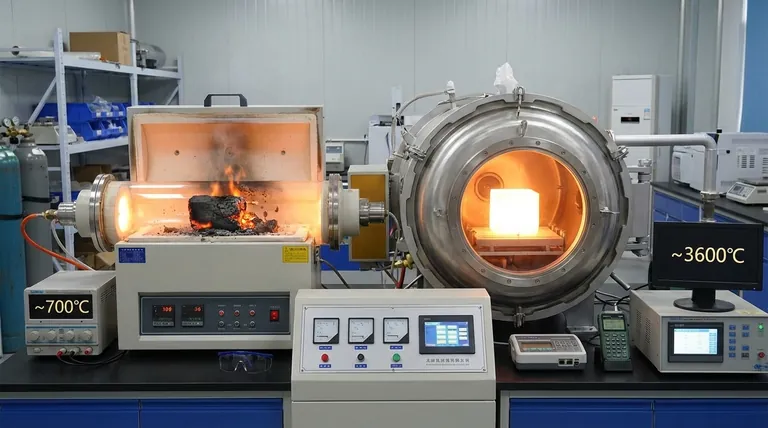
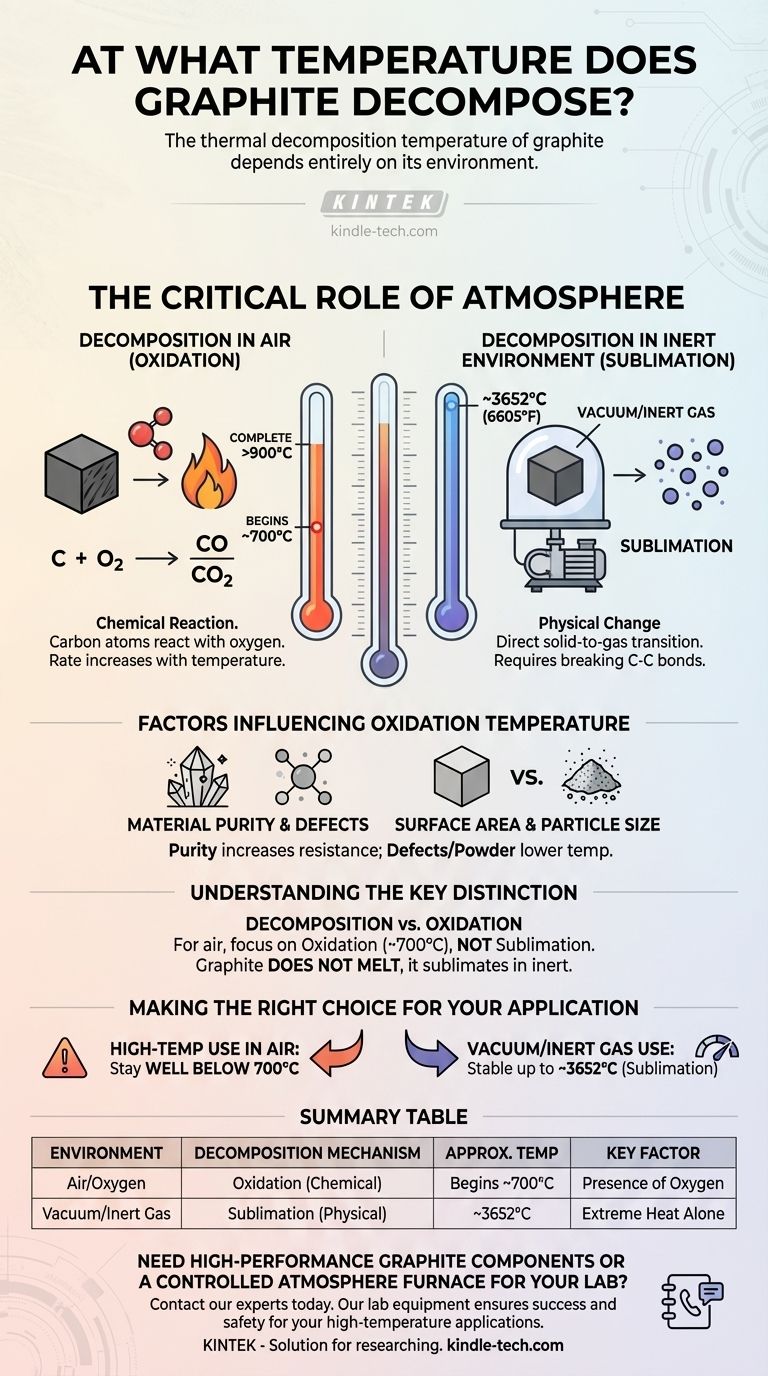
The thermal decomposition temperature of graphite depends entirely on its environment. In a standard air atmosphere, graphite begins to lose mass and oxidize at approximately 700°C, with complete decomposition occurring after 900°C. However, in the absence of oxygen, its thermal stability is drastically higher.
The most critical factor determining graphite's stability is not temperature alone, but the presence of oxygen. In air, it chemically oxidizes at a relatively low temperature, while in an inert environment, it physically sublimates at an extremely high temperature.

The Critical Role of Atmosphere
Understanding the environment is the key to determining graphite's performance at high temperatures. The mechanism of its breakdown changes completely based on the gases present.
Decomposition in Air (Oxidation)
In the presence of oxygen, graphite's decomposition is a chemical reaction. The carbon atoms react with oxygen to form carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas.
This process, known as oxidation, begins to cause measurable mass loss around 700°C. The rate of this reaction increases with temperature, leading to the complete consumption of the material above 900°C.
Decomposition in an Inert Environment (Sublimation)
When oxygen is removed—for example, in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere like argon or nitrogen—graphite is exceptionally stable. There is no oxygen for it to react with.
In this state, its thermal limit is defined by sublimation, the direct transition from a solid to a gas. This physical change requires breaking the powerful carbon-carbon bonds and occurs at an extremely high temperature, around 3652°C (6605°F).
Factors That Influence the Oxidation Temperature
Even in an air atmosphere, the exact temperature at which oxidation begins can be influenced by the material's specific properties.
Material Purity and Defects
Highly pure, well-ordered crystalline graphite is more resistant to oxidation. Impurities and structural defects can serve as active sites where the reaction with oxygen can begin more easily, potentially lowering the decomposition temperature.
Surface Area and Particle Size
The physical form of the graphite plays a significant role. A fine graphite powder has a much larger surface area exposed to oxygen than a solid, dense block. This increased exposure means the powder will oxidize faster and at a potentially lower temperature.
Understanding the Key Distinction
Failing to distinguish between the two decomposition mechanisms is a common point of failure in high-temperature system design.
"Decomposition" vs. "Oxidation"
For any practical application in air, you are concerned with the oxidation temperature (~700°C), not the sublimation temperature. Using the much higher sublimation point in calculations for an oxygen-rich environment will lead to catastrophic failure.
Graphite Does Not Melt
At normal atmospheric pressure, graphite does not have a melting point. It never becomes a liquid. Instead, it sublimates directly from a solid to a gas, which is its true point of thermal decomposition in an inert environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine graphite's suitability, you must first define the operational atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is on high-temperature use in air: Your operational ceiling is the onset of oxidation, meaning you must design your system to stay well below 700°C.
- If your primary focus is on performance in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite is one of the most thermally stable materials available, with a limit defined by its sublimation point above 3600°C.
Ultimately, correctly identifying your operating environment is the most important factor in leveraging graphite's thermal properties.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Decomposition Mechanism | Approximate Temperature | Key Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air / Oxygen | Oxidation (Chemical Reaction) | Begins ~700°C | Presence of Oxygen |
| Vacuum / Inert Gas | Sublimation (Physical Change) | ~3652°C (6605°F) | Extreme Heat Alone |
Need high-performance graphite components or a controlled atmosphere furnace for your lab?
Graphite's exceptional thermal properties can be fully leveraged only with the right equipment and environment. Whether you require inert atmosphere furnaces or custom graphite parts designed for extreme conditions, KINTEK has the expertise and products to meet your laboratory's precise needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can ensure the success and safety of your high-temperature applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- What is the thermal limit of graphite? Unlock Extreme Heat Performance in Your Lab
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C



















