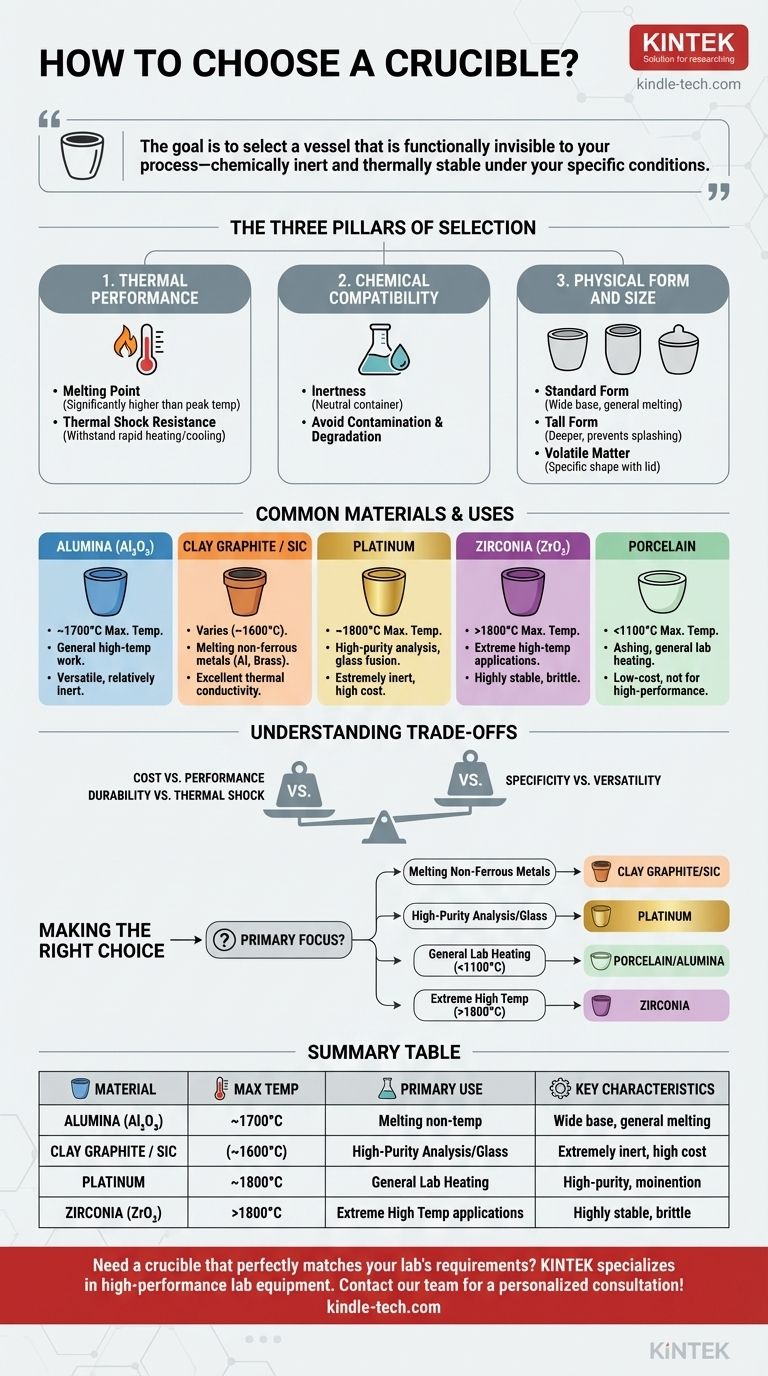
To choose the right crucible, you must match its material and shape to three critical factors: the maximum temperature of your process, the chemical reactivity of the substance being heated, and the specific application, such as melting or analyzing volatile matter. The crucible must have a higher melting point than your material and remain chemically inert to avoid contaminating your sample or degrading the vessel itself.
The wrong crucible doesn't just fail; it can contaminate your sample, damage your equipment, and compromise your results. The goal is to select a vessel that is functionally invisible to your process—chemically inert and thermally stable under your specific conditions.

The Three Pillars of Crucible Selection
Choosing a crucible is a process of balancing requirements. By evaluating your needs against these three core pillars, you can confidently select the appropriate tool for your work.
Pillar 1: Thermal Performance
The most fundamental requirement is that the crucible must withstand your process temperatures without melting, warping, or failing.
Melting Point is the first check. The crucible's maximum use temperature must be significantly higher than your peak operating temperature to provide a safe margin.
Thermal Shock Resistance is also critical. If your process involves rapid heating or cooling, you need a material that can withstand the stress without cracking.
Pillar 2: Chemical Compatibility
A crucible must act as a neutral container. Any chemical reaction between the crucible and the sample is a source of failure and contamination.
Inertness is the goal. The crucible material should not react with, dissolve in, or otherwise contaminate the substance you are heating.
Consequences of Incompatibility include ruining the purity of your sample, creating unwanted byproducts, and weakening the crucible itself, which can lead to a catastrophic failure at high temperatures.
Pillar 3: Physical Form and Size
The geometry of the crucible is dictated by the task at hand. The right shape can improve efficiency, prevent loss of material, and ensure even heating.
Standard Form Crucibles have a wide base and are excellent for general-purpose melting and stable heating of materials.
Tall Form Crucibles are deeper and help prevent splashing or boil-over when working with more reactive or agitated melts.
Volatile Matter Crucibles are often designed with a specific shape and a close-fitting lid to control the release of gases during analysis, a common procedure in materials testing.
Common Crucible Materials and Their Uses
Different materials offer unique combinations of thermal and chemical resistance. Here are some of the most common options.
Alumina (Al₂O₃)
Alumina is a versatile, common choice for high-temperature work (up to ~1700°C). It is relatively inert but can react with highly basic slags or certain metals.
Clay Graphite & Silicon Carbide
These composite materials are the workhorses for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and good thermal shock resistance at a reasonable cost.
Platinum
For applications demanding the highest purity, such as glass sample preparation or analytical chemistry, platinum is the standard. It is extremely inert and has a very high melting point, but it comes at a significant cost.
Zirconia (ZrO₂)
Zirconia crucibles are used for extremely high-temperature applications (above 1800°C) and for materials that are reactive with alumina. They are highly stable but more brittle than other ceramics.
Porcelain
A low-cost option suitable for ashing samples and general heating at lower temperatures (typically below 1100°C). It is not intended for high-performance melting or highly corrosive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "best" crucible. Your selection is always a balance between performance, lifespan, and cost.
Cost vs. Performance
A platinum crucible offers unparalleled inertness but is prohibitively expensive for many applications. A clay-graphite crucible is economical for melting large batches of aluminum but would be useless for high-purity glass analysis.
Durability vs. Thermal Shock Resistance
Some very hard, durable materials can be brittle and may not handle rapid temperature cycles well. Conversely, materials with excellent thermal shock resistance might be softer or have a lower maximum use temperature.
Specificity vs. Versatility
While a material like alumina is a good general-purpose choice, specialized applications often demand a specialized crucible. Attempting to use a "one-size-fits-all" approach often leads to compromised results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your crucible by identifying your primary objective and the constraints of your process.
- If your primary focus is melting common non-ferrous metals: A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible provides the best balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical analysis or glass fusion: Platinum is the industry standard for its extreme chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is general lab heating or ashing below 1100°C: A porcelain or alumina crucible is a reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is working at extremely high temperatures (>1800°C): Zirconia crucibles provide the necessary stability where others would fail.
Ultimately, a well-chosen crucible is an investment in the accuracy and reliability of your work.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Max Temperature | Primary Use Cases | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | ~1700°C | General high-temperature work | Versatile, relatively inert |
| Clay Graphite / Silicon Carbide | Varies (e.g., ~1600°C) | Melting non-ferrous metals (Al, brass) | Excellent thermal conductivity, cost-effective |
| Platinum | ~1800°C | High-purity analysis, glass fusion | Extremely inert, high cost |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | >1800°C | Extreme high-temperature applications | Highly stable, brittle |
| Porcelain | <1100°C | Ashing, general lab heating | Low-cost, not for high-performance melting |
Need a crucible that perfectly matches your lab's requirements? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of crucibles designed for thermal stability and chemical inertness. Our experts can help you select the ideal crucible for your specific application—ensuring accuracy, safety, and efficiency in your processes. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a corundum crucible play in TGA? Ensure High-Temperature Precision for Rock Sample Analysis
- How to maintain a crucible? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Longevity
- Why is the design of laboratory-grade ceramic crucibles critical when determining the volatile matter content of flax straw?
- What are the different types of crucible? A Guide to Material, Shape, and Application
- What makes a good crucible? Choose the Right Crucible for Your Metal Melting Needs
- What is the best material to use for a crucible? Match Your Metal to the Perfect Crucible
- What are the two types of crucibles and their uses? Choose the Right Crucible for Your Application
- Do you need a different crucible for different metals? Ensure Purity and Safety in Your Lab



















