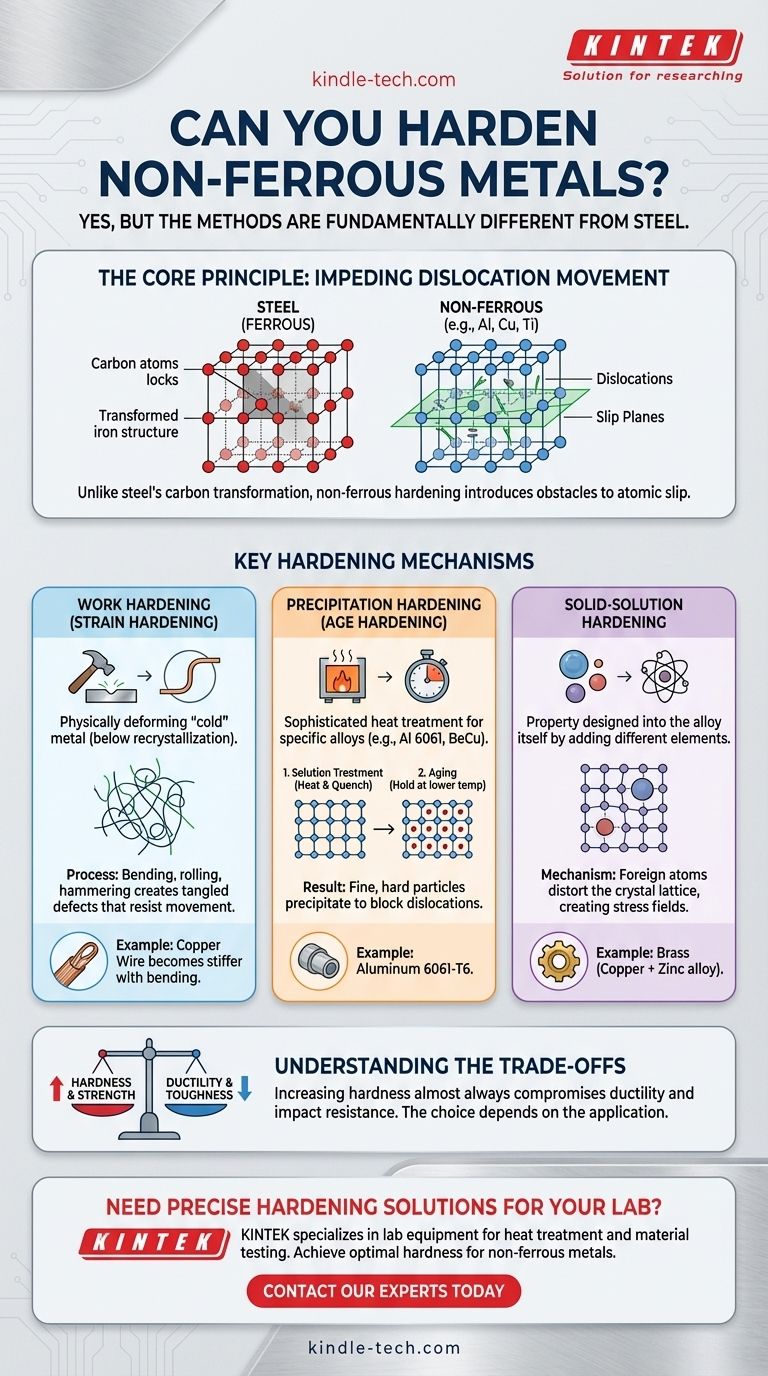
Yes, you can absolutely harden non-ferrous metals, but the methods are fundamentally different from the familiar heat-and-quench process used for steel. While steel hardening relies on changing its carbon-based crystal structure, hardening non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, or titanium is about introducing controlled disruptions into their metallic lattice to resist deformation.
The core principle for hardening any non-ferrous metal is impeding the movement of internal defects, known as dislocations. Unlike steel, this is achieved not by a carbon-based transformation, but through mechanical deformation, controlled precipitation of alloying elements, or strategic alloying from the start.

Why Hardening Non-Ferrous Metals Is Different
The hardening process for carbon steel involves heating it until its crystal structure changes (to austenite), then rapidly cooling (quenching) it to trap this structure in a hard, brittle state (martensite). This mechanism is unique to steel and other ferrous alloys.
Non-ferrous metals lack this specific transformative property. Instead, their hardness is governed by the ease with which atomic planes can slip past one another. To harden them, you must introduce obstacles that make this slipping more difficult.
Key Hardening Mechanisms Explained
There are three primary methods for hardening non-ferrous metals. The effectiveness of each depends entirely on the specific alloy you are working with.
Work Hardening (Strain Hardening)
This is the most direct method: hardening a metal by physically deforming it at a temperature below its recrystallization point (i.e., when it's "cold").
Processes like bending, rolling, drawing, or hammering cause microscopic defects (dislocations) within the metal's crystal structure to multiply and tangle. This tangled structure resists further movement, making the material harder and stronger.
A common example is a copper wire. As you bend it back and forth, it becomes progressively stiffer and more difficult to bend until it eventually fractures.
Precipitation Hardening (Age Hardening)
This is a sophisticated heat treatment used on specific alloys, such as 2000, 6000, and 7000 series aluminum, beryllium copper, and some titanium alloys.
It's a two-step process:
- Solution Treatment: The metal is heated to a high temperature to dissolve the alloying elements into a uniform solid solution, like dissolving sugar in hot water. It's then rapidly cooled to trap this state.
- Aging: The metal is then held at a lower temperature for an extended period. During this time, the dissolved alloying elements precipitate out as extremely small, hard, and uniformly dispersed particles. These particles act as powerful roadblocks, obstructing dislocation movement and dramatically increasing strength and hardness.
The "T" designations in aluminum alloys, like 6061-T6, signify that the material has been solution heat-treated and then artificially aged.
Solid-Solution Hardening
This type of hardening is not a process you perform on a finished part, but rather a property designed into the alloy itself.
It involves adding atoms of a different element to the base metal. These foreign atoms, being a different size, distort the regular crystal lattice. This distortion creates internal stress fields that make it more difficult for dislocations to move, thereby increasing the metal's inherent hardness and strength.
A classic example is brass, which is an alloy of copper and zinc. The zinc atoms disrupt copper's crystal lattice, making brass significantly harder and stronger than pure copper.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Increasing hardness is never free; it almost always involves a compromise with other material properties.
The Cost of Work Hardening
The primary trade-off of work hardening is a significant loss of ductility. As the material gets harder, it becomes more brittle and less capable of being formed or bent without cracking. This is why you cannot infinitely harden a material by bending it.
The Complexity of Precipitation Hardening
This process requires precise control over temperature and time. Over-aging, or holding the metal at the aging temperature for too long, can cause the precipitates to grow too large and lose their hardening effect, actually making the material softer. Furthermore, this method is only applicable to specific "heat-treatable" alloys.
The Inevitable Hardness-Ductility Balance
For nearly all methods, there is an inverse relationship between hardness and ductility/toughness. A harder material is often more susceptible to fracture under sudden impact. Your choice of hardening method must align with the part's final application and required performance characteristics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach should be dictated by the material you have and the properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is strengthening a part after it has been shaped: Investigate if your alloy is precipitation-hardenable (e.g., aluminum 6061, 7075). This offers the most significant strength increase.
- If your primary focus is hardening through a mechanical process: Use work hardening (cold working), but be aware that you will be trading away ductility for strength.
- If your primary focus is choosing a strong material from the start: Select a solid-solution hardened alloy or a material that is already supplied in a precipitation-hardened condition (like aluminum 6061-T6).
Understanding these distinct hardening mechanisms empowers you to select and treat non-ferrous metals with precision for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Hardening Method | Key Process | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Work Hardening | Cold deformation (bending, rolling) | Copper wire, sheet metal |
| Precipitation Hardening | Heat treatment & aging | Aluminum 6061-T6, beryllium copper |
| Solid-Solution Hardening | Alloying with different elements | Brass (copper-zinc alloys) |
Need precise hardening solutions for your lab materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for heat treatment and material testing. Our expertise helps you achieve optimal hardness and performance for non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, and titanium. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the source of energy for pyrolysis? From External Heat to Self-Sustaining Systems
- Why must carbon steel coupons be treated with an ultrasonic cleaner? Ensure Precise Corrosion Rate Measurement
- What is gold coating SEM for? Prevent Charging & Get Clearer SEM Images
- What is the primary function of laboratory ovens in biomass moisture determination? Ensure Accurate Energy Calibration
- What is the importance of the sintering process in manufacturing? Unlocking Precision and Material Durability
- What are the disadvantages of plate and frame filter press? High Labor Costs and Inefficient Batch Processing
- What is direct current pulse magnetron sputtering? Achieve Superior Thin Film Deposition for Insulating Materials
- What is the heating rate for slow and fast pyrolysis? Control Your Biomass Conversion Outcome



















