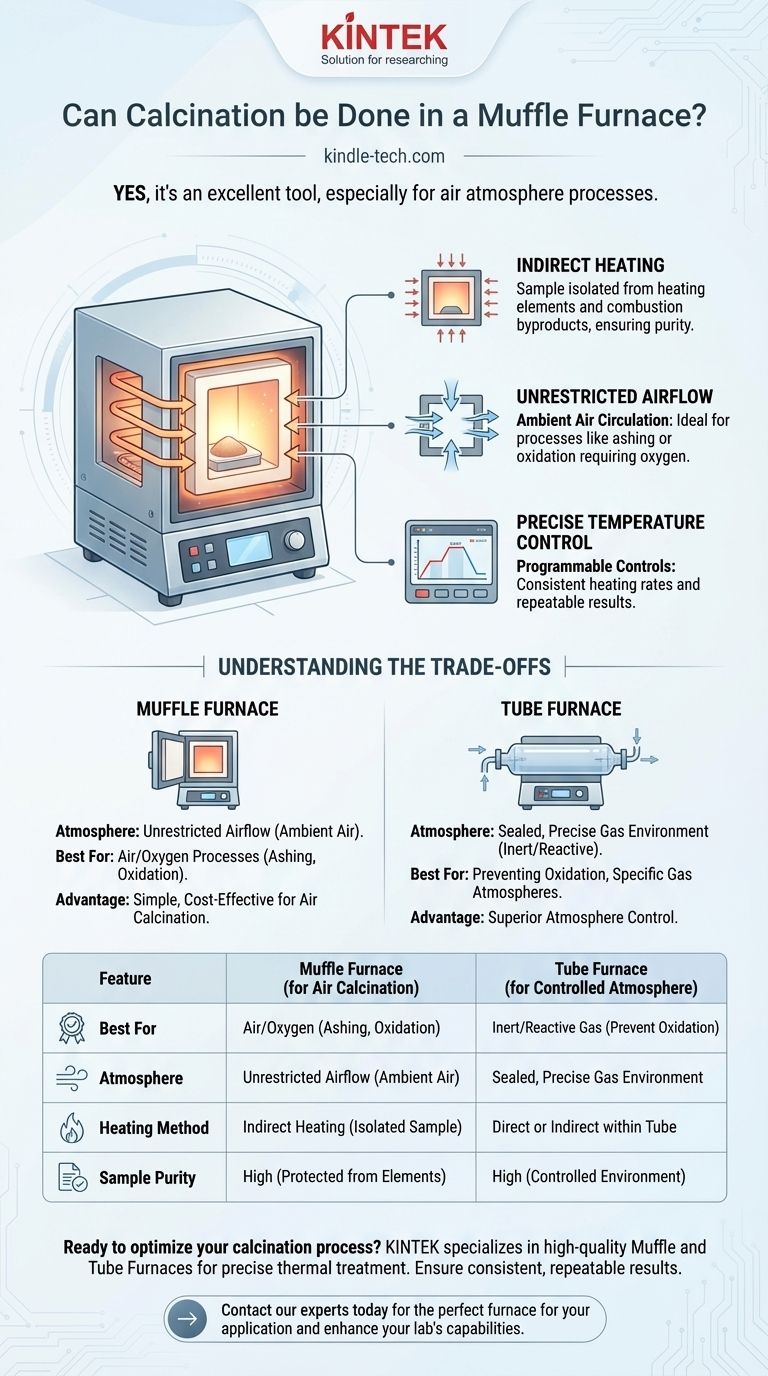
Yes, a muffle furnace is an excellent and common tool for calcination. Its design is particularly well-suited for processes that require heating a sample in the presence of air, as the chamber allows for free air circulation while protecting the sample from direct contact with the heating elements.
The key consideration is atmosphere. A muffle furnace is the standard choice for calcination in an air atmosphere, but if your process requires a specific or inert gas environment, a tube furnace is the superior instrument.
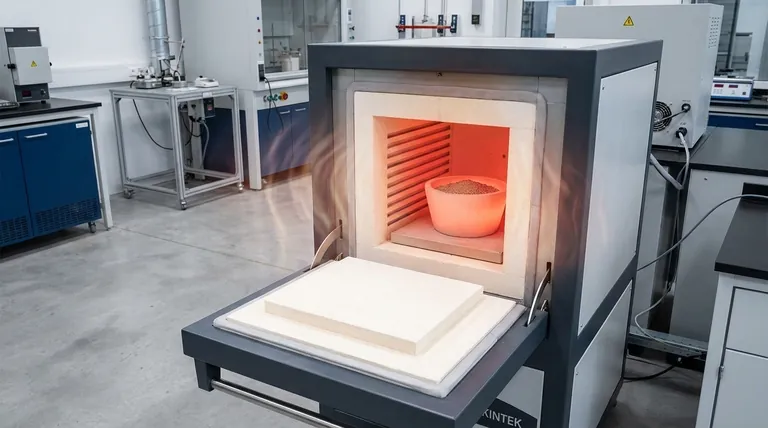

What Makes a Muffle Furnace Suited for Calcination?
Calcination is a thermal treatment process used to bring about a chemical or physical change in a material, often by driving off volatile components. The design of a muffle furnace directly supports this goal in several key ways.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is the "muffle"—a separate chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic or fire-clay, that contains the sample.
The heating elements are outside this chamber. This indirect heating method ensures the sample is never contaminated by the byproducts of combustion or by direct contact with the heat source itself.
Unrestricted Airflow
For many calcination processes, such as ashing organic matter or oxidizing a compound, full contact with oxygen is critical.
The chamber of a typical muffle furnace is not sealed, which allows ambient air to circulate freely. This ensures that the reactions requiring air can proceed to completion.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern muffle furnaces offer programmable temperature controls. This allows you to set precise heating rates, dwell times at a target temperature, and controlled cooling ramps. This level of control is essential for achieving consistent and repeatable results in your calcination process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ideal for many applications, a muffle furnace is not a universal solution. Its primary strength—an open-air environment—is also its main limitation.
The Challenge of Atmosphere Control
The open design that makes a muffle furnace perfect for air calcination makes it highly ineffective for processes that require a controlled atmosphere.
It is difficult and inefficient to purge the large chamber of air and maintain a pure, inert (like nitrogen or argon) or reactive gas environment.
The Alternative: The Tube Furnace
When your process requires a specific gas atmosphere—for instance, to prevent the oxidation of your sample—a tube furnace is the correct choice.
A tube furnace uses a narrow tube to hold the sample, which can be easily sealed and purged with a precise gas. While it can also be used for air calcination, its strength lies in superior atmosphere control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines the right tool. Base your decision on the required atmospheric conditions for your material.
- If your primary focus is calcination in air (e.g., ashing a sample, burning off binders, or simple oxidation): The muffle furnace is the ideal, standard, and most cost-effective tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is calcination in an inert or specific gas atmosphere (e.g., to prevent oxidation): A tube furnace is required to achieve the necessary atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is purity and avoiding contamination from the heat source: The indirect heating mechanism of a muffle furnace makes it fundamentally superior to direct-fire furnaces.
Choosing the correct furnace is the first step toward a successful and repeatable thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace (for Air Calcination) | Tube Furnace (for Controlled Atmosphere) |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Processes requiring air/oxygen (e.g., ashing, oxidation) | Processes requiring inert/reactive gas (e.g., preventing oxidation) |
| Atmosphere | Unrestricted airflow (ambient air) | Sealed, precise gas environment |
| Heating Method | Indirect heating (sample is isolated) | Direct or indirect heating within a tube |
| Sample Purity | High (protected from heating elements) | High (controlled environment) |
Ready to optimize your calcination process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality muffle furnaces and tube furnaces designed for precise thermal treatment. Whether your lab needs reliable air-atmosphere calcination or advanced atmosphere control, our equipment ensures consistent, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific application and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace used in determination of? Precise Ash Content and Material Composition
- What is the role of muffle furnace in fluid mechanics? A Key Tool for Material Preparation
- What is the working principle of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What are the safety precautions for heat experiment? Essential Steps to Prevent Lab Burns and Accidents
- What precautions should you take while using a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe High-Temperature Processing in Your Lab



















