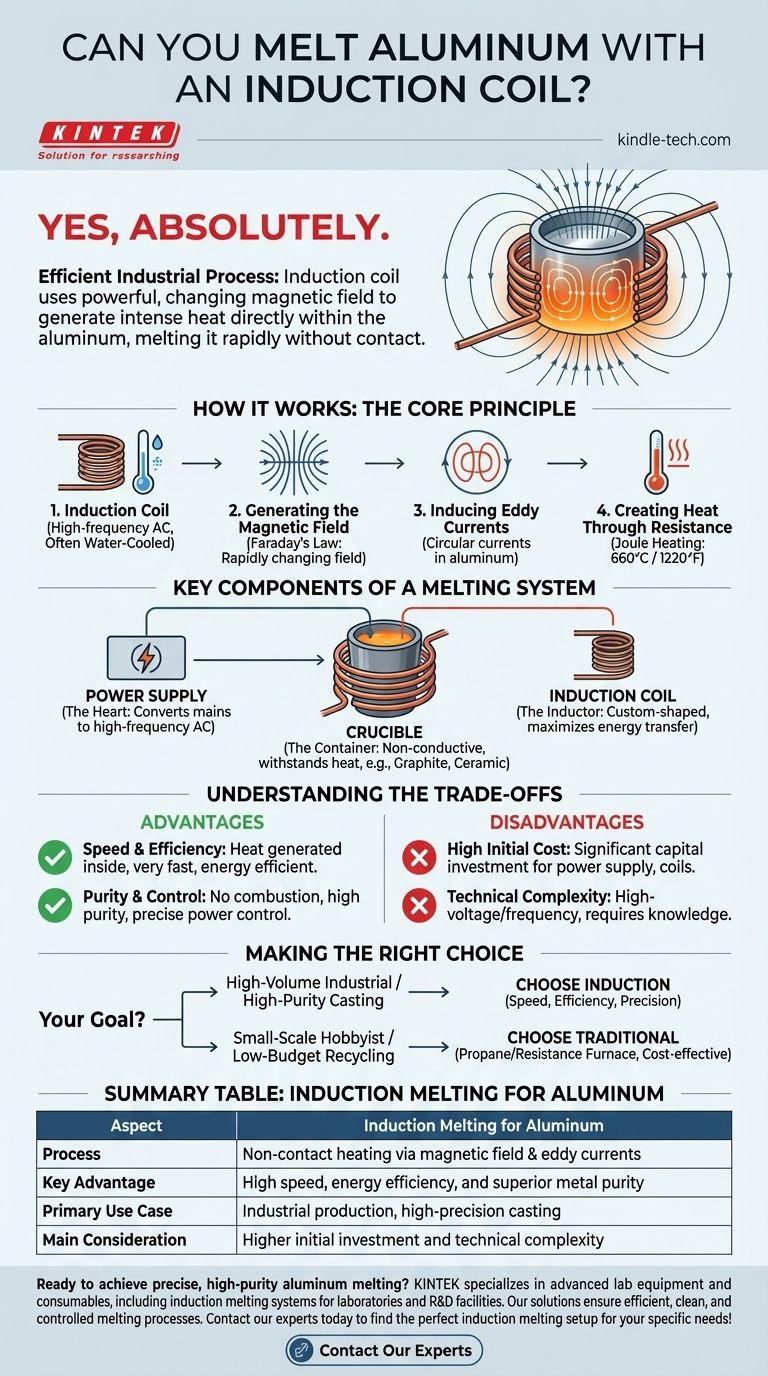
Yes, absolutely. Melting aluminum with an induction coil is not only possible but is a common and highly efficient industrial process. The system uses a powerful, changing magnetic field to generate intense heat directly within the aluminum itself, causing it to melt rapidly without any physical contact from the heat source.
The core principle is straightforward: an induction coil creates a magnetic field that induces strong electrical currents (eddy currents) inside the aluminum. The metal's own electrical resistance causes these currents to generate immense heat, leading to a clean and controlled melt.

How Induction Melting Works for Aluminum
Induction heating is a non-contact process. The coil itself does not get hot; it is the workpiece—in this case, the aluminum—that generates its own heat. The process relies on fundamental principles of electromagnetism.
The Role of the Induction Coil
An induction coil is typically made from hollow copper tubing. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil. For higher-power systems, water is often circulated through the tubing to keep the coil itself cool.
Generating the Magnetic Field
According to Faraday's Law of Induction, any electric current produces a magnetic field. Because the current in the coil is alternating and switching direction thousands of times per second, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When you place an electrical conductor like aluminum inside this changing magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Creating Heat Through Resistance
Aluminum, like any conductor, has electrical resistance. As the powerful eddy currents flow through the aluminum, they encounter this resistance and generate immense heat through a process called Joule heating. This heat raises the temperature of the aluminum to its melting point (approximately 660°C or 1220°F).
Key Components of a Melting System
A functional induction melting setup requires more than just a coil. Each component plays a critical role in the system's efficiency and safety.
The Power Supply
This is the heart of the system. It takes standard mains electricity and converts it into the high-frequency, high-current AC power required to drive the induction coil effectively.
The Crucible
The crucible is the container that holds the aluminum. It must be made from a material that is non-conductive and can withstand extreme temperatures, such as graphite or a specialized ceramic composite. If the crucible were conductive, the induction coil would heat it instead of the metal inside.
The Induction Coil
The coil, or inductor, is custom-shaped to couple effectively with the crucible and its contents. Its design is critical for maximizing the energy transfer from the coil to the aluminum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction melting is not the right solution for every application. Understanding its advantages and disadvantages is key to making an informed decision.
Advantage: Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly within the aluminum, the melting process is extremely fast and energy-efficient. There is very little wasted energy compared to a traditional furnace where heat must first saturate the furnace walls and then radiate into the metal.
Advantage: Purity and Control
Since there is no flame or combustion, there are no byproducts to contaminate the aluminum melt. This results in a much higher purity final product. Power levels can also be controlled with incredible precision, allowing for consistent results.
Disadvantage: High Initial Cost
Professional-grade induction heating systems represent a significant capital investment. The cost of the power supply, custom coils, and cooling systems is considerably higher than that of a simple gas-fired furnace.
Disadvantage: Technical Complexity
These systems involve high-voltage and high-frequency electricity, requiring a greater degree of technical knowledge to operate and maintain safely. They are less forgiving of improper use than a basic forge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether induction is the best method depends entirely on your specific requirements for cost, volume, and quality.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production or high-purity casting: Induction is the superior choice due to its speed, efficiency, and precise control.
- If your primary focus is small-scale hobbyist projects or low-budget metal recycling: A traditional propane or resistance furnace is often more practical and cost-effective.
Ultimately, induction offers unparalleled performance for melting aluminum when precision, speed, and purity are the most critical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Melting for Aluminum |
|---|---|
| Process | Non-contact heating via magnetic field & eddy currents |
| Key Advantage | High speed, energy efficiency, and superior metal purity |
| Primary Use Case | Industrial production, high-precision casting |
| Main Consideration | Higher initial investment and technical complexity |
Ready to achieve precise, high-purity aluminum melting? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including induction melting systems for laboratories and R&D facilities. Our solutions ensure efficient, clean, and controlled melting processes. Contact our experts today to find the perfect induction melting setup for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















