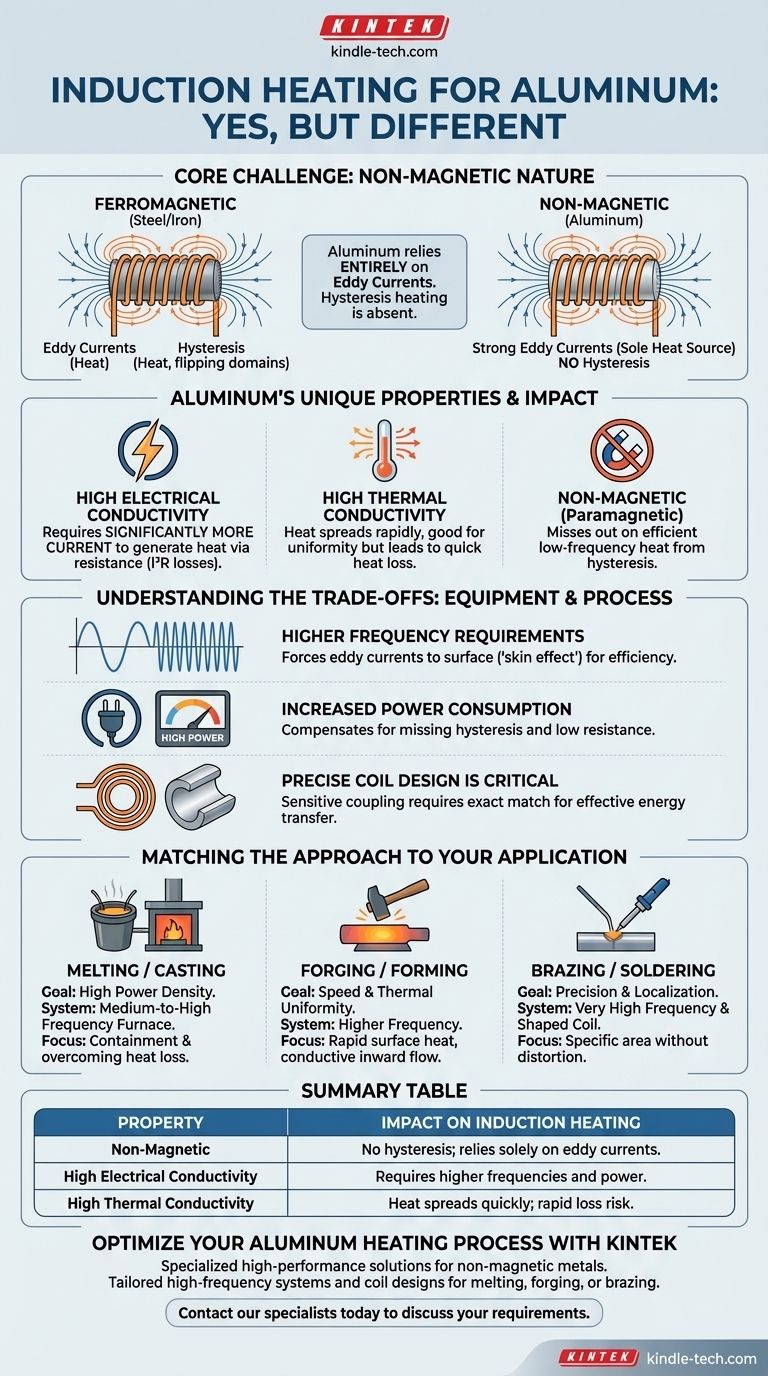
Yes, induction heating works with aluminum, but its effectiveness and the equipment required are fundamentally different from heating magnetic metals like iron and steel. Because aluminum is non-magnetic but highly conductive, the process relies entirely on inducing strong electrical eddy currents within the material, which requires specific frequencies and power levels to be efficient.
The core challenge with induction heating aluminum is its nature as a non-magnetic, highly conductive material. While its conductivity allows heating via eddy currents, its lack of magnetic properties means it misses out on the efficient hysteresis heating effect, demanding higher frequencies and more power to achieve desired results compared to steel.

How Induction Heating Fundamentally Works
To understand the specific challenges with aluminum, we must first review the two core mechanisms of induction heating.
The Role of an Alternating Magnetic Field
An induction coil, powered by a high-frequency alternating current (AC), generates a rapidly changing magnetic field. When a conductive workpiece, like a piece of metal, is placed within this field, it induces electrical currents inside the part itself.
Two Key Heating Mechanisms
There are two distinct ways this process generates heat:
- Eddy Current Heating: The magnetic field induces circular electrical currents, or eddy currents, within the metal. The material's natural electrical resistance causes these currents to generate heat (I²R losses), much like the element in an electric stove.
- Hysteresis Heating: This mechanism only occurs in magnetic materials like iron and steel. The rapidly changing magnetic field causes the magnetic domains within the material to rapidly flip their polarity. This internal friction generates a significant amount of heat.
The Specifics of Heating Aluminum
Aluminum's unique properties mean that only one of these two heating mechanisms is at play, which dictates the entire approach.
The Eddy Current Effect in Aluminum
Aluminum is an excellent electrical conductor. This property allows for the generation of very strong eddy currents when it is placed in a magnetic field, making it the sole source of heat in the induction process.
The Absence of Magnetic Hysteresis
Aluminum is a paramagnetic material, meaning it is effectively non-magnetic. Therefore, it does not experience hysteresis heating. This is the single biggest difference between heating aluminum and heating steel, as the process loses a major source of efficient, low-frequency heat generation.
High Thermal & Electrical Conductivity
Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity means heat spreads very quickly throughout the workpiece, which can be a benefit for uniform heating but also means heat can be lost quickly to the environment. Its high electrical conductivity (low resistivity) also means that generating heat via eddy currents requires significantly more current flow compared to steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The physics of heating aluminum directly impacts the equipment and process required for a successful application.
Higher Frequency Requirements
To compensate for the lack of hysteresis and aluminum's low electrical resistance, the induction power supply must operate at a much higher frequency. Higher frequencies force the eddy currents to flow in a thinner layer near the surface of the part (the "skin effect"), concentrating the heating effect and making the process more efficient.
Increased Power Consumption
Heating aluminum to a target temperature often requires more power and time than an equivalent piece of steel. The energy that would have been generated by hysteresis must be fully compensated for by stronger eddy currents, demanding a more powerful induction system.
Precise Coil Design is Critical
The efficiency of induction heating depends on the "coupling," or how well the magnetic field links with the workpiece. Due to aluminum's properties, the coupling distance is often smaller and more sensitive. The design of the induction coil must be precisely matched to the part geometry to ensure energy is transferred effectively.
Matching the Approach to Your Application
Choosing the right induction strategy depends entirely on your industrial goal, as different applications have different requirements for speed, uniformity, and precision.
- If your primary focus is melting or casting: High power density is essential. The process will rely on a medium-to-high frequency power supply and a well-designed furnace (often a coreless or channel furnace) to contain the molten metal and overcome rapid heat loss.
- If your primary focus is forging or forming: Speed and thermal uniformity are critical. A higher frequency system is needed to rapidly heat the billet's surface, allowing the heat to conduct inward to create a consistent temperature before forming.
- If your primary focus is brazing or soldering: Precision is the main objective. Here, a very high-frequency system and a carefully shaped coil are used to deliver heat to a very specific, localized area without distorting the surrounding material.
By understanding these principles, you can effectively engineer an induction heating process that leverages aluminum's unique properties for successful, efficient results.
Summary Table:
| Property | Impact on Induction Heating |
|---|---|
| Non-Magnetic | No hysteresis heating; relies solely on eddy currents. |
| High Electrical Conductivity | Requires higher frequencies and power for efficient heating. |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Heat spreads quickly; can lead to rapid heat loss if not managed. |
Optimize Your Aluminum Heating Process with KINTEK
Struggling with inefficient heating of aluminum parts? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored induction heating solutions that address the unique challenges of non-magnetic metals. Our experts can help you select the right high-frequency system and coil design for your specific application—whether it's melting, forging, or precision brazing.
We provide the technology and support to ensure rapid, uniform, and energy-efficient results for your laboratory or production needs.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your aluminum heating requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your process efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing



















