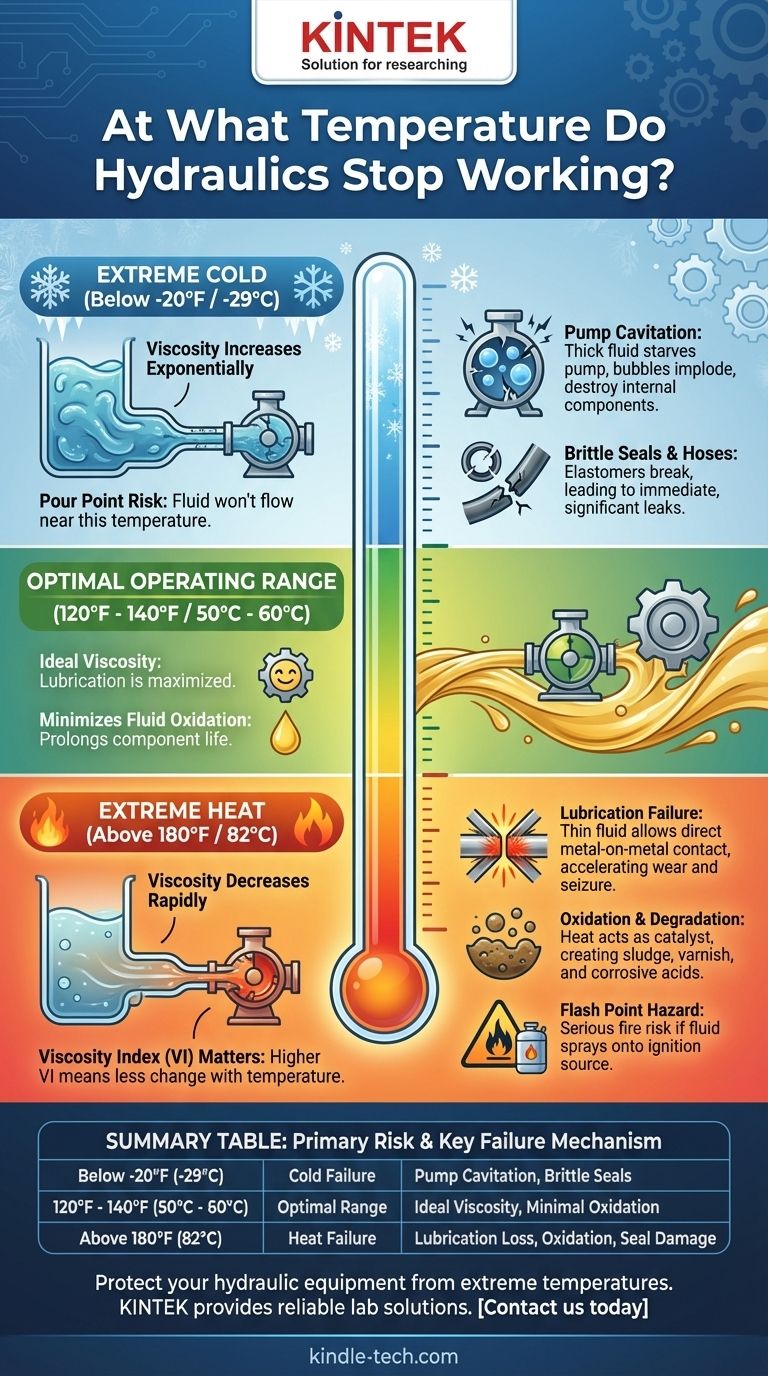
There is no single temperature at which all hydraulic systems stop working. Instead, failure occurs at both extreme cold and extreme heat, driven primarily by the properties of the hydraulic fluid. While most standard mineral oil-based systems are designed to operate between -20°F and 180°F (-29°C to 82°C), performance degrades rapidly and catastrophic failure becomes likely outside this window.
The core issue is fluid viscosity. In extreme cold, the fluid becomes too thick to flow, starving the pump and causing cavitation. In extreme heat, the fluid becomes too thin to lubricate, leading to metal-on-metal contact, component seizure, and seal failure.

The Challenge of Cold: When Fluid Won't Flow
Operating a hydraulic system in extreme cold presents a unique set of challenges that can lead to rapid and severe damage, often during startup.
Understanding Viscosity and Pour Point
Viscosity is a fluid's resistance to flow. As temperature drops, the viscosity of hydraulic oil increases exponentially.
The pour point is the lowest temperature at which the oil will still flow under specific conditions. Attempting to operate a system near or below its fluid's pour point is a primary cause of cold-weather failure.
The Risk of Pump Cavitation
When the oil is too thick, the pump cannot draw it from the reservoir fast enough. This creates vacuum voids, or bubbles, within the fluid.
As these bubbles travel to the high-pressure side of the pump, they implode violently. This process, called cavitation, generates immense force and heat, eroding and destroying critical internal pump components.
Impact on Seals and Hoses
The elastomers used in seals and hoses become hard and brittle at very low temperatures. When the system is started and pressurized, these brittle components can easily crack or fracture, leading to immediate and significant leaks.
The Danger of Heat: When Fluid Breaks Down
While cold-weather problems are often immediate, high temperatures cause a slower, but equally destructive, degradation of the entire hydraulic system.
Viscosity Loss and Lubrication Failure
As temperature rises, hydraulic fluid becomes thinner, and its viscosity drops. If the oil becomes too thin, it can no longer maintain the critical lubricating film between moving parts.
This leads to direct metal-on-metal contact, which generates more friction, more heat, and accelerates wear, quickly leading to component seizure and catastrophic failure.
Oxidation and Fluid Degradation
Heat is a catalyst for oxidation, a chemical reaction between the oil and oxygen. For every 18°F (10°C) increase in temperature above 140°F (60°C), the rate of oxidation roughly doubles.
This process breaks down the oil, creating sludge, varnish, and corrosive acids that clog filters, cause valves to stick, and damage system components.
The Flash Point Safety Limit
Every hydraulic fluid has a flash point—the lowest temperature at which its vapors can ignite when exposed to a flame. Operating a system near this temperature creates a serious fire hazard, especially if a leak develops and the hot fluid sprays onto an ignition source.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limiting Factors
The fluid is the lifeblood of the system, but it's not the only factor. The entire system must be considered when operating in extreme environments.
It's Not Just About the Fluid
While the fluid's properties are the primary concern, other components have limits. Hoses, seals, and electronic controls are all rated for specific temperature ranges. Exceeding these limits will cause failures regardless of the fluid's condition.
Mineral vs. Synthetic Fluids
Mineral oils are the standard for most applications and offer a good balance of performance and cost.
Synthetic fluids, however, are engineered to have a much wider operating temperature range. They have lower pour points for better cold-weather performance and superior thermal stability for high-heat applications. This performance comes at a significantly higher cost.
The Importance of the Viscosity Index (VI)
The Viscosity Index (VI) measures how much a fluid's viscosity changes with temperature. A fluid with a high VI is more stable, meaning its viscosity changes less dramatically across a wide temperature range. This is a critical property for equipment that operates in environments with large temperature swings.
How to Apply This to Your System
To ensure reliability, you must match your hydraulic fluid and system components to your specific operating environment.
- If your primary focus is operating in extreme cold: Select a fluid with a very low pour point and a high VI, and consider implementing a system heater or a prolonged warm-up procedure before placing the system under load.
- If your primary focus is operating in high-heat environments: Choose a fluid with high thermal stability and ensure your system has adequate cooling, such as a properly sized reservoir or an efficient heat exchanger.
- If your primary focus is maximizing component life: Maintain the fluid temperature within the optimal range of 120°F to 140°F (50°C to 60°C), as this provides the best balance of fluid viscosity and minimizes fluid oxidation.
Ultimately, proactively managing temperature is the single most effective strategy for ensuring the longevity and reliability of any hydraulic system.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Primary Risk | Key Failure Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Below -20°F (-29°C) | Cold Failure | Fluid thickens, causing pump cavitation and brittle seals. |
| 120°F - 140°F (50°C - 60°C) | Optimal Range | Ideal viscosity for lubrication and minimal oxidation. |
| Above 180°F (82°C) | Heat Failure | Fluid thins, leading to lubrication loss, oxidation, and seal damage. |
Protect your hydraulic equipment from extreme temperatures. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including systems that rely on precise hydraulic performance. Our expertise ensures your laboratory operations run reliably, regardless of environmental challenges. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and maximize your equipment's lifespan.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
People Also Ask
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- How does process temperature influence film deposition and what are its limitations? Balancing Quality and Heat Constraints
- What is the difference between VAR and ESR? A Guide to Understanding Tail Risk in Financial Modeling
- Does a graphite crucible need to be seasoned? The Critical First-Use Safety Guide
- How is sputtering done? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition


















