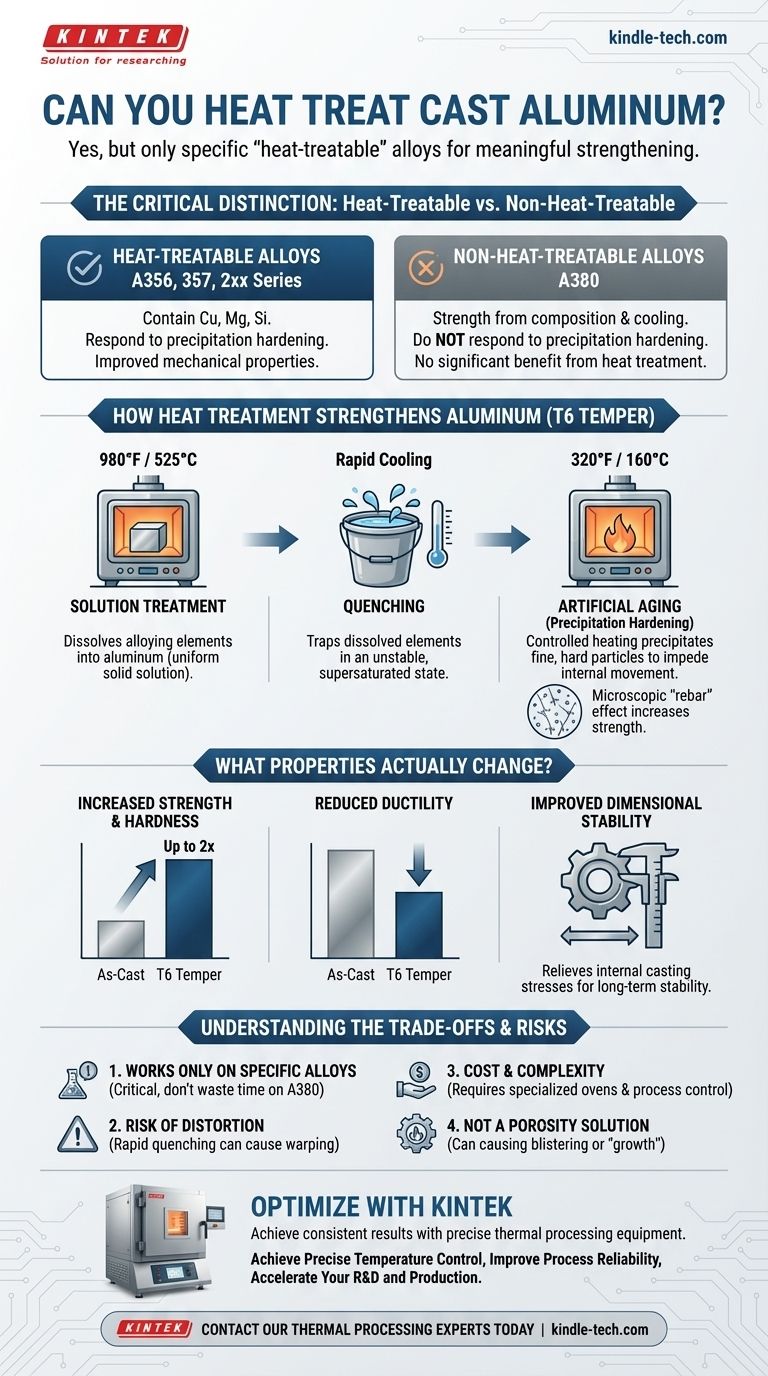
Yes, but only specific "heat-treatable" aluminum alloys can be meaningfully strengthened through this process. While many aluminum castings are used in their 'as-cast' state, certain alloys are specifically designed to have their mechanical properties—like strength and hardness—dramatically improved by a precise thermal treatment. Applying this process to a 'non-heat-treatable' alloy will yield no significant benefit.
The ability to heat treat cast aluminum is not universal; it is a metallurgical capability engineered into specific alloys. The process works by manipulating the alloy's microstructure to create internal strengthening, a technique known as precipitation hardening.

How Heat Treatment Strengthens Aluminum
The most common and effective heat treatment for aluminum castings is the T6 temper. This is a three-stage process that fundamentally changes the material's internal structure to increase its strength and hardness.
The Critical Distinction: Heat-Treatable vs. Non-Heat-Treatable
The key difference lies in the alloying elements. Heat-treatable alloys contain elements like copper, magnesium, and silicon that can be dissolved into the aluminum and later precipitated out.
Common heat-treatable casting alloys include A356, 357, and the 2xx series.
Non-heat-treatable alloys, like the very common die-casting alloy A380, derive their strength primarily from their base chemical composition and the rapid cooling of the casting process. They lack the right elements to respond to precipitation hardening.
The Three Stages of a T6 Temper
1. Solution Treatment The casting is heated to a high temperature (around 980°F / 525°C) and held there for several hours. This dissolves the alloying elements into the aluminum, creating a uniform solid solution, much like dissolving sugar in hot water.
2. Quenching Immediately after solution treatment, the casting is rapidly cooled, typically in water. This "freezes" the dissolved alloying elements in place, creating an unstable, supersaturated state. This is analogous to flash-cooling the sugar water before the sugar has a chance to crystallize.
3. Artificial Aging (Precipitation Hardening) The casting is then reheated to a lower temperature (around 320°F / 160°C) and held for several hours. This controlled heating gives the trapped alloying elements just enough energy to precipitate out as extremely fine, hard, and widely dispersed particles throughout the material's structure.
These tiny particles act like microscopic rebar, impeding the internal slip planes (dislocations) within the metal's crystal structure. This resistance to internal movement is what makes the final part significantly stronger and harder.
What Properties Actually Change?
Heat treatment is not a magic bullet; it is a tool for achieving specific engineering outcomes.
Increased Strength and Hardness
This is the primary goal. A T6 temper can double the tensile and yield strength of an alloy like A356 compared to its 'as-cast' state. Hardness increases proportionally, which improves wear resistance.
Reduced Ductility
The trade-off for increased strength is a decrease in ductility. A harder, stronger part is typically more brittle and will stretch or deform less before fracturing.
Improved Dimensional Stability
The heat treatment process, particularly the aging step, helps to relieve internal stresses that are locked into the part during the casting process. This results in a more dimensionally stable component over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, heat treatment is a deliberate engineering choice with clear consequences.
It Only Works on Specific Alloys
This cannot be overstated. Attempting to apply a T6 temper to a non-heat-treatable alloy like A380 is a waste of time and money. It will not result in significant mechanical property improvement.
The Risk of Distortion
The rapid temperature changes involved in quenching can cause significant internal stress, leading to warping or distortion. Complex or thin-walled parts are especially vulnerable and may require specialized fixtures to hold their shape.
Cost and Process Complexity
Heat treatment is an additional manufacturing step that requires specialized, calibrated ovens and careful process control. This adds significant cost and lead time to the production of a component.
Not a Solution for Porosity
Heat treatment does not fix underlying casting defects. In fact, the high temperatures of solution treatment can cause trapped gas porosity to expand, a phenomenon known as "growth" or blistering, potentially ruining the part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right alloy and thermal condition is critical to meeting your design goals without incurring unnecessary costs.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: Specify a heat-treatable alloy like A356 or A357 and call for a T6 temper, but plan for potential part distortion.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a general-purpose part: Select a common non-heat-treatable alloy like A380 and use it in the 'as-cast' (F) condition.
- If your primary focus is stability and stress relief in a harsh environment: For a heat-treatable alloy, consider an "over-aged" temper like T7, which trades a small amount of peak strength for better stress corrosion resistance.
- If you only need to relieve casting stress without changing properties: A simple, low-temperature thermal stress relief (anneal) may be a more appropriate and less costly process.
By understanding that heat treatment is a specific metallurgical tool, you can make an informed decision that ensures your component achieves its required performance efficiently.
Summary Table:
| Heat-Treatable Alloys | Non-Heat-Treatable Alloys | Key Property Changes (T6 Temper) |
|---|---|---|
| A356, A357, 2xx Series | A380 | Strength & Hardness: Dramatically Increased |
| Ductility: Decreased | ||
| Dimensional Stability: Improved |
Optimize Your Cast Aluminum Components with KINTEK
Understanding the complexities of heat treatment is the first step. Achieving consistent, high-quality results requires precise thermal processing equipment. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and ovens designed for the exacting demands of aluminum heat treatment processes like the T6 temper.
Our solutions help you:
- Achieve Precise Temperature Control: Ensure uniform heating during solution treatment and accurate aging temperatures for optimal material properties.
- Improve Process Reliability: Minimize distortion and defects with equipment built for repeatable performance.
- Accelerate Your R&D and Production: From prototyping to full-scale manufacturing, get the right equipment for your specific alloy and application needs.
Whether you are developing a new high-strength component or optimizing an existing process, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment is your partner in success.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover the right furnace solution for your cast aluminum heat treatment needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering



















