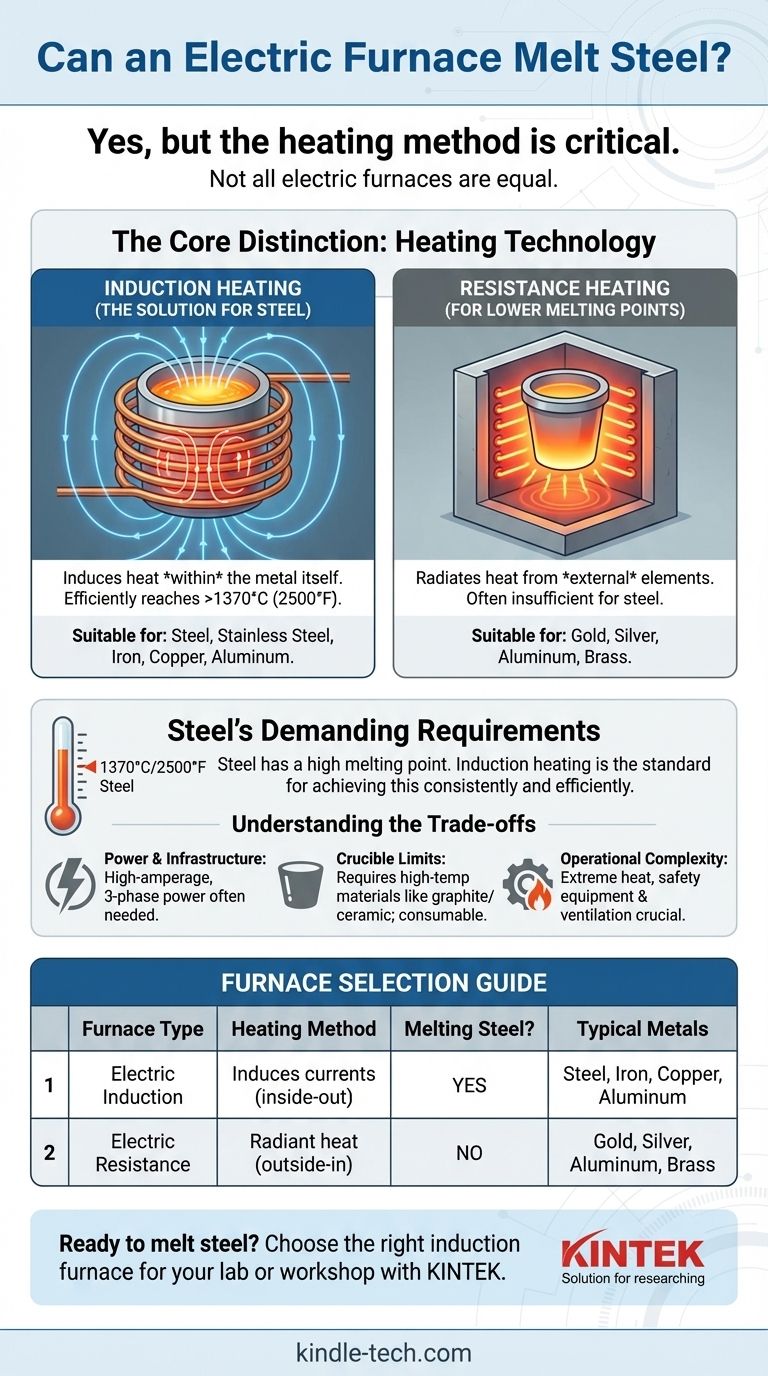
Yes, specific types of electric furnaces are designed to melt steel. The critical factor is not that the furnace is electric, but how it generates heat. For a high-melting-point metal like steel, the standard technology is an electric induction furnace, which is capable of reaching the required temperatures of over 1370°C (2500°F).
The ability to melt steel is determined by the furnace's heating technology, not just its power source. While many electric furnaces exist, only those using induction heating are consistently suitable for melting steel, carbon steel, and stainless steel.

The Principle of Induction Heating
How Induction Creates Intense Heat
An electric induction furnace does not use a traditional heating element. Instead, it uses a powerful copper coil through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed.
This current generates a rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil. When a conductive material like steel is placed within this field (typically inside a container called a crucible), the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents within the steel itself.
These internal currents, known as eddy currents, create immense heat due to the metal's natural electrical resistance. This process heats the metal from the inside out, allowing it to reach its melting point efficiently.
Meeting the Demands of Steel
Steel has a very high melting point, typically around 1370°C (2500°F).
The induction process is powerful enough to consistently and quickly reach these temperatures, making it the go-to technology for smelting steel, stainless steel, and various other alloys in industrial and workshop settings.
Not All Electric Furnaces Are Equal
It is a common misconception that any furnace labeled "electric" can handle any metal. The heating method dictates the furnace's true capability.
Induction Furnaces: The Standard for Steel
As established, electric induction furnaces are the correct tool for the job. They are specifically engineered for the high-temperature demands of ferrous metals like iron and steel, as well as other metals like copper and aluminum.
Resistance Furnaces: For Lower-Temperature Metals
Other electric furnaces operate on the principle of resistance heating. These function more like a conventional oven or kiln, using heating elements that glow hot and radiate heat toward the metal.
While effective, resistance furnaces are generally designed for metals with lower melting points, such as gold, silver, aluminum, and brass. They often cannot reach or sustain the extreme temperatures required to melt steel efficiently and safely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Power and Infrastructure
Induction furnaces, particularly those large enough to melt significant quantities of steel, have substantial power requirements. They often demand high-amperage, three-phase electrical service that is not standard in most residential settings.
Crucible and Refractory Limits
The crucible holding the molten metal must be made of a material, like graphite or ceramic, that has a much higher melting point than steel itself. These crucibles are consumable items that degrade over time and with use, representing an ongoing operational cost.
Operational Complexity
Melting steel is an inherently dangerous process that involves extreme temperatures and molten metal. Proper safety equipment, ventilation, and a clear understanding of the metallurgical process are non-negotiable for safe operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct equipment, you must match the technology to the material you intend to work with.
- If your primary focus is melting steel, stainless steel, or iron: You must use an electric induction furnace specifically rated for these materials.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, gold, or copper: An electric resistance furnace is a viable and often more accessible option, though an induction furnace will also work.
Ultimately, the key is to choose a furnace based on the specific melting point of the metal you wish to work with.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Heating Method | Suitable for Melting Steel? | Typical Metals Melted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Induction Furnace | Induces currents inside the metal (inside-out heating) | Yes | Steel, Stainless Steel, Iron, Copper, Aluminum |
| Electric Resistance Furnace | Radiates heat from external elements (outside-in heating) | No | Gold, Silver, Aluminum, Brass |
Ready to melt steel in your lab or workshop?
Choosing the right furnace is critical for safety, efficiency, and achieving your metallurgical goals. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including industrial-grade induction furnaces designed for demanding applications like melting steel and other alloys.
Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace for your specific materials and volume requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a personalized recommendation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the equipment used for heat treatment? A Complete Guide to Furnaces and Systems
- What is the temperature of a calcination furnace? Precise Control from 800°C to 1300°C
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum drying oven for graphite electrode sheets? Ensure Battery Safety & Performance
- What is a multi-position furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Flexible HVAC Installation
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What is the function of a Drop Tube Reactor in flash-reduced iron powder study? Precision Simulation for Rapid Reduction
- What is the vacuum level of a vacuum furnace? Match the Right Vacuum to Your Process
- What is vacuum furnace brazing? Achieve Superior Metal Joining with Unmatched Purity



















