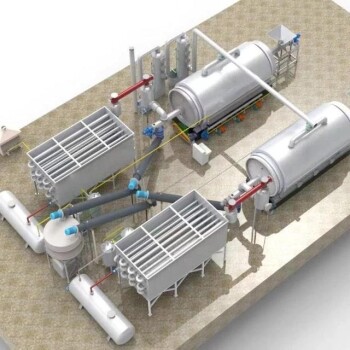
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that occurs in the absence of oxygen, transforming waste materials into valuable byproducts such as gases, liquids, and solids. The temperature at which waste is treated in pyrolysis varies depending on the type of waste, the desired end products, and the specific pyrolysis method used. Generally, pyrolysis temperatures range from 200°C to 1200°C, with most processes falling between 300°C and 900°C. Lower temperatures (200°C–550°C) are typical for slow pyrolysis, which produces more solid char, while higher temperatures (600°C–1200°C) are used for fast or high-temperature pyrolysis, yielding more gases and liquids. The choice of temperature is critical as it directly influences the efficiency of the process and the quality of the output products.
Key Points Explained:
-
Temperature Range in Pyrolysis:
- Pyrolysis temperatures typically range from 200°C to 1200°C, depending on the feedstock and desired products.
- Lower temperatures (200°C–550°C) are used for slow pyrolysis, which favors the production of solid char.
- Medium temperatures (600°C–700°C) are common for medium-temperature pyrolysis, balancing the production of gases, liquids, and solids.
- Higher temperatures (700°C–1200°C) are employed in fast pyrolysis or high-temperature pyrolysis, which maximizes the yield of gases and liquids.
-
Factors Influencing Temperature Selection:
- Feedstock Type: Different materials decompose at different temperatures. For example, plastics and biomass have distinct thermal degradation profiles.
- Desired Products: Higher temperatures favor gas and liquid production, while lower temperatures yield more solid residues like char.
- Process Type: Slow pyrolysis operates at lower temperatures with longer residence times, whereas fast pyrolysis requires higher temperatures and shorter reaction times.
-
Slow Pyrolysis:
- Conducted at 300°C–550°C.
- Heating rates are typically 1–30°C per minute.
- Produces a higher proportion of solid char and is often used for biomass conversion.
- Operates in an oxygen-free or oxygen-limited environment to prevent combustion.
-
Medium-Temperature Pyrolysis:
- Occurs between 600°C and 700°C.
- Balances the production of gases, liquids, and solids.
- Suitable for processing mixed waste streams, including plastics and organic materials.
-
High-Temperature Pyrolysis:
- Operates at 700°C–1200°C.
- Maximizes the production of syngas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide) and pyrolysis oil.
- Often used in industrial settings for energy recovery from waste.
-
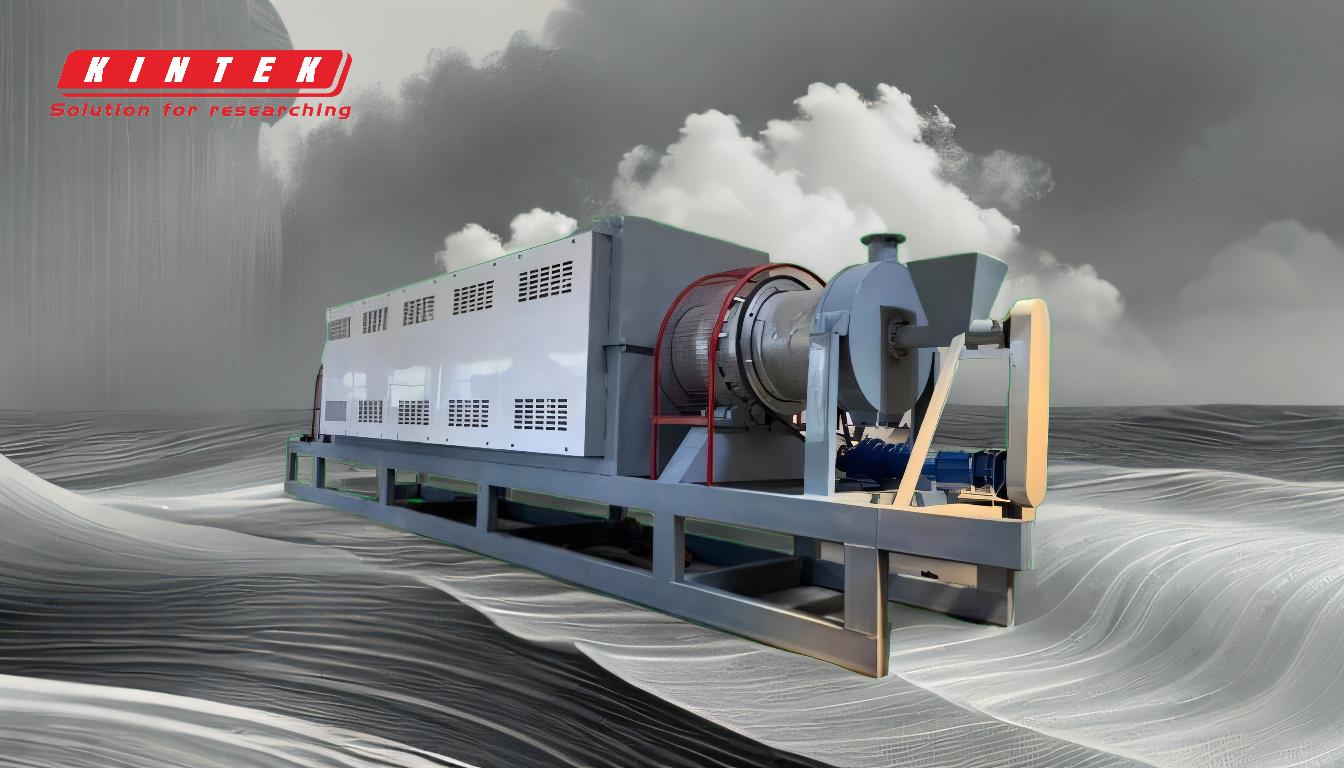
Reactor Design and Temperature Control:
- Pyrolysis reactors are designed to withstand high temperatures and are often made of refractory alloys.
- External heating sources, such as gas burners or electric heaters, are used to maintain precise temperature control.
- Reactors can be long and thin (20–30 meters in length, 1–2 inches in diameter) to ensure uniform heating.
-
Impact of Temperature on Byproducts:
- Gases: Higher temperatures increase the production of gases like methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide.
- Liquids: Pyrolysis oil is a primary liquid product, with its yield and composition influenced by temperature.
- Solids: Char production decreases at higher temperatures, as more material is converted into gases and liquids.
-
Applications of Pyrolysis:
- Waste-to-Energy: Converts municipal solid waste, plastics, and biomass into fuels and energy.
- Chemical Production: Produces valuable chemicals and feedstocks for industrial processes.
- Carbon Capture: Generates biochar, which can be used for soil amendment or carbon sequestration.
-
Challenges and Considerations:
- Energy Input: High-temperature pyrolysis requires significant energy, which can affect the overall efficiency and cost of the process.
- Feedstock Pre-Treatment: Waste materials often need to be cleaned, sorted, and ground to ensure consistent pyrolysis performance.
- Byproduct Management: Proper handling and refining of pyrolysis oil, gas, and char are essential to maximize their value.
In summary, the temperature at which waste is treated in pyrolysis is highly variable and depends on the specific goals of the process. By carefully selecting the appropriate temperature range, operators can optimize the conversion of waste into valuable products, making pyrolysis a versatile and sustainable waste management solution.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 200°C–1200°C, depending on feedstock and desired products |
| Slow Pyrolysis | 300°C–550°C; produces more solid char |
| Medium Pyrolysis | 600°C–700°C; balances gases, liquids, and solids |
| Fast Pyrolysis | 700°C–1200°C; maximizes gases and liquids |
| Key Factors | Feedstock type, desired products, and process type |
| Applications | Waste-to-energy, chemical production, carbon capture |
| Challenges | Energy input, feedstock pre-treatment, byproduct management |
Discover how pyrolysis can transform your waste into valuable resources—contact our experts today!