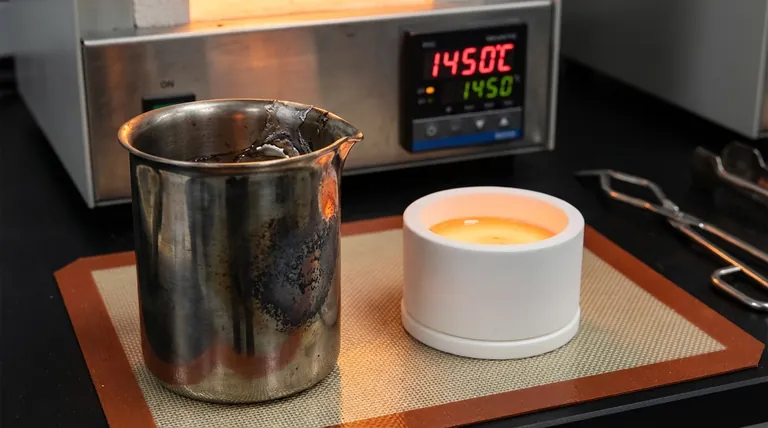
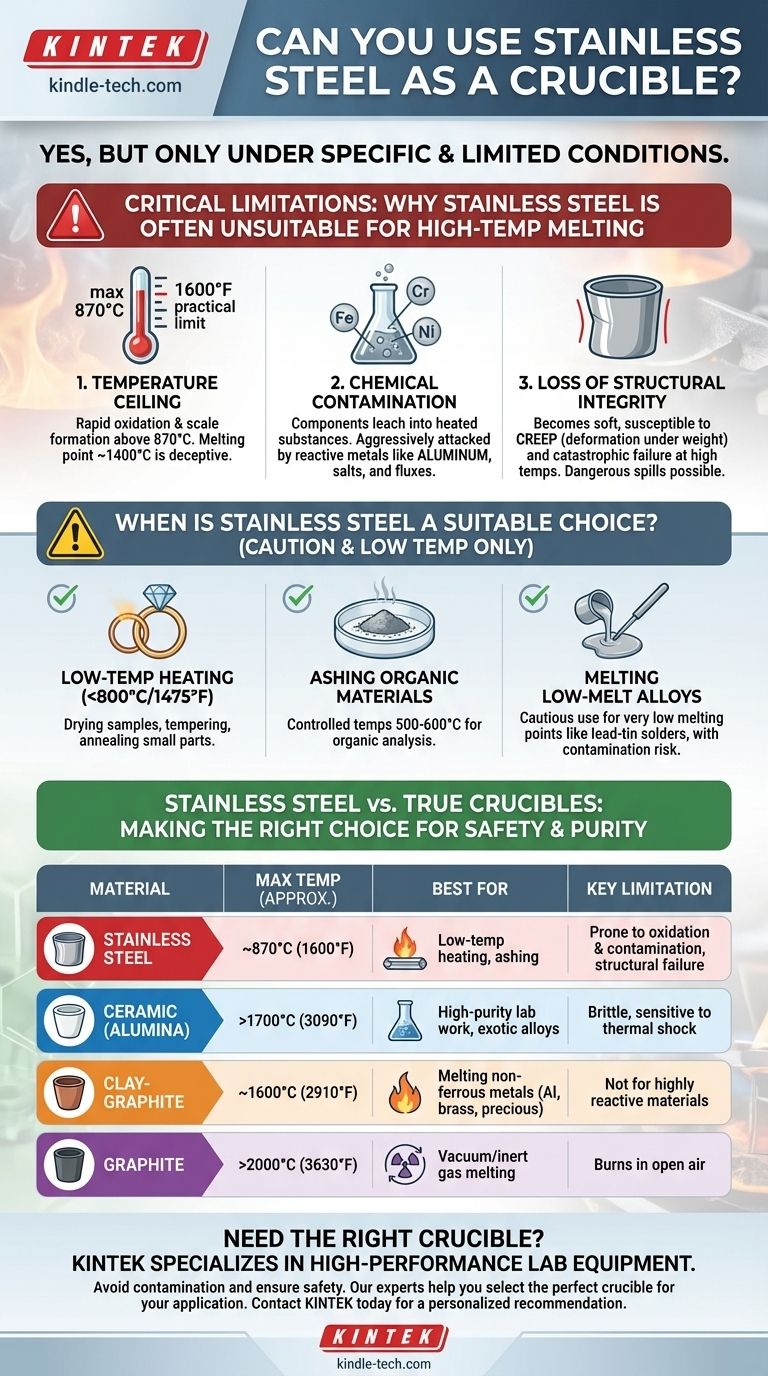
Yes, you can use stainless steel as a crucible, but only under very specific and limited conditions. Its suitability is not universal and depends entirely on your target temperature and the chemical reactivity of the material you are heating. For most high-temperature melting applications, it is an unsuitable and potentially dangerous choice.
While commonly available and mechanically tough, stainless steel is a poor substitute for a true crucible in most scenarios. Its relatively low working temperature and high chemical reactivity when hot make it prone to contaminating your material or failing catastrophically.

The Critical Limitations of Stainless Steel
To understand why stainless steel is rarely the right tool, you must consider its behavior at high temperatures. Its properties in a furnace are vastly different from its properties at room temperature.
The Temperature Ceiling
The melting point of most common stainless steel alloys (like 304 or 316) is around 1400°C (2550°F). However, its practical maximum use temperature is significantly lower.
Above approximately 870°C (1600°F), stainless steel begins to rapidly oxidize and form scale. This dark, flaky layer will contaminate whatever is inside the container.
The Risk of Chemical Contamination
Heating materials in a stainless steel container is a recipe for contamination. The primary components of stainless steel—iron, chromium, and nickel—will leach into the heated substance.
This is especially true when melting reactive metals like aluminum, which will aggressively attack the steel, dissolving it and ruining your melt. The same is true for many chemical salts and fluxes.
Loss of Structural Integrity
Metals lose their strength long before they melt. At elevated temperatures, stainless steel becomes soft and is susceptible to a process called creep, where it will slowly deform and sag under its own weight or the weight of its contents.
A container that seems robust when cold can easily buckle, warp, or fail in a hot furnace, leading to a dangerous spill of molten material.
When is Stainless Steel a Suitable Choice?
Despite these serious limitations, there are a few specific applications where a stainless steel container is a practical choice. The key is keeping temperatures and chemical reactivity low.
Low-Temperature Heating and Annealing
For processes below 800°C (1475°F) that do not involve melting, stainless steel is often perfectly adequate. This includes tasks like drying samples, tempering steel parts, or annealing small pieces of jewelry.
Ashing Organic Materials
In a laboratory setting, stainless steel dishes are commonly used to turn organic samples (like plant matter or food) into ash for analysis. These processes typically occur at controlled temperatures between 500-600°C, well within the safe operating range.
Melting Low-Melt-Point Alloys
You can cautiously use stainless steel to melt certain alloys with very low melting points, such as some lead-tin solders. However, you must still accept that some contamination from the steel is likely.
Stainless Steel vs. True Crucibles: A Comparison
The decision to use stainless steel comes down to a trade-off between convenience and performance. Understanding the alternatives clarifies why they are the standard for high-temperature work.
Stainless Steel: The Compromise
Its advantages are its low cost, widespread availability, and high mechanical durability when cold. Its disadvantages—low working temperature, chemical reactivity, and contamination risk—make it unsuitable for serious melting.
Ceramic Crucibles (Alumina, Zirconia)
These are the standard for high-purity and high-temperature work. They are chemically inert and have extremely high melting points, but they are brittle and can crack from thermal shock if heated or cooled too quickly.
Clay-Graphite Crucibles
This is the workhorse for foundries and hobbyist metal casters. A composite of clay and graphite, these crucibles are durable, resistant to thermal shock, and suitable for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and precious metals.
Graphite Crucibles
Used for melting metals in oxygen-free or vacuum environments, graphite offers excellent thermal conductivity. It will, however, burn away rapidly if heated to high temperatures in open air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your container based on your material and target temperature, not convenience.
- If your primary focus is melting metals like aluminum, brass, silver, or gold: Do not use stainless steel. Use a clay-graphite or ceramic crucible designed for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is high-purity lab analysis or melting exotic alloys: Use a high-purity ceramic (like alumina) or quartz crucible.
- If your primary focus is a low-temperature task below 800°C (1475°F) with non-reactive materials: Stainless steel is often a practical and cost-effective choice.
- If you are unsure about reactivity or temperature: Default to a proper ceramic or clay-graphite crucible to ensure safety and prevent contamination.
By understanding these material properties, you can select the right tool for your specific application, ensuring both safety and success.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Max Temp (Approx.) | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | ~870°C (1600°F) | Low-temp heating, ashing | Prone to oxidation & contamination |
| Ceramic (Alumina) | >1700°C (3090°F) | High-purity lab work, exotic alloys | Brittle, sensitive to thermal shock |
| Clay-Graphite | ~1600°C (2910°F) | Melting non-ferrous metals (Al, brass, precious) | Not for highly reactive materials |
| Graphite | >2000°C (3630°F) | Vacuum/inert gas melting | Burns in open air |
Need the Right Crucible for Your Lab?
Choosing the wrong crucible can lead to contamination, equipment failure, and unsafe conditions. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles designed for specific temperatures and materials. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible for your application—ensuring purity, safety, and optimal results.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized recommendation and elevate your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What protective role do ceramic crucibles play? Ensure Equipment Longevity and Catalyst Purity in Synthesis
- Do you need to heat the clean crucible before using it? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Process Accuracy
- What is the function of the silicon melt crucible below the hot zone? Essential Role in Airtight SiC Coating Production
- What are the primary advantages of using a magnesium oxide (MgO) crucible for Fe2Ti alloys? Maximize Purity & Stability
- What is a crucible used for in chemistry? Withstand Extreme Heat for Accurate Analysis
- What are the benefits of using a tubular crucible? Ensure Uniform Corrosion Analysis with Better Gas Flow
- Do you have to temper your crucible? A Critical Safety Step for Melting Metal
- Can a crucible withstand heat? Yes, with the right material and thermal properties.



















