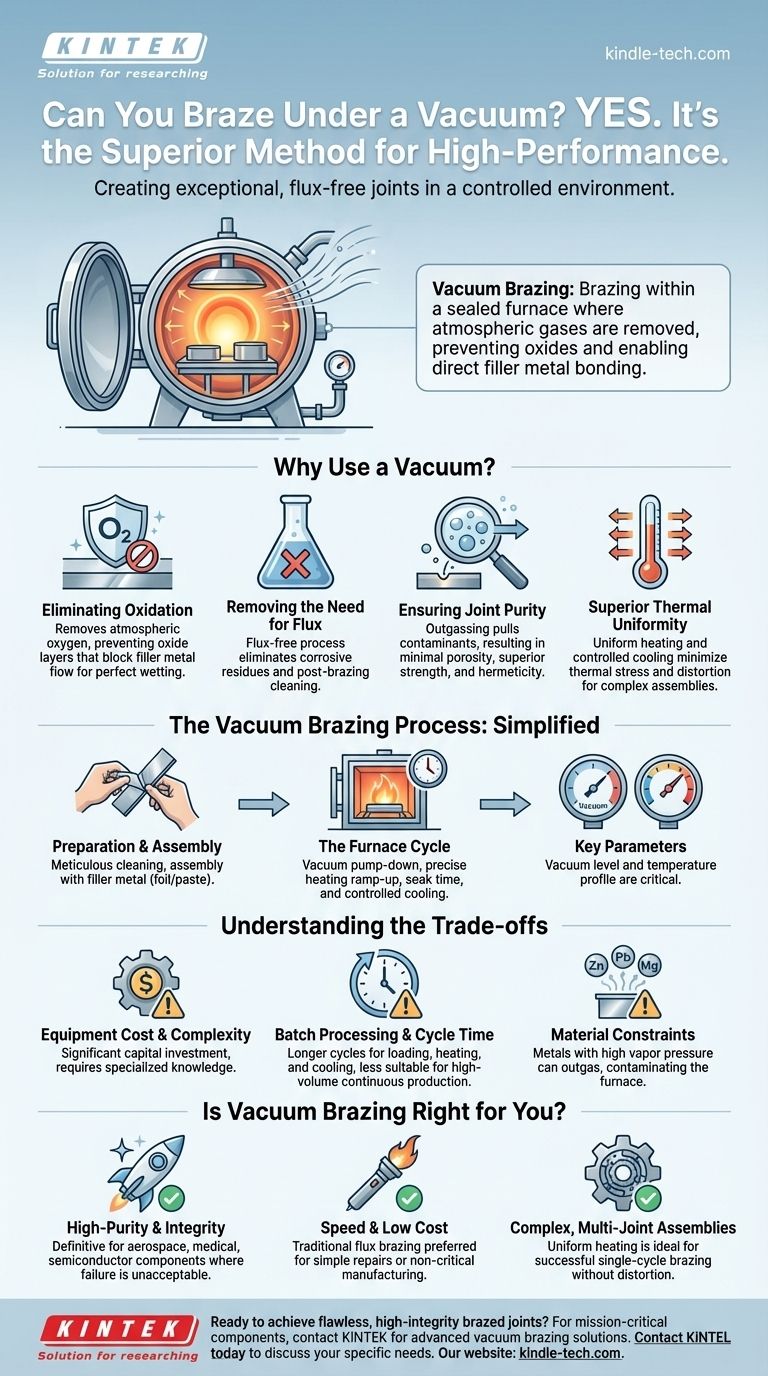
Yes, not only can you braze under a vacuum, it is the preferred and often superior method for high-performance applications. This process, known as vacuum brazing, takes place within a sealed furnace where atmospheric gases are removed. By eliminating oxygen and other reactive gases, it prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces, allowing the braze filler metal to bond directly and create exceptionally strong, clean, and flux-free joints.
The core purpose of using a vacuum for brazing is not merely to remove air, but to create a highly controlled, active environment that protects the assembly from contamination and ensures the highest possible joint integrity.

Why Use a Vacuum for Brazing?
Understanding the benefits of vacuum brazing reveals why it is essential for mission-critical components in industries like aerospace, medical, and defense. The vacuum is not a passive environment; it is an active part of the process.
Eliminating Oxidation
Atmospheric oxygen is the primary enemy of a good braze joint. It rapidly forms oxide layers on heated metal surfaces, which act as a barrier and prevent the filler metal from wetting and flowing properly.
By removing the vast majority of oxygen molecules, a vacuum furnace ensures the parent metals and filler alloy remain perfectly clean at brazing temperatures.
Removing the Need for Flux
In traditional brazing methods, a chemical flux is required to dissolve and displace oxides. However, flux can become trapped in the joint, leading to corrosion and potential failure points over time.
Vacuum brazing completely eliminates the need for flux. This results in a cleaner final assembly, removes the post-brazing cleaning step, and guarantees no corrosive flux residues are left behind.
Ensuring Joint Purity
The vacuum actively pulls volatile contaminants and trapped gases out of the base materials as they are heated, a process known as outgassing.
This purification effect results in a braze joint with minimal porosity and voids, significantly increasing its strength, ductility, and hermeticity (leak-tightness).
Superior Thermal Uniformity
As noted in process documentation, temperature uniformity is critical. A vacuum furnace excels at this, heating the entire assembly slowly and evenly through radiation.
This uniform heating and controlled cooling minimizes thermal stress and distortion, which is vital for complex, precision-machined assemblies.
The Vacuum Brazing Process: A Simplified View
While the equipment is complex, the core principles of the vacuum brazing cycle are straightforward and focused on control.
Preparation and Assembly
Parts must be meticulously cleaned and degreased before being assembled. The filler metal, often in the form of foil or paste, is placed at the joint interfaces.
The Furnace Cycle
The assembled component is loaded into the furnace, which is then sealed and pumped down to the required vacuum level. The furnace then executes a precise, pre-programmed heating cycle.
This involves ramping up to the brazing temperature, holding it for a specified time to ensure the filler metal flows completely throughout the joints, and then cooling down in a controlled manner.
Key Parameters
The two most important parameters are the vacuum level and the temperature profile. The required vacuum depends on the reactivity of the base metals. The temperature must be high enough to melt the filler alloy but low enough not to damage the parent materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum brazing is a powerful process, but it is not the solution for every situation. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. They are complex machines that require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance, making them far more expensive than a simple torch or induction setup.
Batch Processing and Cycle Time
Vacuum brazing is a batch process. Loading, pumping down, heating, soaking, and cooling can take several hours. This makes it less suitable for high-volume, continuous production compared to other automated methods.
Material Constraints
Certain materials are not suitable for vacuum brazing. Metals with high vapor pressures, such as zinc, lead, magnesium, or cadmium, can vaporize under a vacuum at brazing temperatures.
This "outgassing" of the alloying elements can contaminate the furnace interior and, more importantly, alter the composition and performance of both the base metal and the filler alloy.
Is Vacuum Brazing the Right Choice for Your Application?
Selecting the correct brazing method depends entirely on the requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is high-purity and structural integrity: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice for aerospace, medical implant, or semiconductor components where joint failure is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is speed and low cost for simple assemblies: Traditional torch or induction brazing with flux is far more practical and economical for repairs or non-critical manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, multi-joint assemblies without distortion: The uniform heating of a vacuum furnace is ideal, ensuring all joints braze successfully in a single, stress-free cycle.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum brazing is a decision to prioritize the quality and purity of the final joint above all other considerations.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters in Vacuum Brazing |
|---|---|
| Oxidation Prevention | Eliminates oxygen, preventing oxide layers that block filler metal flow. |
| Flux-Free Process | Creates clean joints with no corrosive residue, removing post-braze cleaning. |
| Joint Purity & Strength | Outgasses contaminants for minimal porosity and superior hermeticity. |
| Thermal Uniformity | Ensures even heating to minimize stress and distortion in complex assemblies. |
| Material Constraints | Not suitable for metals with high vapor pressure (e.g., zinc, cadmium). |
Ready to achieve flawless, high-integrity brazed joints?
For mission-critical components in aerospace, medical, or defense, the quality of your brazing process is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum brazing systems designed for maximum purity and reliability.
Let our experts help you determine if vacuum brazing is the right choice for your application. We provide the equipment and support to ensure your most demanding projects succeed.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your specific laboratory or production needs and discover the benefits of our specialized lab equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a sintering furnace for metal? The Key to High-Performance Powder Metallurgy
- What is the heat treatment of metals? Unlock Superior Strength and Durability
- How does heat affect tensile strength? Understand the Strength-Ductility Trade-Off
- What are the units for vacuum pressure? Torr, mbar, and Pascal Explained
- How does a vacuum diffusion bonding furnace contribute to titanium laminates? Precision for Near-Alpha Alloys
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of sintering? A Guide to High-Performance Powder Processing
- Why do industrial high-temperature diffusion furnaces require precise temperature control? Essential for Engine Blades
- How does physical vapor deposition work? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Coating



















