, making it more useful for subsequent manufacturing steps or for its final application.
The Purpose of Annealing
The primary goals are to increase ductility (the ability to be drawn into a wire or deformed without fracturing) and reduce hardness. This is often done to reverse the effects of work hardening, a condition where metal becomes brittle and hard after being shaped or bent while cold.
Another critical application is to remove internal stresses that can build up during processes like welding or casting, preventing premature failure or distortion.
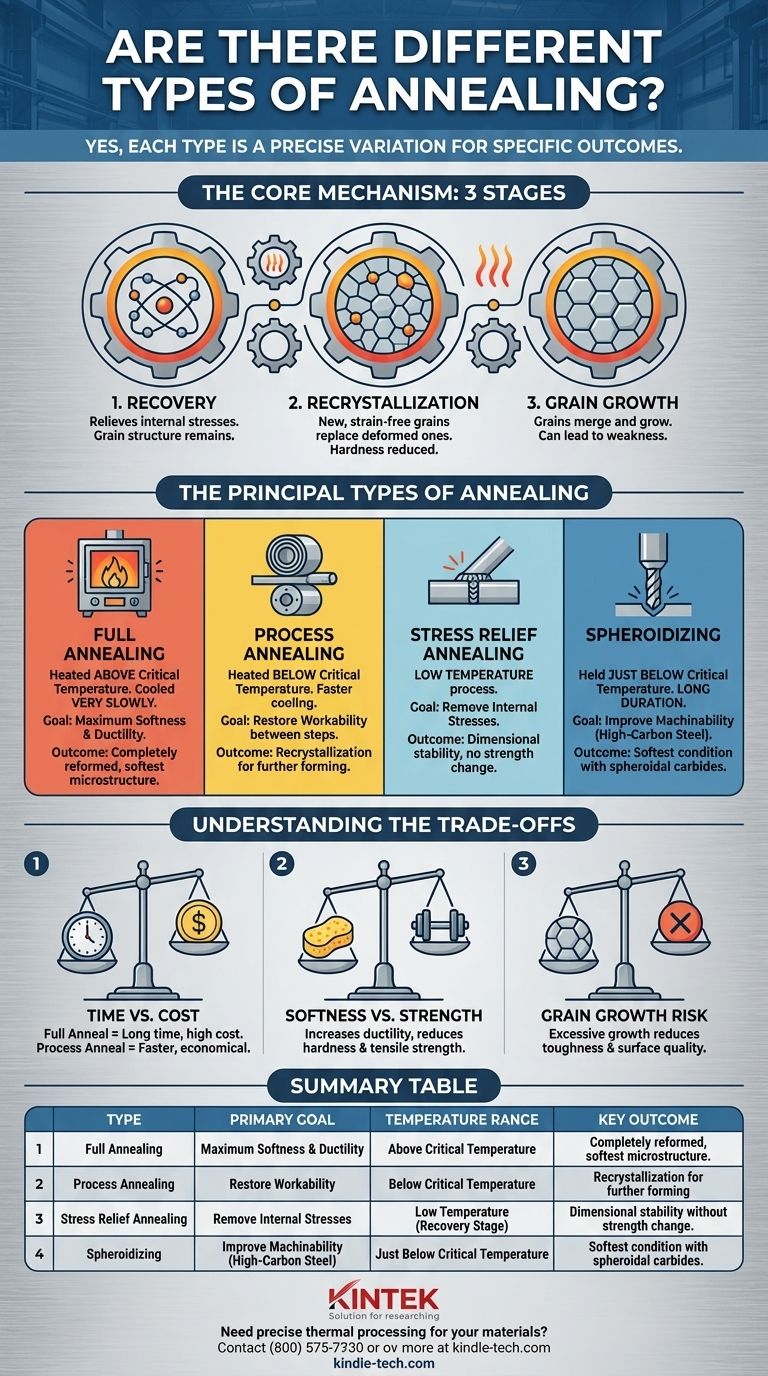
The Core Mechanism: Three Stages
As the temperature of the material increases during the annealing process, its internal structure progresses through three distinct stages. The different types of annealing are essentially methods for controlling how far a material proceeds through these stages.
- Recovery: At lower temperatures, the material begins to relieve internal stresses. The atoms inside the crystal lattice move into more stable positions, but the grain structure remains largely unchanged.
- Recrystallization: As the temperature rises further, new, strain-free grains begin to form and replace the old, deformed grains that resulted from work hardening. This is the stage where the material's hardness is significantly reduced and its ductility is restored.
- Grain Growth: If the material is held at a high temperature for too long, the new, strain-free grains will begin to merge and grow larger. This can further soften the material but may sometimes be undesirable if it makes the final product too weak or brittle.
The Principal Types of Annealing
By targeting specific temperatures and using different cooling rates, we can emphasize certain stages of the annealing process to achieve a desired result.
Full Annealing
This process involves heating the metal above its critical temperature (where a phase change in its crystal structure occurs) and then cooling it very slowly, often by leaving it in the furnace to cool. This allows the microstructure to fully reform into its softest, most ductile state. It is the most "complete" form of annealing.
Process Annealing
Also known as subcritical annealing, this is a more common and economical method used between different cold-working steps. The material is heated to a temperature below its critical point—just enough to allow for recrystallization to occur. This restores enough ductility for further forming without the time and expense of a full anneal.
Stress Relief Annealing
This is a low-temperature process designed solely to remove internal stresses without significantly changing the material's overall strength or structure. The temperature is high enough for the recovery stage but too low for recrystallization. This is critical for stabilizing components after welding, casting, or heavy machining.
Spheroidizing
This is a specialized, long-duration annealing process used on high-carbon steels to make them easier to machine. It involves holding the steel just below its critical temperature for an extended period, which causes the hard carbide structures to form into small, round spheroids within the softer base metal. This results in the softest possible condition for high-carbon steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an annealing process involves balancing desired properties with practical constraints. There is no single "best" method; the right choice depends entirely on the goal.
Time vs. Cost
The most significant trade-off is often time. A full anneal with its extremely slow cooling rate can take many hours or even days, occupying valuable furnace time and increasing energy costs. Faster methods like process annealing are far more economical for intermediate manufacturing steps.
Softness vs. Strength
Annealing is fundamentally a softening process. While it increases ductility and workability, it simultaneously reduces the material's tensile strength and hardness. You must anneal only to the degree necessary to perform the next step, as over-softening the material can compromise its final performance.
The Risk of Excessive Grain Growth
If a material is held at too high a temperature or for too long, the grains can grow excessively large. While this produces a very soft material, it can also lead to reduced toughness, poor surface finish after forming, and a condition known as "orange peel" on the surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct annealing process requires a clear understanding of your material and what you need to do with it next.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness and ductility for severe forming: Full annealing is the most effective choice to completely reset the material's microstructure.
- If your primary focus is restoring workability between manufacturing steps: Process annealing offers a fast and cost-effective way to regain ductility without a full heat treatment cycle.
- If your primary focus is removing internal stresses from welding or machining: Stress relief annealing is the correct low-temperature process to ensure dimensional stability without altering the material's strength.
- If your primary focus is improving the machinability of high-carbon steel: Spheroidizing is the specialized, time-intensive process required to achieve the necessary softness.
Understanding these annealing variants allows you to precisely control a material's properties to meet your specific engineering demands.
Summary Table:
| Type of Annealing | Primary Goal | Typical Temperature Range | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Annealing | Maximum Softness & Ductility | Above Critical Temperature | Completely reformed, softest microstructure |
| Process Annealing | Restore Workability | Below Critical Temperature | Recrystallization for further forming |
| Stress Relief Annealing | Remove Internal Stresses | Low Temperature (Recovery Stage) | Dimensional stability without strength change |
| Spheroidizing | Improve Machinability (High-Carbon Steel) | Just Below Critical Temperature | Softest condition with spheroidal carbides |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials?
The right annealing process is critical to achieving the exact material properties your project demands—whether it's maximum ductility for forming, stress relief after welding, or improved machinability.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support you need to perfect your heat treatment processes. From furnaces with precise temperature control to consumables that ensure consistent results, we help laboratories achieve reliable and repeatable outcomes.
Let's discuss your specific annealing requirements. Contact our thermal processing experts today to find the ideal solution for your laboratory's challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease



















