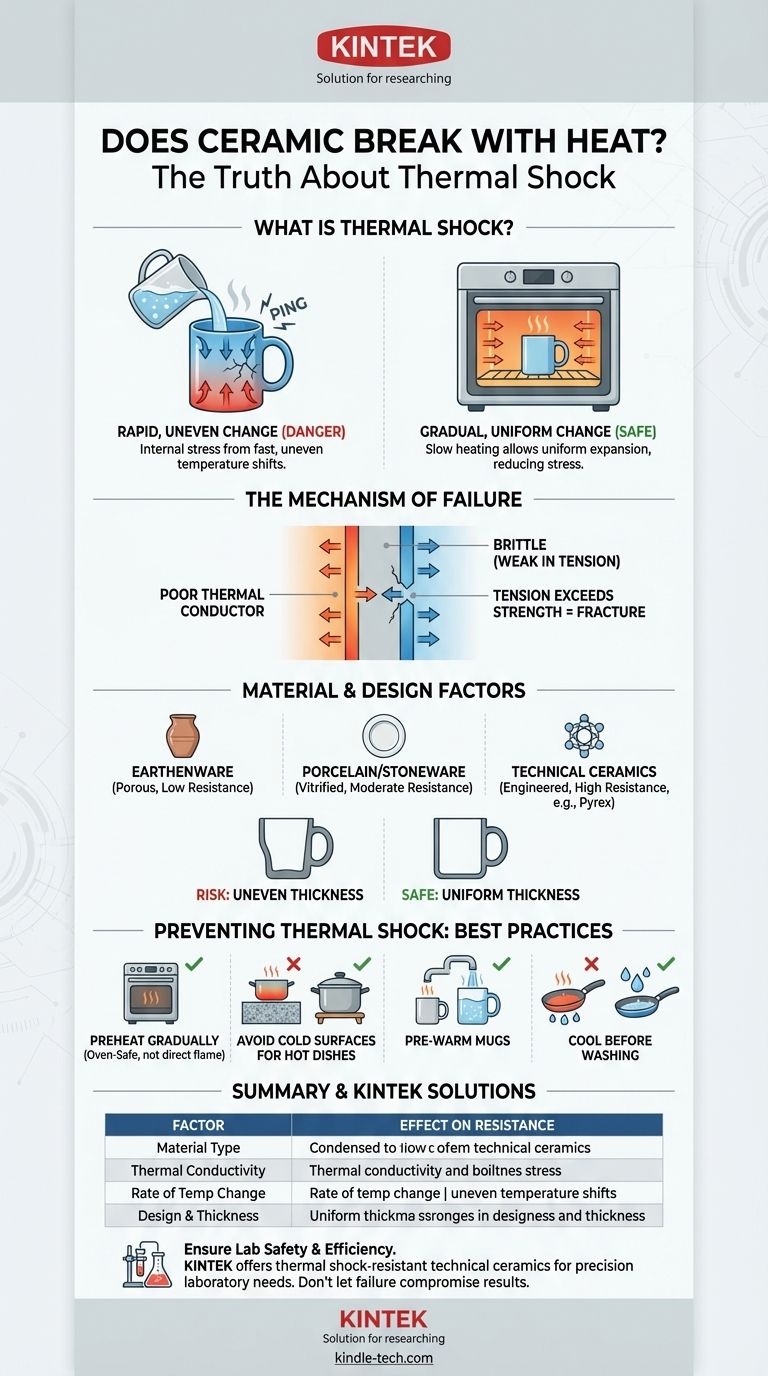
In short, yes, ceramic can break with heat, but the situation is more nuanced than you might think. It is not the high temperature itself that fractures the material. The true culprit is a rapid, uneven change in temperature known as thermal shock, which creates internal stresses that exceed the material's strength.
The risk to ceramic isn't the presence of heat, but the rate of change in temperature. Understanding that thermal shock—the stress from one part of the material expanding or contracting faster than another—is the primary cause of failure is the key to preventing breakage.

What Is Thermal Shock?
To properly use ceramic items, from a coffee mug to bakeware, you must understand the powerful physical forces at play when temperatures change.
The Science of Expansion and Contraction
Nearly all materials expand when heated and contract when they cool. This is a fundamental principle of physics. The atoms in the material move more energetically at higher temperatures, pushing each other farther apart.
How Stress Builds in Ceramic
Ceramic is a poor thermal conductor, meaning heat does not travel through it quickly.
When you apply heat to one part of a ceramic object (like pouring boiling water into a cold mug), that area tries to expand immediately. However, the adjacent, cooler parts of the mug remain unexpanded. This difference in expansion creates immense internal tension.
The Tipping Point: Fracture
Ceramic is a brittle material. It is very strong when compressed but exceptionally weak when pulled apart (under tension).
When the tensile stress from uneven expansion becomes too great, the material fails catastrophically to release that energy. This failure is the crack you see, often accompanied by a distinct "ping" or "pop." A classic example is a glass taken from the freezer and immediately filled with hot water.
Why Some Ceramics Are Stronger Than Others
Not all ceramics are created equal. Their ability to withstand thermal shock depends heavily on their composition and manufacturing process.
Material Composition Matters
Different types of clay and firing temperatures produce ceramics with vastly different properties.
- Earthenware: Fired at low temperatures, it remains porous and is highly susceptible to thermal shock.
- Stoneware and Porcelain: These are fired at much higher temperatures until they become vitrified (glass-like and non-porous). This dense structure makes them significantly more durable and resistant to thermal shock.
- Technical Ceramics: Materials like borosilicate (used in Pyrex) or specialty alumina ceramics are engineered with a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, making them exceptionally resistant to thermal shock for lab and industrial use.
The Role of Glazing
The glaze on a ceramic piece can also be a point of weakness. If the glaze and the clay body expand and contract at different rates, it can introduce stress. You may have seen "crazing," a fine network of cracks in the glaze, which is a sign of this tension.
Design and Thickness
Uniform thickness is crucial for thermal stability. A piece with both very thick and very thin sections is at high risk, as the thin areas will heat and cool much faster than the thick ones, guaranteeing a significant temperature difference and high stress.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The properties that make ceramic useful also contribute to its primary vulnerability.
"Oven-Safe" vs. "Stovetop-Safe"
This is a critical distinction. An item labeled "oven-safe" is designed to handle the slow, even heating of an oven environment. The entire piece heats up gradually and uniformly.
Placing that same dish on a stovetop burner delivers intense, localized heat to a small area. This is a perfect recipe for thermal shock and will almost certainly cause it to crack. Never use standard ceramic cookware on a direct flame or electric burner unless it is explicitly marketed for that purpose (like a tagine or specific flameware).
The Danger of Hidden Flaws
Even a microscopic crack or a tiny air bubble from the manufacturing process can become a "stress concentrator." When thermal stress is applied, all the force focuses on that weak point, making a fracture far more likely. This is why a dish you've used for years might suddenly crack.
How to Safely Use Your Ceramic Items
Preventing thermal shock is entirely about controlling the rate of temperature change. By following a few simple rules, you can eliminate the vast majority of risks.
- If your primary focus is baking: Always place your ceramic dish in a cool oven and let it preheat with the oven. Never put a cold dish into a hot oven, and avoid using the broiler with standard ceramic bakeware.
- If your primary focus is serving food or drinks: Avoid pouring boiling liquid into a very cold mug. To be extra safe, pre-warm the ceramic with hot tap water before adding the boiling liquid.
- If your primary focus is handling hot dishes: Never place a hot ceramic dish on a cold or wet surface, such as a granite countertop or in a sink. Place it on a dry towel, a wooden cutting board, or a trivet to allow for gradual cooling.
- If your primary focus is cleaning: Always allow hot ceramic cookware to cool down to room temperature before washing it with cool water.
By managing the rate of temperature change, you control the stress on the material and ensure your ceramics can serve you reliably for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Thermal Shock Resistance |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Technical ceramics (e.g., Pyrex) > Porcelain/Stoneware > Earthenware |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low conductivity (like ceramic) increases risk of uneven heating and stress. |
| Rate of Temperature Change | Rapid changes cause high stress; gradual changes are safe. |
| Design & Thickness | Uniform thickness distributes heat evenly, reducing risk. |
Ensure your laboratory processes are safe and efficient with the right equipment. Thermal shock is a critical consideration not just for kitchenware, but for the precision ceramics used in your lab. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including thermal shock-resistant technical ceramics designed for reliability and accuracy. Don't let equipment failure compromise your results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is furnace lining? The Engineered System Protecting Your High-Temperature Processes
- What is the hottest temperature a furnace can be? Exploring Limits from 3,000°C+ to Your Application
- What temperature should a furnace run at? From Home Comfort to Industrial Processes
- What are furnaces usually made of? A Guide to Materials for Extreme Temperatures
- How did the design of muffle furnaces change with the advent of electric heating elements? The Evolution to Precision and Purity



















