Yes, argon can be used for cooling, but its application is highly specialized. While technically effective as a cryogenic fluid, it is most often chosen for its chemical inertness in situations where more common coolants like nitrogen could react with the materials being cooled.
The core reason to use argon for cooling is not its thermal efficiency, but its status as a noble gas. It is the coolant of choice only when the absolute prevention of chemical reactions is more critical than cooling performance or cost.

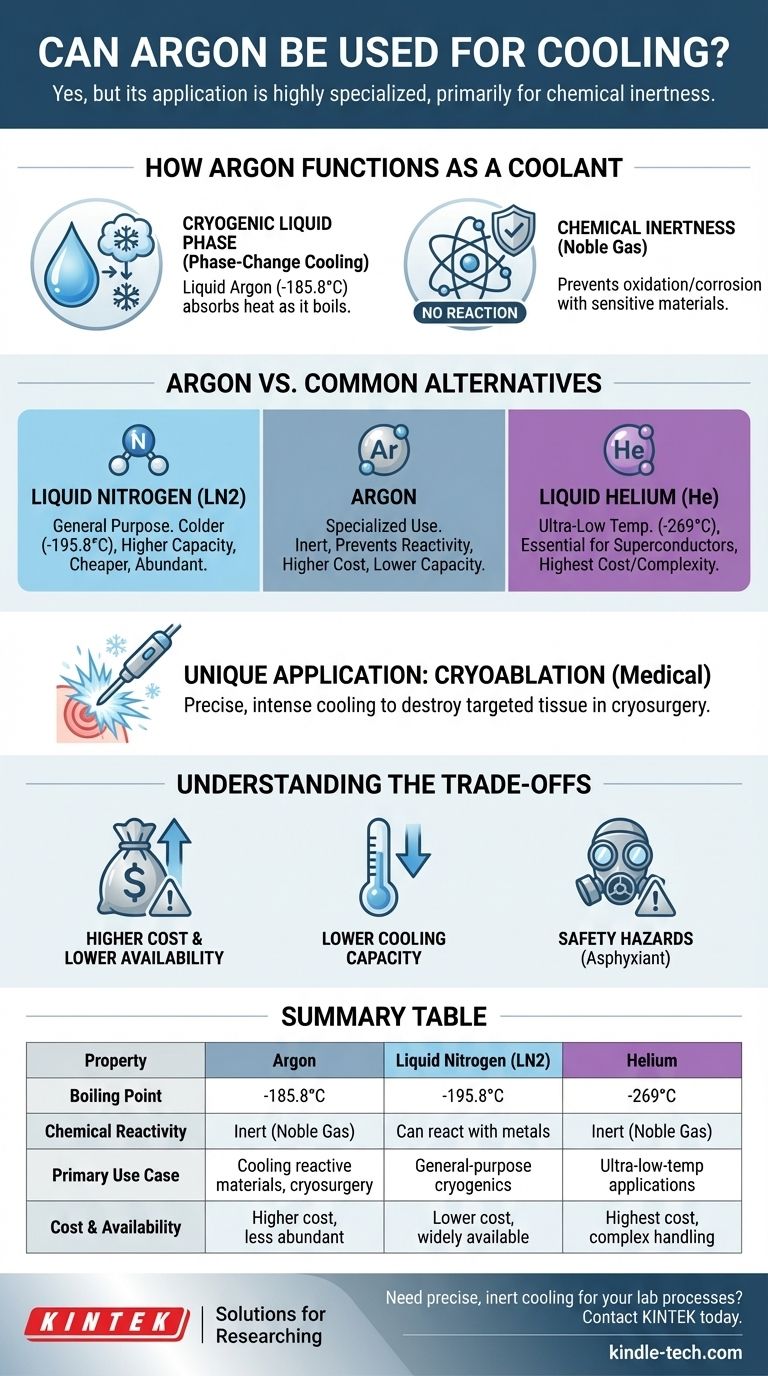
How Argon Functions as a Coolant
Argon's ability to cool stems from its physical properties, primarily its low boiling point and its nature as an inert gas. These two factors define its role in thermal management.
Cryogenic Liquid Phase
Like nitrogen, argon can be cooled and compressed into a liquid state. Liquid argon has a boiling point of -185.8°C (-302.5°F).
When this extremely cold liquid comes into contact with a warmer object, it absorbs a large amount of thermal energy as it boils back into a gas, a process known as phase-change cooling. This is the primary mechanism for its cooling effect.
Chemical Inertness
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically non-reactive under almost all conditions. It will not oxidize, corrode, or form compounds with the materials it touches.
This property is argon's most significant advantage over other coolants, especially nitrogen, which can form unwanted nitrides with certain metals at high temperatures.
Gaseous Cooling
Even as a gas, argon can be used as a heat transfer fluid, similar to air. Chilled argon gas can be circulated over components to carry heat away.
However, its thermal conductivity and heat capacity as a gas are not exceptional, making this a less common application unless its inertness is simultaneously required for the environment.
Argon vs. Common Alternatives
Choosing a coolant involves comparing its properties, cost, and suitability for the specific task. Argon's profile makes it a niche player compared to more mainstream options.
Comparison with Liquid Nitrogen (LN2)
Liquid nitrogen is the workhorse of general-purpose cryogenics. It is colder (boiling point -195.8°C) and has a higher latent heat of vaporization, meaning it can absorb more heat per unit of mass.
Crucially, nitrogen is significantly cheaper and more abundant than argon, as it makes up ~78% of the atmosphere compared to argon's ~1%. Nitrogen is therefore the default choice unless a chemical reaction is a specific concern.
Comparison with Helium
For applications requiring even lower temperatures, liquid helium is used. With a boiling point of -269°C (-452°F), it is essential for cooling superconducting magnets and sensitive scientific instruments.
Helium is far more expensive and complex to handle than argon, placing it in a separate class of ultra-low-temperature cryogenics.
A Unique Medical Application: Cryoablation
One notable area where argon excels is in cryosurgery (cryoablation). In this procedure, thin needles are used to deliver pressurized argon gas to a target, like a tumor.
The rapid expansion of the gas (the Joule-Thomson effect) creates intense, localized cooling, freezing and destroying the targeted tissue. Its precise control and inert nature make it ideal for this medical use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, argon is not a universal solution. Its limitations are important to understand before considering it for any application.
Higher Cost and Lower Availability
Argon is produced by fractional distillation of liquid air. Because it is a much smaller component of the atmosphere than nitrogen, it is inherently more expensive to produce and less widely available.
Lower Cooling Capacity
Compared to liquid nitrogen, liquid argon has a lower heat capacity. This means you need more argon to remove the same amount of heat, which further increases the operational cost.
Safety and Handling
Like any cryogenic liquid or compressed gas, argon poses physical hazards. It is an asphyxiant that can displace oxygen in a confined space, leading to suffocation. Proper ventilation and handling protocols are non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting argon is a decision driven by specific constraints, not general-purpose cooling needs.
- If your primary focus is material integrity: Argon is the superior choice for cooling reactive metals (like titanium or certain steel alloys) during processing to prevent the formation of nitrides or oxides.
- If your primary focus is maximum cooling on a budget: Liquid nitrogen is almost always the correct answer due to its lower cost, better cooling capacity, and wide availability.
- If your primary focus is reaching the lowest possible temperatures: Liquid helium is the only viable option for applications like superconducting magnets or deep-space sensor arrays.
- If your primary focus is targeted medical tissue destruction: Argon-based cryoablation systems are a proven, specialized tool for this purpose.
Ultimately, argon serves as a powerful problem-solver when chemical purity is the most critical factor in a cooling process.
Summary Table:
| Property | Argon | Liquid Nitrogen (LN2) | Helium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boiling Point | -185.8°C | -195.8°C | -269°C |
| Chemical Reactivity | Inert (Noble Gas) | Can react with certain metals | Inert (Noble Gas) |
| Primary Use Case | Cooling reactive materials, cryosurgery | General-purpose cryogenics | Ultra-low-temperature applications (e.g., superconductors) |
| Cost & Availability | Higher cost, less abundant | Lower cost, widely available | Highest cost, complex handling |
Need precise, inert cooling for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering solutions tailored to handle reactive materials and specialized cooling needs. Our expertise ensures your experiments maintain chemical purity and achieve reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's unique requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- lab cryogenic grinding use liquid-nitrogen for pulverizing plastic raw materials and heat sensitive materials
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of controlled atmosphere? Preserve Freshness and Extend Shelf Life
- What is the function of a tube atmosphere furnace in MLM? Optimize Your CNT/Cu Composite Production
- Why is a high-purity hydrogen atmosphere furnace required for W-TiC pre-sintering? Achieve Pure Material Densification
- What function does a high-temperature atmosphere furnace serve in the activation of Aux/TiO2? Master Catalyst Precision
- How does the process control within a high-temperature oxidation furnace enhance wear resistance of Zr-Nb implants?
- What are the primary functions of a nitriding furnace? Achieve Precision Surface Hardening with Advanced Thermal Control
- How does a heating furnace with a hydrogen control system improve deoxidation efficiency? (HAMR Process Explained)
- How do atmosphere or vacuum furnaces protect sulfide electrolytes? Key Insights for Safe & High-Performance Synthesis



















