Yes, heat critically affects graphite, but not in the way most people think. While graphite has an exceptionally high tolerance for heat, its practical performance and lifespan are not defined by its melting point, but by its reaction to oxygen at elevated temperatures. This process, known as oxidation, is the primary factor limiting its use in high-temperature applications.
The core issue isn't whether graphite can "take the heat," but rather the environment it's in. In a vacuum or inert atmosphere, it remains stable at extreme temperatures, but in the presence of air, oxidation begins and accelerates as temperature rises, causing the material to degrade and fail.
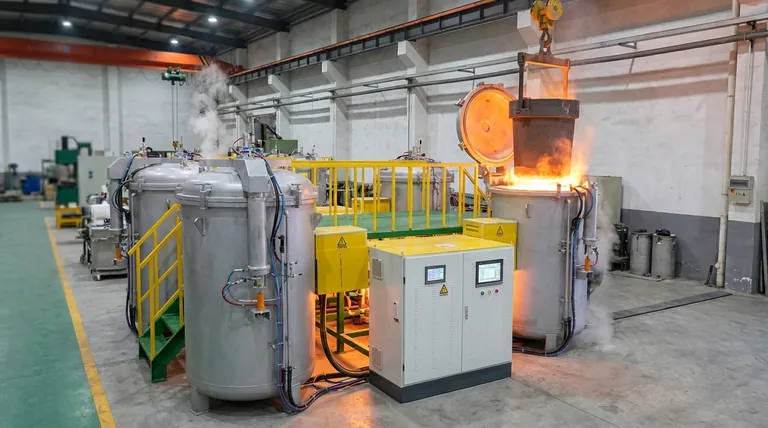

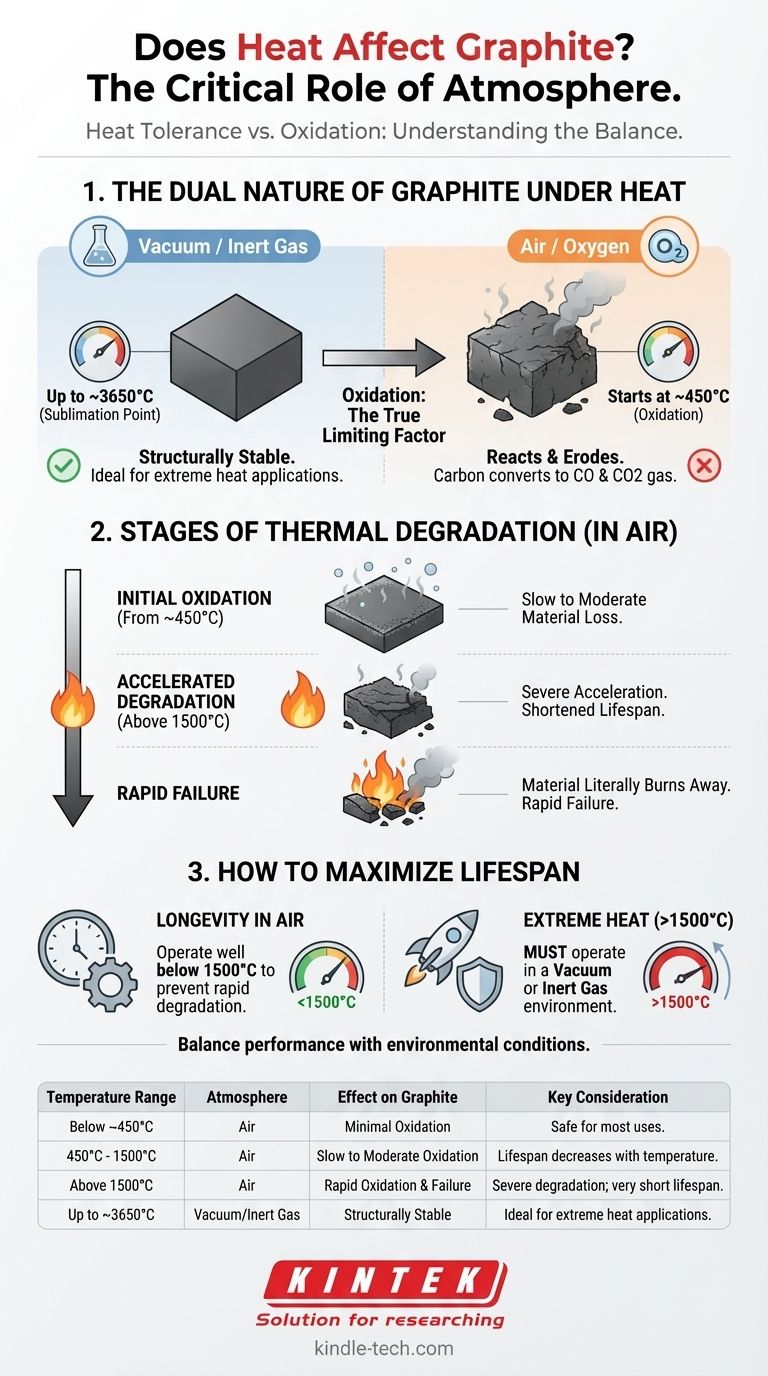
The Dual Nature of Graphite Under Heat
To use graphite effectively, one must understand its two distinct thermal behaviors: its inherent structural stability and its chemical reactivity with the atmosphere.
Exceptionally High Sublimation Point
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; instead, it sublimes (turns directly from a solid to a gas) at an extremely high temperature, around 3,650°C (6,600°F). This fundamental property makes it a candidate for some of the most demanding thermal applications.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
This impressive temperature resistance is only relevant in a vacuum or an inert gas environment (like argon or nitrogen). In these conditions, graphite's structural integrity is maintained close to its sublimation point.
Oxidation: The True Limiting Factor
When exposed to oxygen, as found in air, graphite begins to react and oxidize at a much lower temperature, typically starting around 450°C (842°F). The graphite (carbon) combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) gas, effectively eroding the material away.
Understanding the Stages of Thermal Degradation
The impact of heat on graphite in an oxygen-rich environment is not a simple on/off switch. It is a process that accelerates dramatically with increasing temperature.
Initial Oxidation
While the process can begin at temperatures as low as 450°C, the rate of material loss is relatively slow at first. This allows for effective use in many applications well above this initial threshold.
Accelerated Degradation (Above 1500°C)
As the surface temperature increases, the rate of oxidation accelerates significantly. The reference point of 1500°C (2732°F) is a critical threshold where this acceleration becomes severe.
The Consequence: Shortened Lifespan
Operating graphite components, such as heating rods or crucibles, above this accelerated oxidation temperature will dramatically shorten their service life. The material will literally burn away, becoming thinner, weaker, and eventually failing.
How to Maximize Graphite's Lifespan
Making the right operational choice depends entirely on balancing performance requirements with the environmental conditions of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum longevity in air: Operate well below the accelerated oxidation threshold. Keeping surface temperatures below 1500°C is essential to prevent rapid degradation.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme heat (above 1500°C): You must operate in a vacuum or an inert gas environment to protect the graphite from oxidative failure.
Understanding the critical role of atmosphere is the key to successfully leveraging graphite's remarkable thermal properties.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Atmosphere | Effect on Graphite | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Below ~450°C (842°F) | Air | Minimal Oxidation | Safe for most uses. |
| 450°C - 1500°C | Air | Slow to Moderate Oxidation | Lifespan decreases with temperature. |
| Above 1500°C (2732°F) | Air | Rapid Oxidation & Failure | Severe degradation; very short lifespan. |
| Up to ~3650°C (Sublimation) | Vacuum/Inert Gas | Structurally Stable | Ideal for extreme heat applications. |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your high-temperature processes.
Graphite's exceptional thermal properties can be a game-changer for your lab, but only if used correctly. The team at KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and expert guidance to help you navigate the critical balance between heat and atmosphere.
Whether you need durable graphite components for furnace applications or a complete system designed for inert gas operation, we have the solutions to ensure your experiments run efficiently and reliably.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific high-temperature application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- Why is the thermal conductivity of graphite so high? Unlock Superior Heat Transfer with Its Unique Structure
- Why graphite has high thermal conductivity? Unlock Superior Heat Management with Its Unique Structure
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere



















