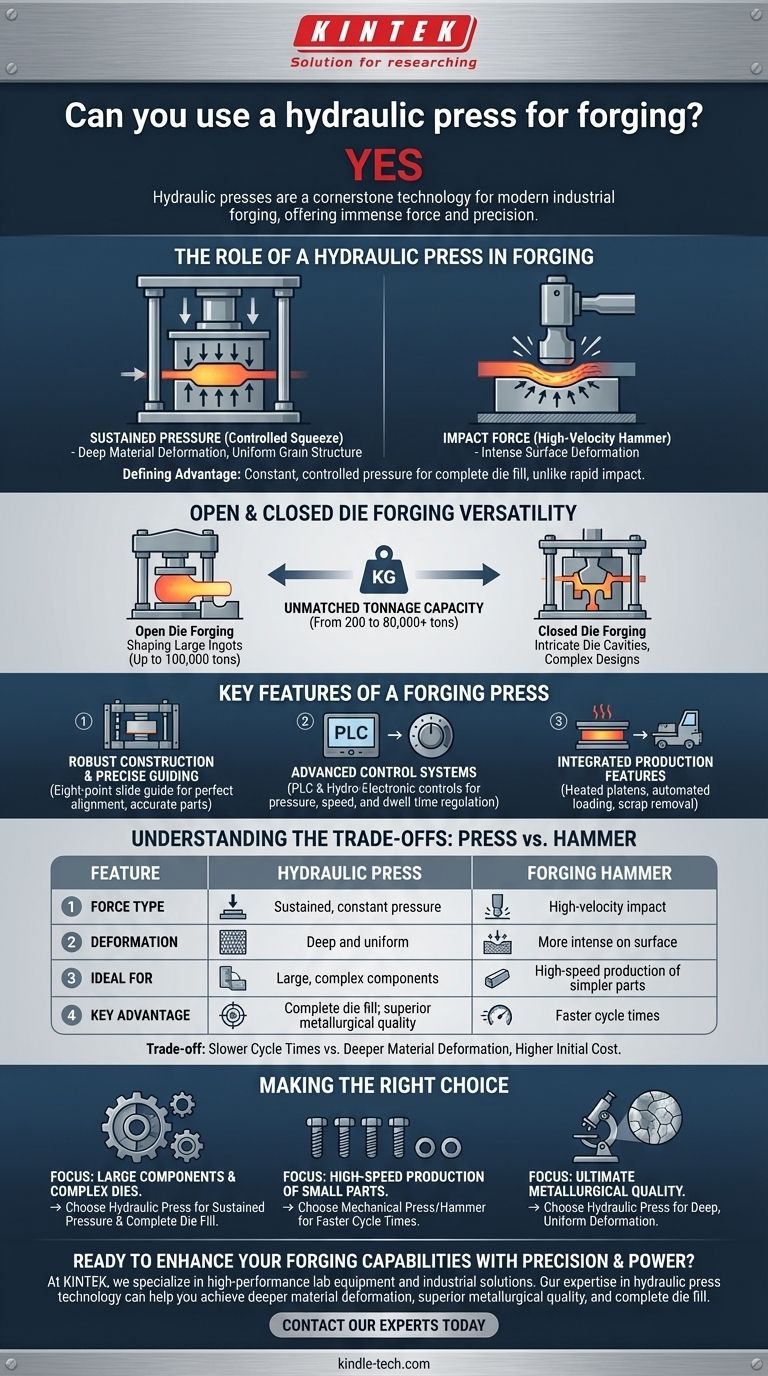
Yes, hydraulic presses are a cornerstone technology for modern industrial forging. They are not only capable of forging but are often the preferred equipment for applications requiring immense force, deep material deformation, and high precision, particularly for large or complex components.
The defining advantage of a hydraulic press in forging is its ability to apply a constant, controlled pressure throughout the entire stroke. This sustained "squeeze" allows the metal to flow completely into intricate die cavities, a feat difficult to achieve with the rapid impact of a forging hammer.

The Role of a Hydraulic Press in Forging
To understand why a hydraulic press is so effective, we must look beyond the simple application of force and examine how that force is delivered.
Sustained Pressure vs. Impact Force
The fundamental difference between a hydraulic press and a mechanical hammer is the method of force application. A hammer delivers a high-velocity impact, deforming the metal's surface layers most intensely.
In contrast, a hydraulic press delivers a continuous, controlled squeeze. This sustained pressure penetrates deep into the workpiece, ensuring a more uniform deformation and grain structure throughout the material.
Open and Closed Die Forging
Hydraulic presses are highly versatile and are used for both major types of forging.
In open die forging, massive presses with capacities up to 100,000 tons are used to shape large ingots. The press slowly squeezes the workpiece between simple dies, gradually working it into the desired shape.
For closed (or impression) die forging, the press forces the hot metal to flow and fill a precisely machined die cavity. The press's ability to maintain full pressure allows the material ample time to conform to complex designs.
Unmatched Tonnage Capacity
Hydraulic systems are capable of generating immense pressure, making them the only practical choice for extremely large forgings. Forging presses commonly range from 200 tons for smaller work to over 80,000 tons for massive industrial components.
Key Features of a Forging Press
A hydraulic press designed for forging is more than just a powerful cylinder; it is a highly engineered system built for precision and durability in harsh environments.
Robust Construction and Precise Guiding
To handle extreme forces without deflection, these presses feature highly robust construction. Many utilize an eight-point slide guide system to ensure the moving platen remains perfectly parallel, which is critical for die alignment and producing accurate parts.
Advanced Control Systems
Modern forging presses use PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and advanced hydro-electronic controls. This allows for precise regulation of pressure, speed, and dwell time, giving engineers fine-tuned control over the final product's quality and metallurgical properties.
Integrated Production Features
Custom forging presses often include features for a complete manufacturing process, such as heated and cooled platens for temperature control, automated die loading systems, and integrated scrap removal.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Press vs. Hammer
Choosing between a press and a hammer involves clear trade-offs tied directly to the forging process itself.
Slower Cycle Times
The primary trade-off of a hydraulic press is its speed. The process of building and releasing hydraulic pressure is inherently slower than the rapid-fire action of a mechanical hammer, resulting in a lower production rate in parts per minute.
Deeper Material Deformation
The key advantage of a press is its ability to work the material more thoroughly. The slow, sustained squeeze provides both force and time, ensuring even the center of a large billet is deformed, leading to a more uniform and refined internal grain structure.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Due to their immense size, sophisticated control systems, and precision engineering, large-scale hydraulic forging presses represent a significant capital investment compared to simpler forging hammers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a hydraulic press is determined by the specific requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is large components or complex dies: A hydraulic press is the ideal choice due to its sustained pressure, which ensures complete die fill and uniform material properties.
- If your primary focus is high-speed production of smaller, simpler parts: A mechanical press or a power hammer may be a more cost-effective solution due to their faster cycle times.
- If your primary focus is ultimate metallurgical quality: The deep, uniform deformation from a hydraulic press offers superior control over the material's internal grain structure.
Ultimately, selecting a hydraulic press for forging is a strategic decision to prioritize power, control, and precision for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hydraulic Press | Forging Hammer |
|---|---|---|
| Force Type | Sustained, constant pressure | High-velocity impact |
| Deformation | Deep and uniform throughout material | More intense on surface layers |
| Ideal For | Large, complex components; intricate dies | High-speed production of simpler parts |
| Key Advantage | Complete die fill; superior metallurgical quality | Faster cycle times |
Ready to enhance your forging capabilities with precision and power? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and industrial solutions. Our expertise in hydraulic press technology can help you achieve deeper material deformation, superior metallurgical quality, and complete die fill for your most demanding forging applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK hydraulic press can transform your manufacturing process and deliver the precision your projects require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation



















