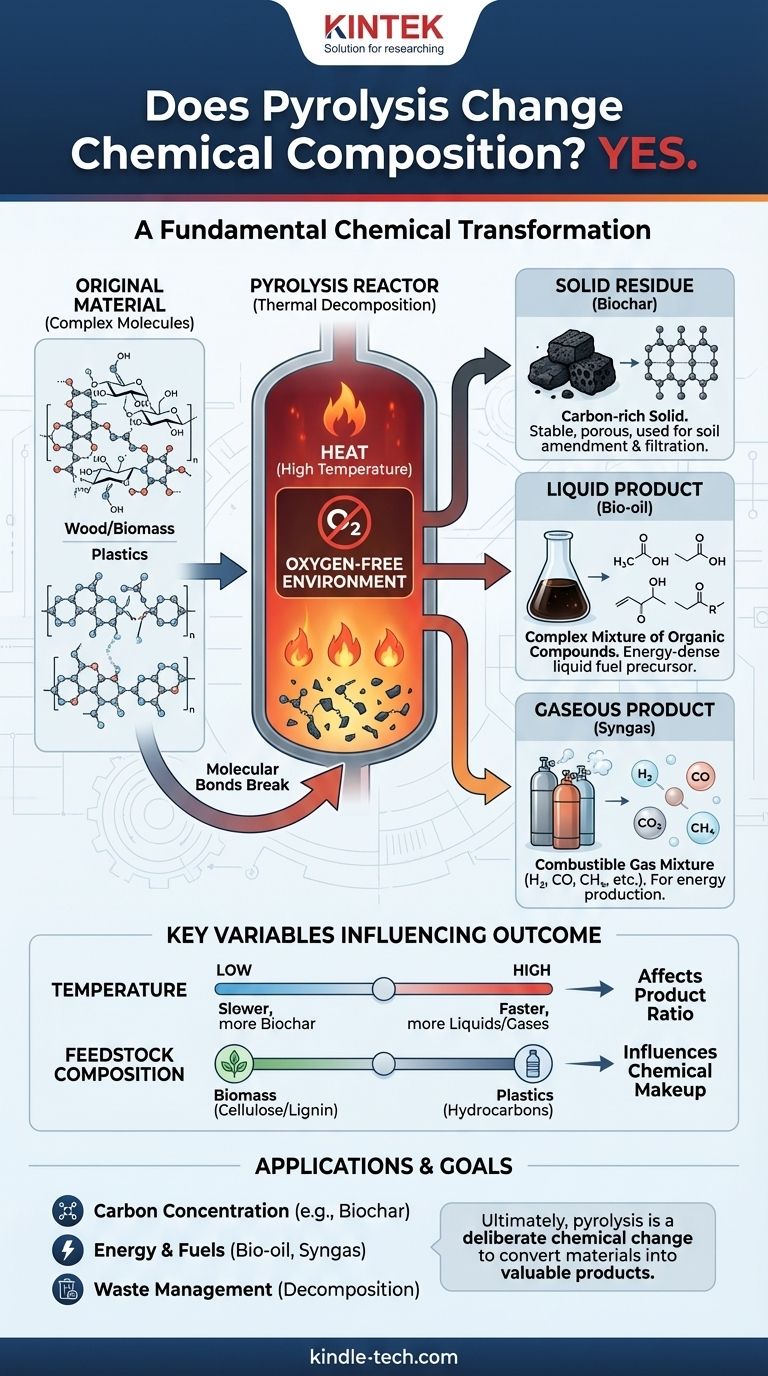
In short, yes. Pyrolysis is defined by its ability to fundamentally change the chemical composition of a substance. It is a process of thermal decomposition, using high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment to break down large, complex molecules into a mixture of smaller, chemically distinct products. The original material ceases to exist, having been transformed into new substances with entirely different properties.
The core principle to understand is that pyrolysis is not a physical change, like melting or boiling. It is a chemical reaction that fractures the molecular backbone of a material, creating new gas, liquid, and solid products that were not present at the start.

What is Pyrolysis at a Molecular Level?
To grasp how pyrolysis works, we need to look at what happens to the molecules themselves. The process is driven by heat and controlled by the environment.
Thermal Decomposition Explained
All organic materials, from wood to plastic, are made of large, complex molecules held together by chemical bonds. Heat is a form of energy. When applied during pyrolysis, this energy causes the molecules to vibrate so intensely that their chemical bonds break apart.
This process is not random. The weakest bonds tend to break first, leading to a cascade of reactions that deconstruct the original material into a variety of smaller, more stable molecules.
The Critical Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. This is what separates it from combustion, or burning.
Without oxygen, the material cannot burn. Instead of reacting with oxygen to produce fire, carbon dioxide, and water, the molecules simply break down under the thermal stress. This controlled decomposition is what allows for the creation of useful products instead of just ash and smoke.
The New Chemical Products of Pyrolysis
The result of this chemical transformation is not one single substance, but a mixture of three distinct product streams, each with its own unique chemical composition.
The Solid Residue (Biochar)
After the volatile components have been driven off by the heat, a solid material remains. This product, known as char, is significantly richer in carbon content than the original substance.
The original molecular structure (like the cellulose in wood or polymers in plastic) has been destroyed and replaced by a new, carbon-dense framework. Elements like hydrogen and oxygen have been largely removed, creating a fundamentally different chemical.
The Liquid Product (Bio-oil)
As the original material breaks down, many of the smaller molecular fragments are volatile enough to become a vapor at high temperatures but will condense into a liquid upon cooling.
This liquid, often called bio-oil or pyrolysis oil, is a complex mixture of dozens or even hundreds of different organic compounds, including acids, alcohols, and ketones. These are new chemicals formed during the decomposition process.
The Gaseous Product (Syngas)
The lightest molecular fragments remain as a gas even after cooling. This is often called syngas (synthesis gas).
It is a mixture of simple gas molecules that are chemically distinct from the original material. Common components include hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄).
Understanding the Key Variables
The exact chemical composition of the final products is not fixed. It depends heavily on the conditions of the pyrolysis process, making it both versatile and complex.
Temperature Dictates the Outcome
The temperature and rate of heating have the most significant impact on the final products. Slower pyrolysis at lower temperatures tends to maximize the yield of solid char. Conversely, very fast pyrolysis at higher temperatures breaks the molecules down even further, favoring the production of liquids and gases.
Feedstock Composition Matters
The chemical makeup of the starting material, or feedstock, directly influences the output. The pyrolysis of wood, which is rich in cellulose and lignin, will produce a different ratio and composition of oil, gas, and char compared to the pyrolysis of waste plastic, which is made of long hydrocarbon polymers.
How This Applies to Your Goal
Understanding pyrolysis as a chemical transformation is essential for applying it correctly. The goal is never to preserve the original substance, but to convert it into something new and more valuable.
- If your primary focus is creating a stable, carbon-rich material: You are using pyrolysis to drive off volatile elements and concentrate carbon, chemically changing a raw biomass into a stable char for agricultural or industrial use.
- If your primary focus is producing energy or fuels: You are leveraging pyrolysis to break down a low-value feedstock into valuable, energy-dense liquid (bio-oil) and gaseous (syngas) chemical compounds.
- If your primary focus is waste management: You are using pyrolysis as a chemical decomposition method to break a large, complex waste material into smaller, often more manageable and valuable components.
Ultimately, recognizing that pyrolysis is a deliberate chemical change is the key to controlling its outputs and harnessing its full potential.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Chemical Composition | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Carbon-rich solid | Stable, porous, used for soil amendment and filtration |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Complex mixture of organic compounds | Energy-dense liquid fuel precursor |
| Syngas (Gas) | Hydrogen, CO, CO₂, methane | Combustible gas for energy production |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis for your laboratory or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for thermal decomposition research and applications. Whether you're developing new biochar formulations, optimizing bio-oil production, or analyzing syngas composition, our precision pyrolysis systems deliver reliable, reproducible results. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can advance your pyrolysis projects and help you transform materials into valuable products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















