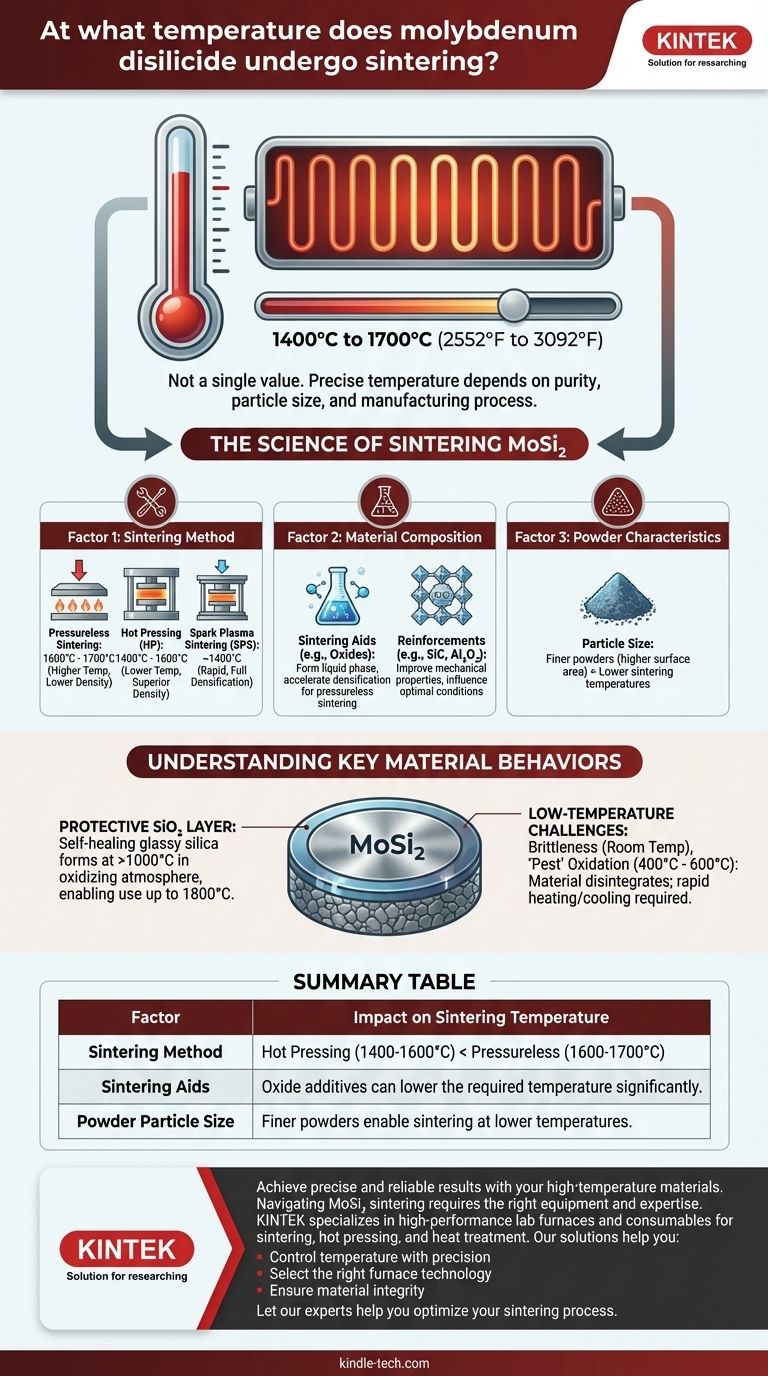
The sintering temperature of molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) is not a single value but typically falls within a range of 1400°C to 1700°C (2552°F to 3092°F). The precise temperature depends heavily on the purity of the material, the size of the powder particles, and the specific manufacturing process being used, such as pressureless sintering versus hot pressing.
Sintering MoSi₂ is a complex thermal process where the goal is to create a dense, solid component from powder. The required temperature is fundamentally a variable, influenced more by the chosen processing technique and material composition than by a fixed physical property of the material itself.

The Science of Sintering Molybdenum Disilicide
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat and/or pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. For a high-melting-point material like MoSi₂, which melts at approximately 2030°C, understanding the factors that control sintering is critical for successful application.
Factor 1: Sintering Method
The technique used to apply heat and pressure has the most significant impact on the required temperature.
- Pressureless Sintering: In this method, compacted powder is simply heated in a furnace. Because no external pressure is applied, it requires higher temperatures, often in the 1600°C to 1700°C range, to achieve high density.
- Hot Pressing (HP): This technique applies high pressure simultaneously with heat. The pressure helps consolidate the powder, significantly lowering the required sintering temperature to around 1400°C to 1600°C while achieving superior density.
- Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): An advanced method that uses a pulsed DC current to generate heat rapidly. SPS is very effective for MoSi₂, often achieving full densification at temperatures as low as 1400°C in a matter of minutes.
Factor 2: Material Composition and Additives
Pure MoSi₂ is notoriously difficult to sinter without pressure due to its strong covalent bonds. To overcome this, manufacturers often create composites.
- Sintering Aids: The reference to an "oxide, glassy phase component" in the Moly-D product is a key insight. These oxides act as sintering aids. They form a liquid phase at a lower temperature than the MoSi₂ matrix, which accelerates particle rearrangement and densification, enabling effective pressureless sintering.
- Reinforcements: Sometimes, other ceramic phases like silicon carbide (SiC) or alumina (Al₂O₃) are added to improve mechanical properties like fracture toughness, which can also influence the optimal sintering conditions.
Factor 3: Powder Characteristics
The starting powder itself plays a crucial role.
- Particle Size: Finer powders (e.g., in the sub-micron or nano range) have a much higher surface area. This increased surface energy provides a stronger driving force for sintering, allowing for densification at lower temperatures compared to coarser powders.
Understanding Key Material Behaviors
Simply knowing the sintering temperature is not enough. To use MoSi₂ effectively, you must understand its unique properties and potential failure modes.
The Protective Silica (SiO₂) Layer
At high temperatures (above approximately 1000°C) in an oxidizing atmosphere, MoSi₂ forms a thin, self-healing layer of glassy silica (SiO₂) on its surface. This passive layer is what makes MoSi₂-based heating elements so exceptionally resistant to oxidation and suitable for use up to 1800°C, as noted in the reference.
Low-Temperature Challenges
MoSi₂ has two well-known weaknesses at lower temperatures that must be managed.
- Brittleness: Like many ceramics, MoSi₂ is very brittle at room temperature. It only becomes ductile at very high temperatures, so it must be handled carefully to avoid mechanical shock.
- "Pest" Oxidation: In a specific temperature range of roughly 400°C to 600°C, MoSi₂ can undergo accelerated, catastrophic oxidation. The material disintegrates into a powder of MoO₃ and SiO₂. This is why MoSi₂ components must be heated and cooled rapidly through this temperature zone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your approach to sintering MoSi₂ should be dictated by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and purity: You should plan to use an advanced technique like Hot Pressing or Spark Plasma Sintering, likely operating in the 1400°C to 1600°C range.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale production: You will likely use a composite formulation with sintering aids, enabling pressureless sintering in a more manageable range of 1500°C to 1650°C.
- If your primary focus is using a finished component (e.g., a heating element): The sintering has already been performed. Your concern is the maximum operating temperature (e.g., 1800°C), while ensuring you pass quickly through the 400-600°C "pest" oxidation range during heat-up and cool-down.
Ultimately, successfully working with molybdenum disilicide requires moving beyond a single temperature value and embracing the processing variables that truly define its performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Sintering Temperature |
|---|---|
| Sintering Method | Hot Pressing (1400-1600°C) < Pressureless (1600-1700°C) |
| Sintering Aids | Oxide additives can lower the required temperature significantly. |
| Powder Particle Size | Finer powders enable sintering at lower temperatures. |
Achieve precise and reliable results with your high-temperature materials.
Navigating the complexities of MoSi₂ sintering requires the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed for demanding thermal processes like sintering, hot pressing, and heat treatment.
Our solutions help you:
- Control temperature with precision for consistent material properties.
- Select the right furnace technology for your specific method (pressureless, hot pressing).
- Ensure material integrity by managing critical temperature zones like the 'pest' oxidation range.
Let our experts help you optimize your sintering process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's specific needs in high-temperature materials processing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Research
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of high temperature muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What is the use of a digital muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis



















