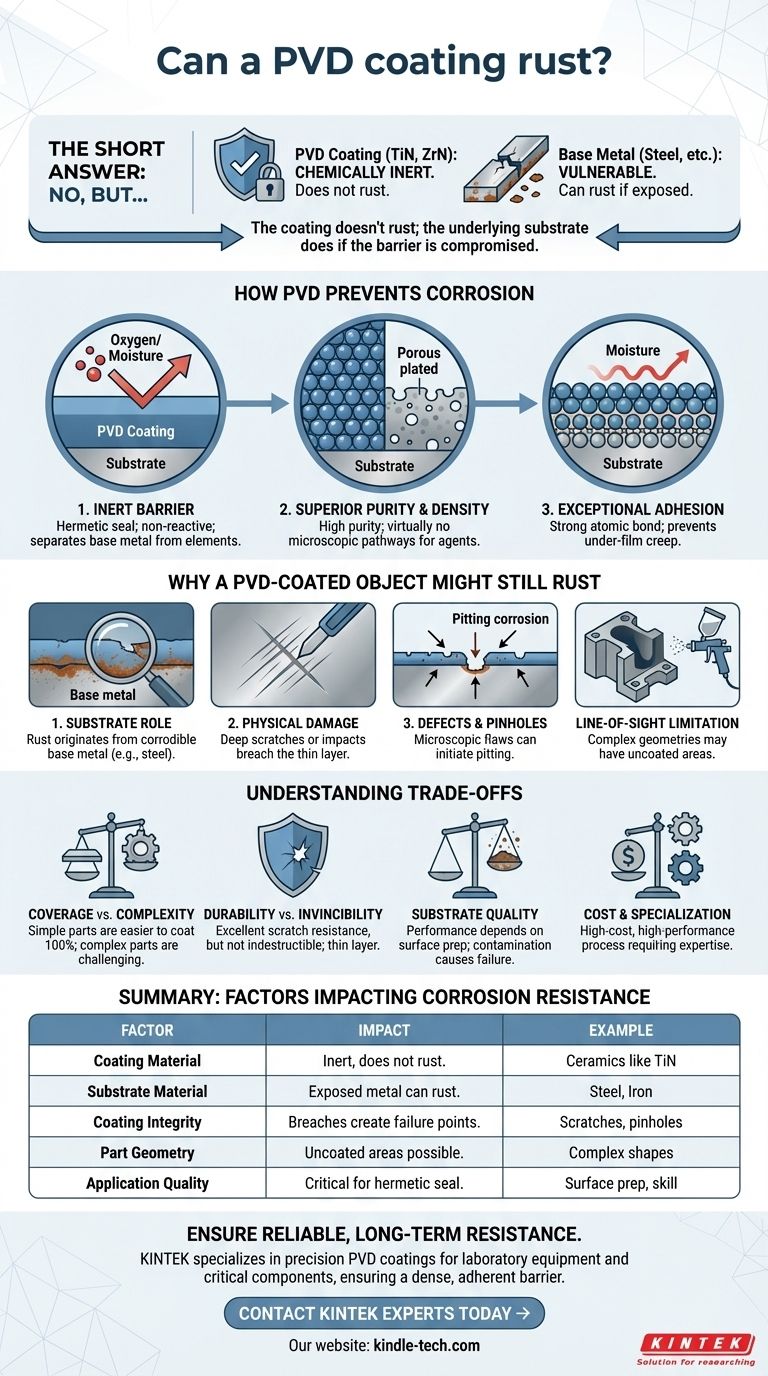
In principle, a PVD coating itself does not rust. The ceramic materials used in Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), such as Titanium Nitride or Zirconium Nitride, are chemically inert and do not undergo the oxidation process that we call rust. However, this is not the complete answer. Rust can still appear on a PVD-coated object if the underlying base metal, or substrate, is exposed to the elements.
The question is not whether the PVD coating will rust, but how effectively it seals the underlying metal. A properly applied PVD coating creates a dense, non-reactive barrier, but any breach—from damage, defects, or incomplete coverage—will expose the substrate and allow it to corrode.

How PVD Coatings Prevent Corrosion
The exceptional corrosion resistance of a PVD coating is not a single feature but the result of several integrated properties working as a system.
The Principle of an Inert Barrier
A PVD coating functions by creating a hermetic seal over the substrate material. This thin, dense film is chemically stable and non-reactive, physically separating the base metal from corrosive elements like oxygen and moisture.
Superior Purity and Density
The PVD process creates coatings of exceptionally high purity and density. Unlike plating, which can have inherent porosity, a well-applied PVD film leaves virtually no microscopic pathways for corrosive agents to penetrate and reach the substrate.
Exceptional Adhesion
PVD coatings form a very strong, atomic-level bond with the substrate. This excellent adhesion is critical, as it prevents moisture from creeping underneath the coating edge and causing delamination or blistering, even if a small area is breached.
Why a PVD-Coated Object Might Still Rust
When you see rust on a PVD-coated part, the corrosion is almost always originating from the base metal underneath, not the coating itself. This happens for a few key reasons.
The Role of the Substrate
Most rust seen on PVD-coated items originates from a corrodible substrate, such as steel. The PVD coating is a shield, but the material it is protecting remains vulnerable if exposed.
Failure from Physical Damage
While PVD coatings are extremely hard and abrasion-resistant, they are not invincible. A deep scratch or a significant impact can penetrate the thin coating layer, creating an opening that exposes the substrate to the environment and initiates corrosion.
Defects and Pinholes
Even high-quality PVD coatings can have microscopic pinholes or defects. These tiny imperfections can act as focal points for "pitting" corrosion, where rust begins in a very small area and can then spread under the coating.
The "Line-of-Sight" Limitation
The PVD process is a "line-of-sight" technique, meaning the coating material can only deposit on surfaces it can "see" from the source. Complex parts with deep recesses, internal channels, or undercuts may not receive complete coverage, leaving uncoated areas vulnerable to rust.
Understanding the Trade-offs
PVD offers world-class protection, but success depends on understanding its operational limits. Acknowledging these trade-offs is crucial for proper application.
Coverage vs. Complexity
The superior barrier of PVD is most effective on parts with simple geometry. For highly complex parts, ensuring 100% coverage is a significant challenge and may require specialized fixtures and rotation within the chamber.
Durability Is Not Invincibility
The hardness of PVD provides excellent scratch resistance against everyday wear. However, the coating is very thin. It can be breached by sharp, hard objects or in high-impact industrial environments, compromising its protective function.
The Importance of Substrate Quality
The performance of the PVD coating is directly dependent on the surface it is applied to. A poorly prepared, contaminated, or inherently porous substrate will lead to poor adhesion and premature failure, regardless of the coating's quality.
Cost and Specialization
PVD is a high-cost, high-performance process that requires skilled operators and expensive equipment. It is an investment in surface engineering, not a simple, inexpensive finish.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To leverage PVD effectively, you must align the technology's capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum corrosion resistance for a critical part: Ensure the design allows for 100% coating coverage and work closely with your PVD provider to verify it.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish with enhanced durability: PVD is an excellent choice, but recognize that deep scratches on items like faucets or watches can eventually lead to localized corrosion of the base metal.
- If you are coating geometrically complex parts: You must make addressing line-of-sight limitations a top priority, potentially using multi-axis rotation or accepting that some internal areas may remain uncoated.
Ultimately, viewing PVD not as a simple rust-proof paint but as an integrated surface engineering system is the key to achieving reliable, long-term performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|
| Coating Material | Ceramics like TiN are inert and do not rust. |
| Substrate Material | Exposed steel or iron underneath can rust. |
| Coating Integrity | Scratches, pinholes, or poor adhesion create failure points. |
| Part Geometry | Complex shapes may have uncoated areas due to line-of-sight deposition. |
| Application Quality | Proper surface prep and skilled application are critical for a hermetic seal. |
Ensure your components have reliable, long-term corrosion resistance. The performance of a PVD coating is an integrated system, highly dependent on expert application and high-quality substrate preparation. At KINTEK, we specialize in precision PVD coatings for laboratory equipment and critical components. Our expertise ensures a dense, adherent barrier that maximizes protection for your specific application. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance the durability and performance of your parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer



















