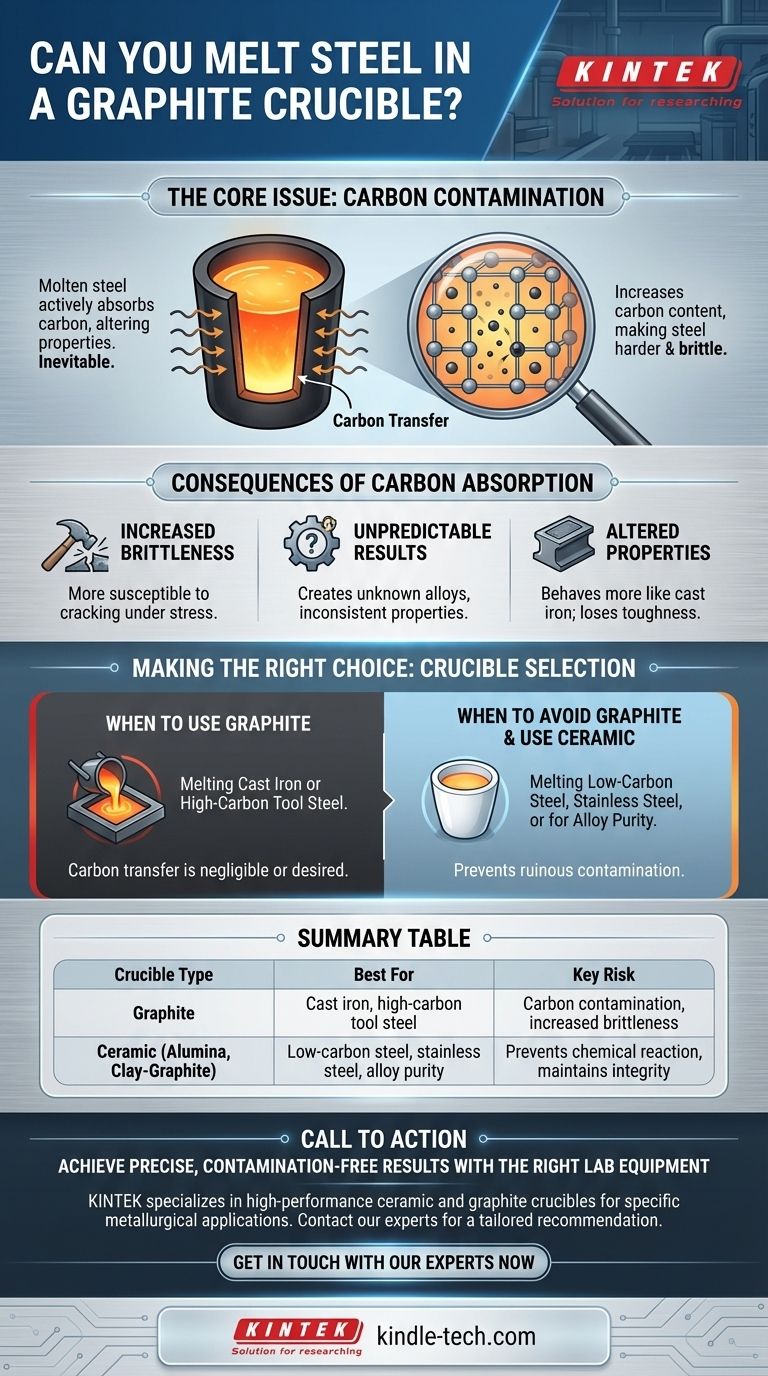
Yes, but it is a decision with significant consequences. You can physically melt steel in a pure graphite crucible due to graphite's extremely high melting point. However, molten steel will actively absorb carbon directly from the crucible walls, fundamentally altering the properties of your final metal.
The core issue is not thermal failure but chemical contamination. Using a graphite crucible is a metallurgical choice, not just a practical one, as it will increase the steel's carbon content, making it harder and more brittle.

The Fundamental Interaction: Carbon and Iron
Graphite is a common material for high-temperature applications, but its relationship with molten iron (the primary component of steel) is unique and must be understood.
Why Graphite is a Tempting Choice
Graphite crucibles can withstand temperatures far exceeding the melting point of steel (around 2500°F or 1370°C). They are also highly resistant to thermal shock, meaning they are less likely to crack from rapid temperature changes.
The Inevitable Carbon Transfer
Molten iron is an excellent solvent for carbon. When steel is held at melting temperatures inside a graphite crucible, carbon atoms will naturally dissolve from the crucible and enter the molten metal. This process is unavoidable.
The Role of Temperature and Time
The rate of this carbon absorption is not constant. The higher the temperature and the longer the steel remains molten, the more carbon the steel will absorb from the crucible.
The Consequences of Carbon Contamination
Uncontrolled carbon absorption is rarely a good thing. It changes the steel from its original specification into a new, often unpredictable, alloy.
Increased Hardness and Brittleness
The primary effect of adding carbon to steel is an increase in hardness and a decrease in ductility. The resulting steel becomes much more brittle and susceptible to cracking under stress, which is often a critical failure point.
Altered Mechanical Properties
This change makes the steel behave more like cast iron. While extremely hard, it loses the toughness and workability that might have been the reason for choosing that specific steel alloy in the first place.
Unpredictable Results
Without precise control and measurement, you are essentially creating an unknown alloy. This lack of control makes it impossible to achieve consistent, reliable results for any application that demands specific mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
Choosing a crucible is about matching the material to the metallurgical goal. Graphite is not inherently "bad," but it is often incorrect for melting steel.
When Graphite is Acceptable
A graphite crucible is a perfectly valid choice if your goal is to melt cast iron or to intentionally create a very high-carbon tool steel. In these cases, the carbon transfer is either negligible (for cast iron, which is already saturated) or desired.
When to Avoid Graphite at All Costs
You must avoid pure graphite crucibles when melting low-carbon steels, stainless steels, or any alloy where maintaining the original, precise carbon content is critical. The contamination will ruin the properties of these metals, particularly the corrosion resistance of stainless steel.
The Professional Standard: Ceramic Crucibles
For melting most steels, the industry standard is to use a ceramic crucible. Materials like clay-graphite (which is mostly clay with some graphite flakes), alumina, magnesia, or zirconia are effectively inert. They do not react with the molten steel, ensuring the alloy's chemistry remains unchanged.
Making the Right Choice for Your Melt
Your choice of crucible is a foundational step that dictates the quality and properties of your final cast part.
- If your primary focus is to melt cast iron or create high-carbon steel: A graphite crucible is an effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is to melt low-carbon steel, stainless steel, or any alloy requiring chemical purity: You must use a ceramic-based crucible (like clay-graphite or alumina) to prevent ruinous contamination.
- If you are unsure of your alloy's sensitivity to carbon: Always default to a ceramic crucible to guarantee the integrity of your material.
Selecting the correct crucible is the foundation for achieving predictable and successful results in your foundry work.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Type | Best For | Key Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Cast iron, high-carbon tool steel | Carbon contamination, increased brittleness |
| Ceramic (e.g., alumina, clay-graphite) | Low-carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy purity | Prevents chemical reaction, maintains alloy integrity |
Achieve precise, contamination-free results with the right lab equipment.
Melting the correct alloy is critical for your project's success. Using the wrong crucible can lead to failed casts and inconsistent material properties.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of ceramic and graphite crucibles designed for specific metallurgical applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible to maintain your steel's chemical purity and ensure reliable, repeatable outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and get a recommendation tailored to your lab's requirements.
Get in touch with our experts now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- Does a graphite crucible need to be seasoned? The Critical First-Use Safety Guide
- What are five applications of soldering? From Electronics to Art, Master Material Joining
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- What is the difference between VAR and ESR? A Guide to Understanding Tail Risk in Financial Modeling



















